elasticsearch使用painless的一些简单例子
创始人
2024-05-23 20:03:17
文章目录
- 1、背景
- 2、准备数据
- 2.1 mapping
- 2.2 插入数据
- 3、例子
- 3.1 (update)更新文档 id=1 的文档,将 age 加 2岁
- 3.2 (update_by_query)如果 province 是北京的话,就将 age 减少1岁
- 3.3 (ctx.op)如果张三的年龄小于20岁就不处理,否则就删除这个文档
- 3.4 (stored script)如果是湖南省则增加地市字段,值为长沙
- 3.4.1 创建存储脚本
- 3.4.2 使用存储脚本
- 3.5 (pipeline)通过pipeline如果插入的文档的age<10则放入到index_person_small索引中
- 3.5.1 创建pipeline
- 3.5.2 使用pipeline
- 3.5.3 运行结果
- 3.6 function_score中使用script_score算分
- 3.6.1 需求
- 3.6.2 dsl
- 3.6.3 运行结果
- 3.7 script_fields 增加字段
- 3.8 runtime field 增加字段
- 3.8.1 需求
- 3.8.2 dsl
- 3.9 _reindex 中使用
- 3.9.1 dsl
- 3.9.2 运行结果
- 3.10 script query 查询age<25
- 3.11 script 聚合
- 4、painless脚本调试
- 5、脚本中的doc[..]和params._source[..]
- 6、painless脚本中的上下文
1、背景
此篇文档仅仅是简单的记录一下painless的一些简单的例子,防止以后忘记,不过多涉及painless的语法。
2、准备数据
2.1 mapping
PUT /index_person
