驱动 | Linux | NVMe | 2. nvme_probe
本文主要参考这里 [^nvme驱动详解]’ [^nvme概述及nvme_core_init函数] 的解析和 linux 源码 [^linux源码]。
此处推荐一个可以便捷查看 linux 源码的网站 bootlin [^bootlin]。
更新:2022 / 02 / 11
驱动 | Linux | NVMe | 2. nvme_probe
- nvme_pci_alloc_dev
- nvme_reset_work
- nvme_pci_enable
- pci_alloc_irq_vectors
- pci_alloc_irq_vectors_affinity
- nvme_pci_configure_admin_queue
- 1. 读取 NVM Subsystem Reset 寄存器
- 2&5. nvme_disable_ctrl / nvme_enable_ctrl
- nvme_wait_ready
- 3. nvme_alloc_queue
- 4. lo_hi_writeq
- 6. nvme_init_queue
- 7. queue_request_irq
- nvme_init_ctrl
- dev_set_name
- kobject_set_name_vargs
- nvme_dev_map
- pci_request_mem_regions
- pci_select_bars
- pci_request_selected_regions
- nvme_remap_bar
- nvme_setup_prp_pools
- nvme_alloc_admin_tag_set
- nvme_alloc_admin_tag_set
- nvme_alloc_admin_tag_set
先来回忆一下 nvme_probe 的定义:
static int nvme_probe(struct pci_dev *pdev, const struct pci_device_id *id)
{struct nvme_dev *dev;int result = -ENOMEM;// 1.dev = nvme_pci_alloc_dev(pdev, id);if (!dev)return -ENOMEM;// 2. 获得PCI Bar的虚拟地址result = nvme_dev_map(dev);if (result)goto out_uninit_ctrl;// 3. 设置 DMA 需要的 PRP 内存池result = nvme_setup_prp_pools(dev);if (result)goto out_dev_unmap;// 4.result = nvme_pci_alloc_iod_mempool(dev);if (result)goto out_release_prp_pools;// 5. 打印日志dev_info(dev->ctrl.device, "pci function %s\n", dev_name(&pdev->dev));// 6.result = nvme_pci_enable(dev);if (result)goto out_release_iod_mempool;// 7. 对nvme_alloc_admin_tag_set结构体初始化,在这个过程中特别提一下ops的赋值(后续会用到)。result = nvme_alloc_admin_tag_set(&dev->ctrl, &dev->admin_tagset,&nvme_mq_admin_ops, sizeof(struct nvme_iod));if (result)goto out_disable;/** Mark the controller as connecting before sending admin commands to* allow the timeout handler to do the right thing.*/// 8.if (!nvme_change_ctrl_state(&dev->ctrl, NVME_CTRL_CONNECTING)) {dev_warn(dev->ctrl.device,"failed to mark controller CONNECTING\n");result = -EBUSY;goto out_disable;}// 9. 初始化NVMe Controller结构result = nvme_init_ctrl_finish(&dev->ctrl, false);if (result)goto out_disable;// 10.nvme_dbbuf_dma_alloc(dev);// 11.result = nvme_setup_host_mem(dev);if (result < 0)goto out_disable;// 12.result = nvme_setup_io_queues(dev);if (result)goto out_disable;// 13.if (dev->online_queues > 1) {nvme_alloc_io_tag_set(&dev->ctrl, &dev->tagset, &nvme_mq_ops,nvme_pci_nr_maps(dev), sizeof(struct nvme_iod));nvme_dbbuf_set(dev);}// 14.if (!dev->ctrl.tagset)dev_warn(dev->ctrl.device, "IO queues not created\n");// 15.if (!nvme_change_ctrl_state(&dev->ctrl, NVME_CTRL_LIVE)) {dev_warn(dev->ctrl.device,"failed to mark controller live state\n");result = -ENODEV;goto out_disable;}// 16. 为设备设置私有数据指针 pci_set_drvdata(pdev, dev);nvme_start_ctrl(&dev->ctrl);nvme_put_ctrl(&dev->ctrl);flush_work(&dev->ctrl.scan_work);return 0;out_disable:nvme_change_ctrl_state(&dev->ctrl, NVME_CTRL_DELETING);nvme_dev_disable(dev, true);nvme_free_host_mem(dev);nvme_dev_remove_admin(dev);nvme_dbbuf_dma_free(dev);nvme_free_queues(dev, 0);
