Qt之线程运行指定函数(含源码+注释,优化速率)
一、线程示例图
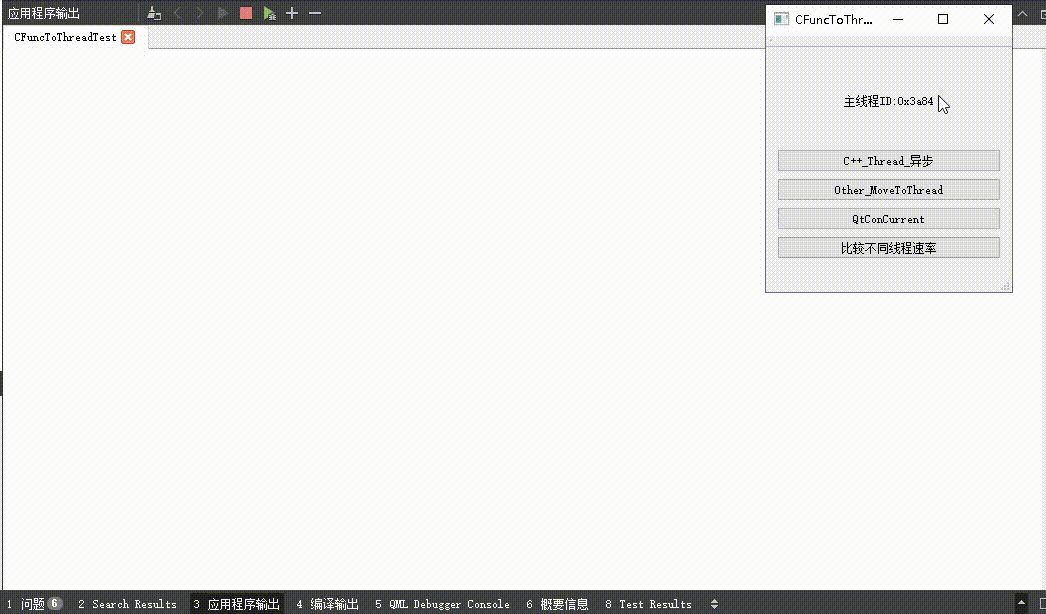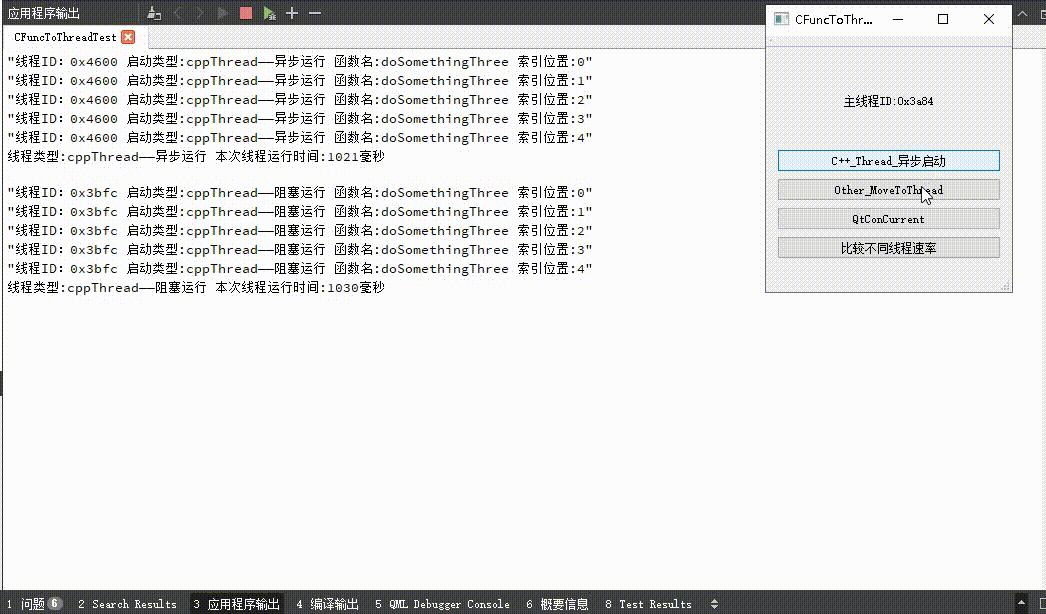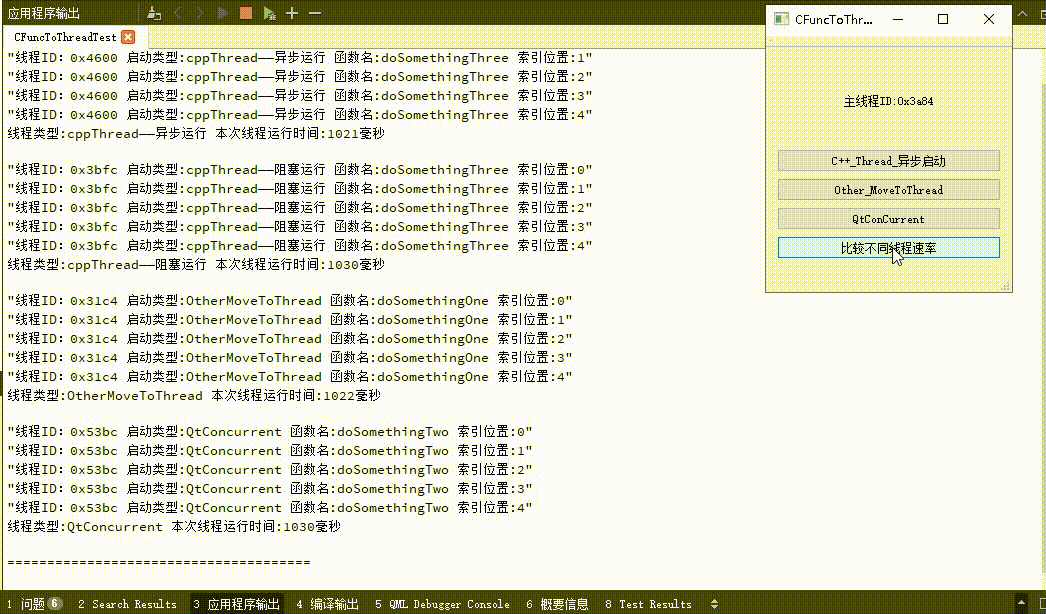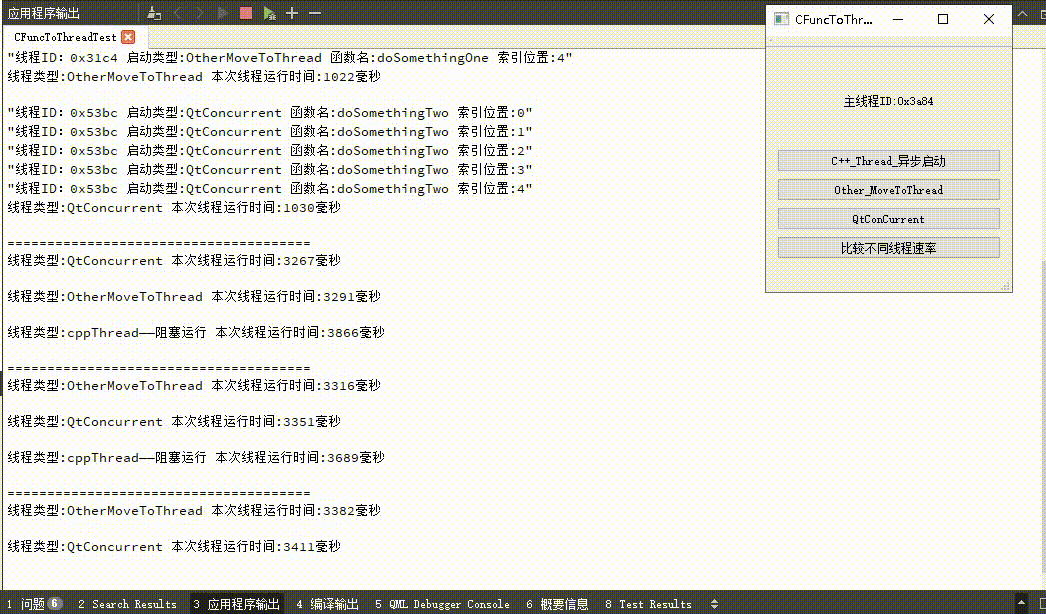
下图包含三种不同方式启动线程的示例图和各自运行速率的对比;C++线程的启动方式包括阻塞运行和异步运行,可以从C++线程启动按钮看出两者区别,异步启动时按钮文本立即更新,当阻塞启动时按钮文本在线程运行完成后更新;并且从输出文本可以看出,启动的线程的线程ID和主线程ID不同,说明指定函数的确是在子线程中运行。
二、三种方式须知(个人理解)
2.1 C++线程
C++线程有不同的启动方式,分别是阻塞启动(join()函数)和异步启动(detach()函数);阻塞启动,顾名思义阻塞主线程,等待子线程运行完成后回到主线程中;异步启动,主线程和子线程分开各自运行,但是传输的数据不能是局部变量(当为局部变量时,主线程跳出局部变量作用域,该变量将释放,子线程有极大可能出问题),并且数据类型得为void *,在使用时自己转换即可。
2.2 MoveToThread
学习Qt的过程中,移动方法启动线程是我们刚刚接触线程时必了解的两种启动线程方法之一,其操作比其他两个方式略微麻烦(需要创建对象、关联信号、发送信号才能启动),具体看实际情况使用。
2.3 QtConcurrent
QtConcurrent中包含run的静态函数,可通过类名直接调用;该方法时三种方法中使用最方便的,只需要导入头文件、调用run函数,传入对应参数即可运行(详情见Qt帮助)。
三、源码
CTestClass.h
#ifndef CTESTCLASS_H
#define CTESTCLASS_H#include typedef struct StData
{int range; // 函数循环次数QString type; // 函数循环类型bool flag; // 函数循环标记// 默认构造StData(){range = 0;type = "";flag = false;}// 有参构造StData(int range, QString type, bool flag = true){this->range = range;this->type = type;this->flag = flag;}
}stData;class CTestClass : public QObject
{Q_OBJECT
public:explicit CTestClass(QObject *parent = nullptr);signals:public slots:/*** @brief doSomethingOne 线程运行函数1* @param data 包含线程信息的数据*/void doSomethingOne(const stData &data);
};#endif // CTESTCLASS_H CTestClass.cpp
#include "CTestClass.h"#include
#include
#include CTestClass::CTestClass(QObject *parent) : QObject(parent)
{}void CTestClass::doSomethingOne(const stData &data)