{"mappings": {"properties": {"name": {"type": "keyword"},"age": {"type": "integer"},"province": {"type": "keyword"}}}
}
2.2 插入数据
PUT /index_person/_bulk
{"index":{"_id":1}}
{"name":"张三","age":20,"province":"湖北"}
{"index":{"_id":2}}
{"name":"李四","age":25,"province":"北京"}
{"index":{"_id":3}}
{"name":"王五","age":30,"province":"湖南"}
3、例子
3.1 (update)更新文档 id=1 的文档,将 age 加 2岁
POST index_person/_update/1
{"script": {"lang": "painless","source": """ctx['_source']['age'] += params['incrAge']""","params": {"incrAge": 2}}
}
3.2 (update_by_query)如果 province 是北京的话,就将 age 减少1岁
POST index_person/_update_by_query
{"query": {"term": {"province": {"value": "北京"}}},"script": {"lang": "painless","source": """ctx['_source']['age'] -= params['decrAge']""","params": {"decrAge": 1}}
}
3.3 (ctx.op)如果张三的年龄小于20岁就不处理,否则就删除这个文档
POST index_person/_update/1
{"script": {"lang": "painless","source": """// 这是默认值,表示的是更新值,重新索引记录ctx.op = 'index';if(ctx._source.age < 20){// 表示不处理ctx.op = 'none';}else{// 表示删除这个文档ctx.op = 'delete'; }"""}
}
3.4 (stored script)如果是湖南省则增加地市字段,值为长沙
3.4.1 创建存储脚本
PUT _scripts/add_city
{"script":{"lang": "painless","source": "ctx._source.city = params.city"}
}
add_city为脚本的id
3.4.2 使用存储脚本
POST index_person/_update_by_query
{"query": {"term": {"province": {"value": "湖南"}}},"script": {"id": "add_city","params": {"city": "长沙"}}
}
3.5 (pipeline)通过pipeline如果插入的文档的age<10则放入到index_person_small索引中
3.5.1 创建pipeline
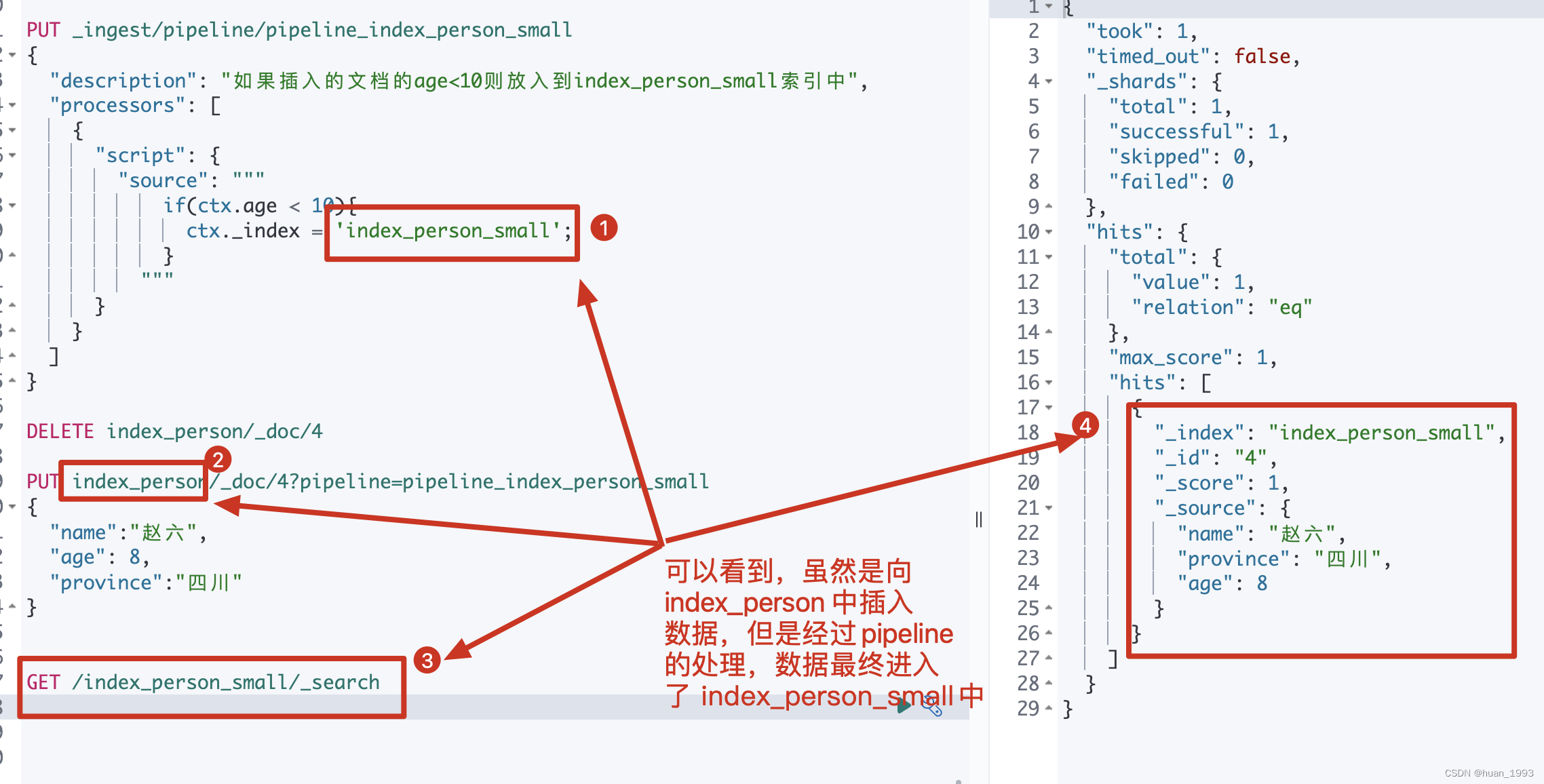
PUT _ingest/pipeline/pipeline_index_person_small
{"description": "如果插入的文档的age<10则放入到index_person_small索引中","processors": [{"script": {"source": """if(ctx.age < 10){ctx._index = 'index_person_small';}"""}}]
}
3.5.2 使用pipeline
PUT index_person/_doc/4?pipeline=pipeline_index_person_small
{"name":"赵六","age": 8,"province":"四川"
}
3.5.3 运行结果
3.6 function_score中使用script_score算分
3.6.1 需求
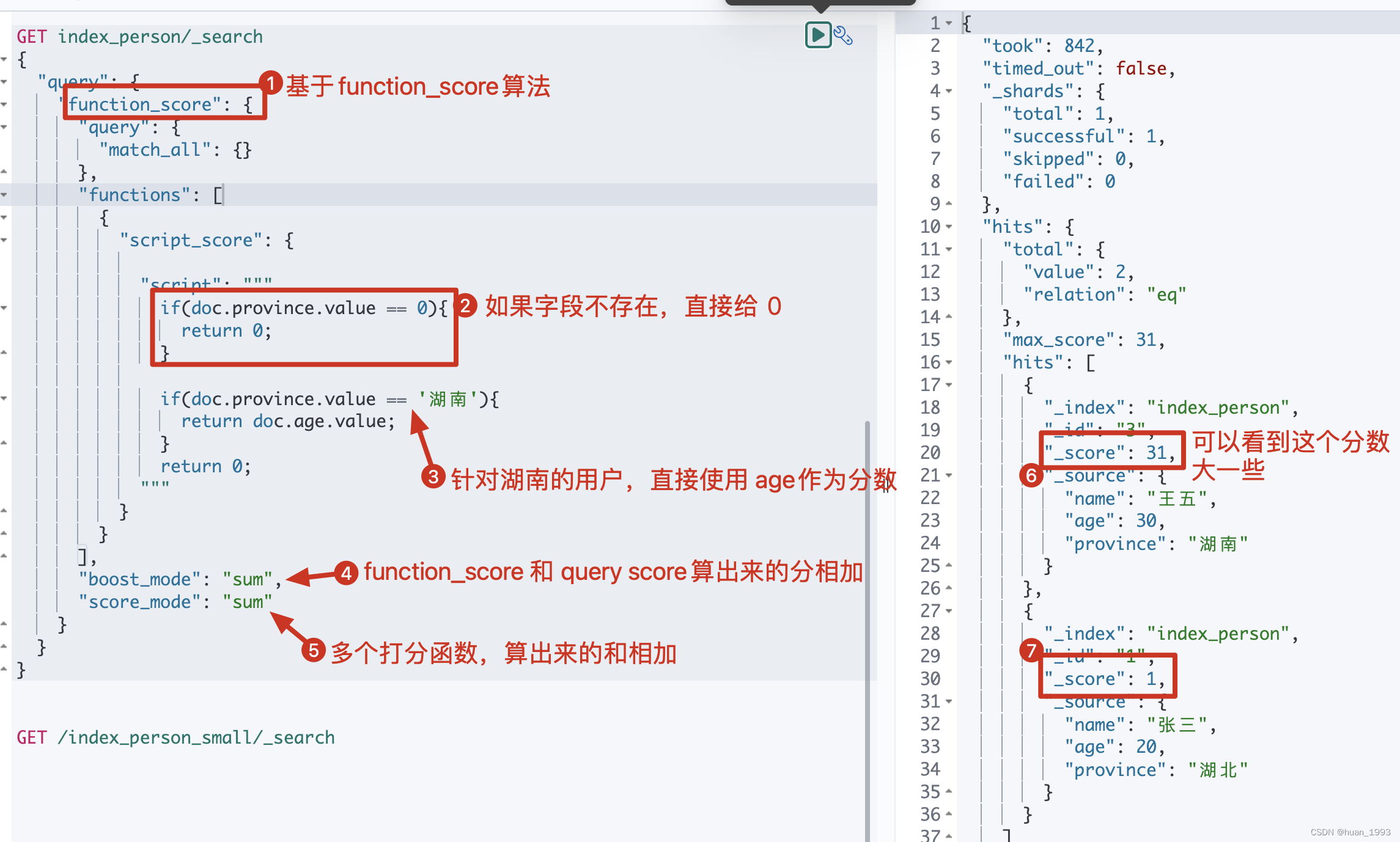
如果这个用户是湖南的,则使用 age作为分数
3.6.2 dsl
GET index_person/_search
{"query": {"function_score": {"query": {"match_all": {}},"functions": [{"script_score": {"script": """if(doc.province.value == 0){return 0;}if(doc.province.value == '湖南'){return doc.age.value;}return 0;"""}}],"boost_mode": "sum","score_mode": "sum"}}
}
3.6.3 运行结果
3.7 script_fields 增加字段
GET index_person/_search
{"query": {"match_all": {}},"fields": ["double_age"], "script_fields": {"double_age": {"script": {"lang": "painless","source": "doc.age.value * 2"}}}
}
3.8 runtime field 增加字段
3.8.1 需求
针对age<25的文档,返回double_age字段,否则不处理。
3.8.2 dsl
GET index_person/_search
{"query": {"match_all": {}},"fields": ["double_age"],"runtime_mappings": {"double_age":{ "type": "keyword","script": """if(doc.age.size() == 0){return;}if(doc.age.value < 25){emit(doc.age.value * 2 + '');}"""}}