{// 获取线程启动时间qint64 startTime = QDateTime::currentMSecsSinceEpoch();for(int index = 0; index != data.range; ++index){if(data.flag){// 拼接信息字符串QString text = QString("线程ID:0x%1 启动类型:%2 函数名:%3 索引位置:%4").arg(QString::number((int64_t)QThread::currentThreadId(), 16)).arg(data.type).arg(__func__).arg(QString::number(index));// 打印信息字符串qDebug() << text;// 延迟QThread::msleep(200);}}// 计算运行时间QString info = QString("线程类型:%1 本次线程运行时间:%2毫秒").arg(data.type).arg(QDateTime::currentMSecsSinceEpoch() - startTime);//! noquote():自动插入引号字符,并返回对流的引用(此处功能为使‘\n’生效,达到换行效果)qDebug().noquote() << info + '\n';
} CFuncToThreadTest.h
#ifndef CFUNCTOTHREADTEST_H
#define CFUNCTOTHREADTEST_H#include "CTestClass.h"#include
#include namespace Ui {
class CFuncToThreadTest;
}class CFuncToThreadTest : public QMainWindow
{Q_OBJECTpublic:explicit CFuncToThreadTest(QWidget *parent = nullptr);~CFuncToThreadTest();signals:void moveToClassThreadSig(stData);private slots:/*** @brief doSomethingTwo 线程运行函数2* @param data 包含线程信息的数据*/void doSomethingTwo(const stData &data);/*** @brief on_qtConCurrentBtn_clicked QtConcurrent线程槽函数*/void on_qtConCurrentBtn_clicked();/*** @brief on_otherMoveToBtn_clicked moveToThread槽函数*/void on_otherMoveToBtn_clicked();/*** @brief on_cppThreadBtn_clicked C++线程槽函数*/void on_cppThreadBtn_clicked();/*** @brief on_compareThreadBtn_clicked 比较各线程速率槽函数*/void on_compareThreadBtn_clicked();private:Ui::CFuncToThreadTest *ui;QThread *m_moveClassThread; // 移动线程对象CTestClass *m_testClass; // 包含移动线程运行函数的对象StData *m_stData; // C++线程指针数据