}
在runtime field 中,需要使用emit来返回数据,但是不是emit(null)
3.9 _reindex 中使用
3.9.1 dsl
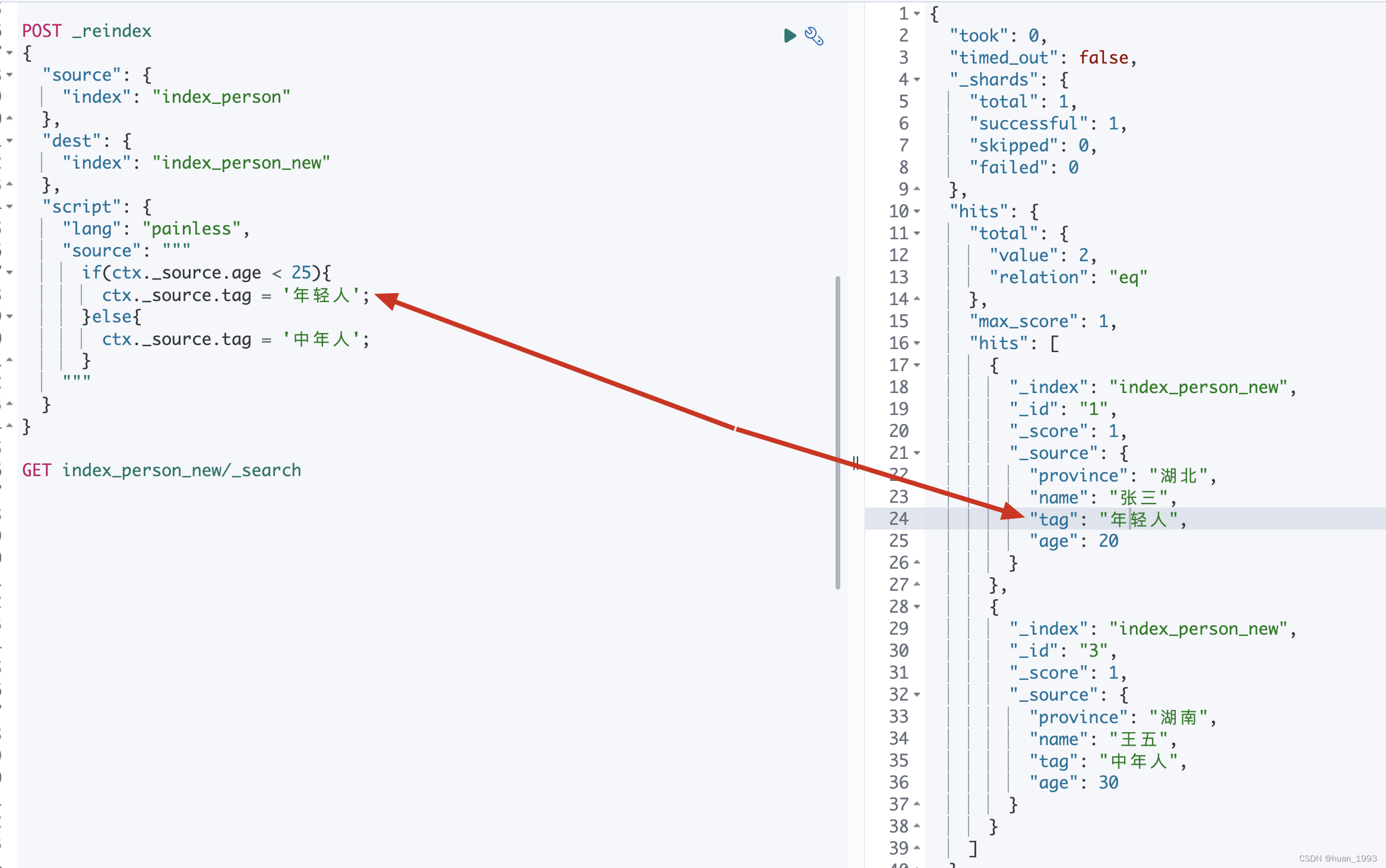
POST _reindex
{"source": {"index": "index_person"},"dest": {"index": "index_person_new"},"script": {"lang": "painless","source": """if(ctx._source.age < 25){ctx._source.tag = '年轻人';}else{ctx._source.tag = '中年人';}"""}
}
3.9.2 运行结果
3.10 script query 查询age<25
GET index_person/_search
{"query": {"script": {"script": {"lang": "painless","source": """if(doc.age.size() == 0){return false;}return doc.age.value < 25;"""}}}
}
3.11 script 聚合
GET index_person/_search
{"size": 0, "aggs": {"agg_province": {"terms": {"script": {"lang": "painless","source": """return doc.province"""}, "size": 10}},"agg_age":{"avg": {"script": "params._source.age"}}}
}
4、painless脚本调试
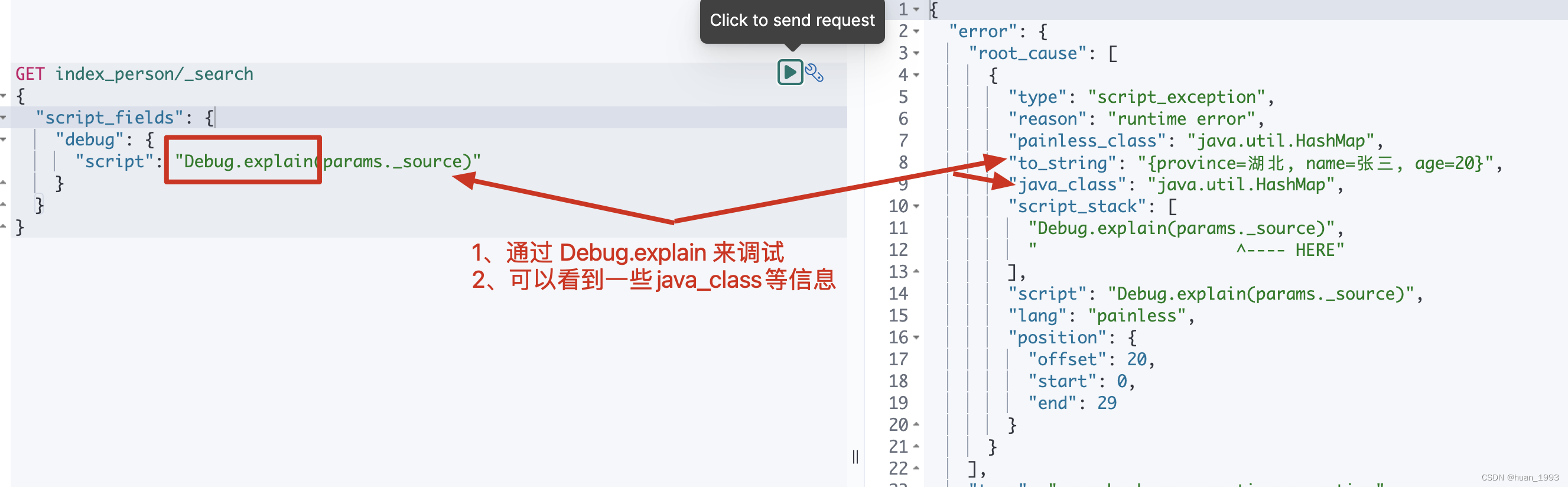