};#endif // CFUNCTOTHREADTEST_H CFuncToThreadTest.cpp
#include "CFuncToThreadTest.h"
#include "ui_CFuncToThreadTest.h"#include
#include
#include #define COMPARE_RANGE_VAL 1000000000/*** @brief doSomethingThree 线程运行函数3* @param dataPtr 包含线程信息的数据指针*/
void doSomethingThree(void *dataPtr)
{// 获取线程启动时间qint64 startTime = QDateTime::currentMSecsSinceEpoch();// 将指针强转为stData类型stData *data = static_cast(dataPtr);for(int index = 0; index != data->range; ++index){if(data->flag){// 拼接信息字符串QString text = QString("线程ID:0x%1 启动类型:%2 函数名:%3 索引位置:%4").arg(QString::number((int64_t)QThread::currentThreadId(), 16)).arg(data->type).arg(__func__).arg(QString::number(index));// 打印信息字符串qDebug() << text;// 延迟QThread::msleep(200);}}// 计算运行时间QString info = QString("线程类型:%1 本次线程运行时间:%2毫秒").arg(data->type).arg(QDateTime::currentMSecsSinceEpoch() - startTime);//! noquote():自动插入引号字符,并返回对流的引用(此处功能为使‘\n’生效,达到换行效果)qDebug().noquote() << info + '\n';
}CFuncToThreadTest::CFuncToThreadTest(QWidget *parent): QMainWindow(parent), ui(new Ui::CFuncToThreadTest), m_stData(nullptr)
{ui->setupUi(this);// 拼接主线程IDui->mainThreadIdLab->setText("主线程ID:0x" + QString::number((int64_t)QThread::currentThreadId(), 16));qRegisterMetaType("stData");qRegisterMetaType("const stData &");// 创建其他类对象m_testClass = new CTestClass;// 创建其他类使用的线程对象m_moveClassThread = new QThread;//! 链接启动槽函数//! 链接其他类线程信号和线程结束信号connect(this, &CFuncToThreadTest::moveToClassThreadSig, m_testClass, &CTestClass::doSomethingOne);connect(m_moveClassThread, &QThread::finished, m_testClass, &CTestClass::deleteLater);// 调用moveToThread添加线程m_testClass->moveToThread(m_moveClassThread);// 启动其他类线程m_moveClassThread->start();// 创建C++线程指针数据m_stData = new StData(5, "cppThread——异步运行");}CFuncToThreadTest::~CFuncToThreadTest()
{// 其他类线程退出m_moveClassThread->quit();m_moveClassThread->wait(1);delete m_stData;delete m_moveClassThread;delete ui;
}void CFuncToThreadTest::doSomethingTwo(const stData &data)
{// 获取线程启动时间qint64 startTime = QDateTime::currentMSecsSinceEpoch();for(int index = 0; index != data.range; ++index){if(data.flag){// 拼接信息字符串QString text = QString("线程ID:0x%1 启动类型:%2 函数名:%3 索引位置:%4").arg(QString::number((int64_t)QThread::currentThreadId(), 16)).arg(data.type).arg(__func__).arg(QString::number(index));// 打印信息字符串qDebug() << text;// 延迟QThread::msleep(200);}}// 计算运行时间QString info = QString("线程类型:%1 本次线程运行时间:%2毫秒").arg(data.type).arg(QDateTime::currentMSecsSinceEpoch() - startTime);//! noquote():自动插入引号字符,并返回对流的引用(此处功能为使‘\n’生效,达到换行效果)qDebug().noquote() << info + '\n';
}void CFuncToThreadTest::on_qtConCurrentBtn_clicked()
{// 启动线程QtConcurrent::run(this, &CFuncToThreadTest::doSomethingTwo, stData(5, "QtConcurrent"));
}void CFuncToThreadTest::on_otherMoveToBtn_clicked()
{// 发送其他类线程信号emit moveToClassThreadSig(stData(5, "OtherMoveToThread"));
}void CFuncToThreadTest::on_cppThreadBtn_clicked()