可以通过Debug.explain来进行一些简单的调试。
5、脚本中的doc[…]和params._source[…]
doc[…]:使用doc关键字,将导致该字段的术语被加载到内存(缓存),这将导致更快的执行,但更多的内存消耗。此外,doc[…]表示法只允许简单的值字段(您不能从中返回json对象),并且仅对非分析或基于单个术语的字段有意义。然而,如果可能的话,使用doc仍然是访问文档值的推荐方法。
params[_source][…]: 每次使用_source都必须加载和解析, 因此使用_source会相对而言要慢点。
![脚本中的doc[..]和params._source[..]](/uploadfile/202405/8967adcefdccb5e.png)
6、painless脚本中的上下文
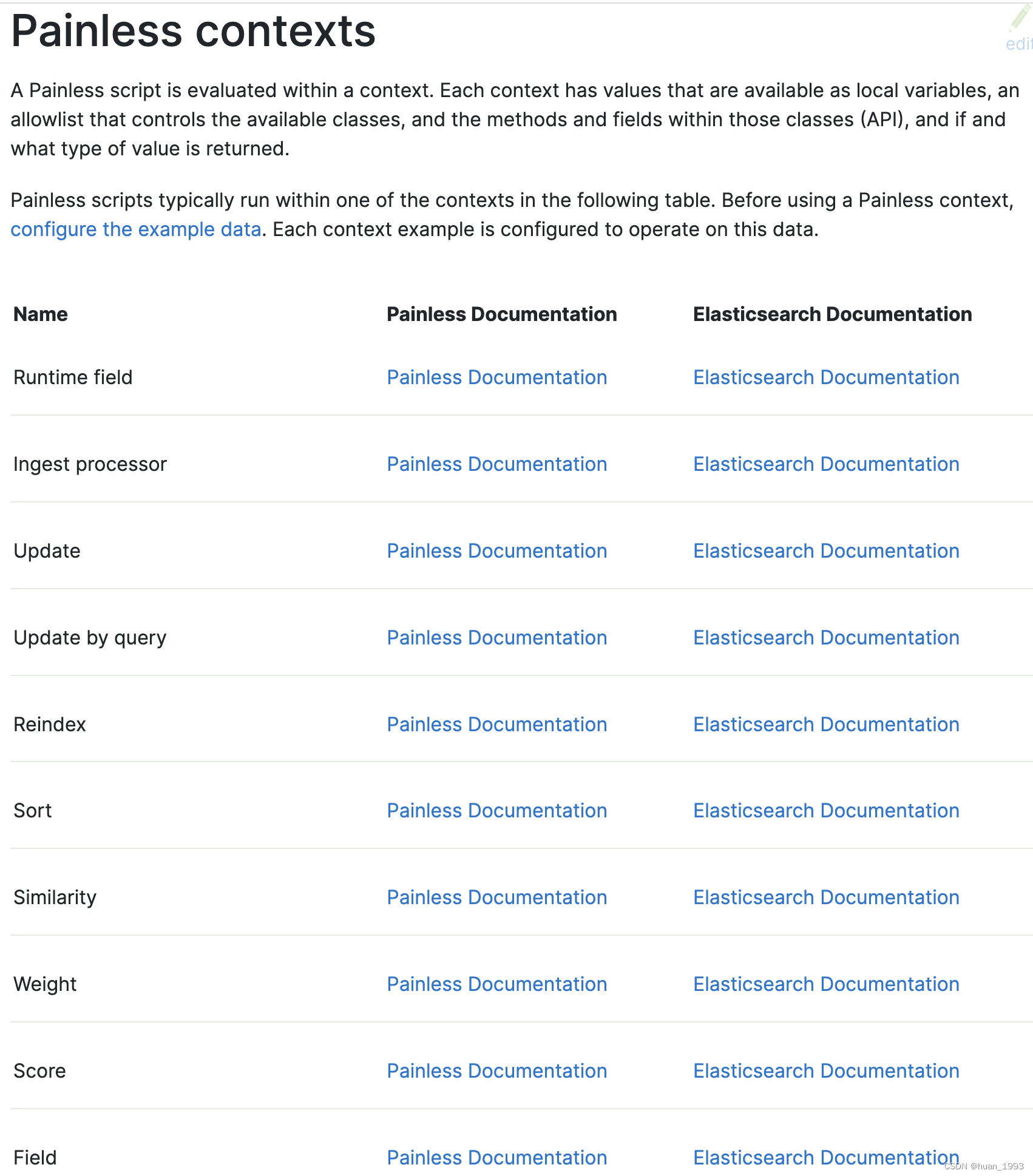
详细了解,请参考这个文档https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/painless/current/painless-contexts.html
上一篇:linux性能优化-内存原理
下一篇:Jenkins创建多分支流水线
相关内容
热门资讯
北京的名胜古迹 北京最著名的景...
北京从元代开始,逐渐走上帝国首都的道路,先是成为大辽朝五大首都之一的南京城,随着金灭辽,金代从海陵王...
苗族的传统节日 贵州苗族节日有...
【岜沙苗族芦笙节】岜沙,苗语叫“分送”,距从江县城7.5公里,是世界上最崇拜树木并以树为神的枪手部落...
世界上最漂亮的人 世界上最漂亮...
此前在某网上,选出了全球265万颜值姣好的女性。从这些数量庞大的女性群体中,人们投票选出了心目中最美...
长白山自助游攻略 吉林长白山游...
昨天介绍了西坡的景点详细请看链接:一个人的旅行,据说能看到长白山天池全凭运气,您的运气如何?今日介绍...