{// 创建静态标记值(作用为交替调用线程启动方式)static bool flag = false;// 赋值的同时改值,并使用赋值后的变量判断if(flag = !flag){//! 此处不能传入局部变量//! 线程为异步运行,此处传入局部变量,局部变量将释放// 创建线程对象并传入数据std::thread thread(doSomethingThree, m_stData);// 线程异步启动thread.detach();// 更改按钮文本ui->cppThreadBtn->setText("C++_Thread_阻塞启动");}else{//! 可传入局部变量//! 线程为阻塞运行,此处传入局部变量,局部变量不会释放// 创建线程数据stData data(5, "cppThread——阻塞运行");// 创建线程对象,并传入数据std::thread thread(doSomethingThree, &data);// 线程阻塞启动thread.join();// 更改按钮文本ui->cppThreadBtn->setText("C++_Thread_异步启动");}
}void CFuncToThreadTest::on_compareThreadBtn_clicked()
{// 打印分割线qDebug() << "======================================";/// moveToThread// 发送信号启动线程emit moveToClassThreadSig(stData(COMPARE_RANGE_VAL, "OtherMoveToThread", false));/// QtConcurrentQtConcurrent::run(this, &CFuncToThreadTest::doSomethingTwo, stData(COMPARE_RANGE_VAL, "QtConcurrent", false));/// C++线程// 标记值更新为false,防止进入ifm_stData->flag = false;// 更新循环次数为宏定义值m_stData->range = COMPARE_RANGE_VAL;// 设置线程类型文本m_stData->type = "cppThread——阻塞运行";// 创建c++线程并运行std::thread thread(doSomethingThree, m_stData);// 线程阻塞启动thread.detach();
}
总结
总所周知,当程序运行卡顿,速率不理想时,可通过线程提高运行速率;本文提到的三种方式在想要提高速率的情况时还是蛮有用的,当然具体使用那种方式还得看实际情况。
相关文章
启动QThread线程的两种方法(含源码+注释)
Qt互斥锁(QMutex)、条件变量(QWaitCondition)讲解+QMutex实现多线程循环输出ABC(含源码+注释)
Qt互斥锁(QMutex)的使用、QMutexLocker的使用(含源码+注释)
QSemaphore的使用+QSemaphore实现循环输出ABC(含源码+注释)
QRunnable线程、QThreadPool(线程池)的使用(含源码+注释)
Qt读写锁(QReadWriteLock)的使用、读写锁的验证(含源码+注释)
Qt读写锁(QWriteLocker、QReadLocker)的理解和使用(含部分源码)
友情提示——哪里看不懂可私哦,让我们一起互相进步吧
(创作不易,请留下一个免费的赞叭 谢谢 ^o^/)
注:文章为作者编程过程中所遇到的问题和总结,内容仅供参考,若有错误欢迎指出。
注:如有侵权,请联系作者删除