out_release_iod_mempool:mempool_destroy(dev->iod_mempool);
out_release_prp_pools:nvme_release_prp_pools(dev);
out_dev_unmap:nvme_dev_unmap(dev);
out_uninit_ctrl:nvme_uninit_ctrl(&dev->ctrl);return result;
}
再来对 nvme_probe 过程中的一些函数的使用进行进一步分析:
nvme_pci_alloc_dev
先看它的定义,如下:
static struct nvme_dev *nvme_pci_alloc_dev(struct pci_dev *pdev,const struct pci_device_id *id)
{unsigned long quirks = id->driver_data;// 1. 通过调用 dev_to_node 得到这个 pci_dev 的 numa 节点。// 如果没有制定的话,默认用 first_memory_node,也就是第一个 numa 节点. int node = dev_to_node(&pdev->dev);struct nvme_dev *dev;int ret = -ENOMEM;if (node == NUMA_NO_NODE)set_dev_node(&pdev->dev, first_memory_node);// 2. 为 nvme dev 节点分配空间dev = kzalloc_node(sizeof(*dev), GFP_KERNEL, node);if (!dev)return NULL;// 3. 初始化两个work变量, 放在nvme_workq中执行// 4. 调用nvme_reset_work进行reset操作INIT_WORK(&dev->ctrl.reset_work, nvme_reset_work);// 初始化互斥锁mutex_init(&dev->shutdown_lock);// 5. 分配queuedev->nr_write_queues = write_queues;dev->nr_poll_queues = poll_queues;dev->nr_allocated_queues = nvme_max_io_queues(dev) + 1;dev->queues = kcalloc_node(dev->nr_allocated_queues,sizeof(struct nvme_queue), GFP_KERNEL, node);if (!dev->queues)goto out_free_dev;// 6. 增加设备对象的引用计数dev->dev = get_device(&pdev->dev);quirks |= check_vendor_combination_bug(pdev);if (!noacpi && acpi_storage_d3(&pdev->dev)) {/** Some systems use a bios work around to ask for D3 on* platforms that support kernel managed suspend.*/dev_info(&pdev->dev,"platform quirk: setting simple suspend\n");quirks |= NVME_QUIRK_SIMPLE_SUSPEND;}// 初始化 NVMe Controller 结构ret = nvme_init_ctrl(&dev->ctrl, &pdev->dev, &nvme_pci_ctrl_ops,quirks);if (ret)goto out_put_device;dma_set_min_align_mask(&pdev->dev, NVME_CTRL_PAGE_SIZE - 1);dma_set_max_seg_size(&pdev->dev, 0xffffffff);/** Limit the max command size to prevent iod->sg allocations going* over a single page.*/dev->ctrl.max_hw_sectors = min_t(u32,NVME_MAX_KB_SZ << 1, dma_max_mapping_size(&pdev->dev) >> 9);dev->ctrl.max_segments = NVME_MAX_SEGS;/** There is no support for SGLs for metadata (yet), so we are limited to* a single integrity segment for the separate metadata pointer.*/dev->ctrl.max_integrity_segments = 1;return dev;out_put_device:put_device(dev->dev);kfree(dev->queues);
out_free_dev:kfree(dev);return ERR_PTR(ret);
}
nvme_pci_alloc_dev 做了什么呢?
nvme_reset_work
在 nvme_pci_alloc_dev 中有调用 nvme_reset_work,
static void nvme_reset_work(struct work_struct *work)
{struct nvme_dev *dev =container_of(work, struct nvme_dev, ctrl.reset_work);bool was_suspend = !!(dev->ctrl.ctrl_config & NVME_CC_SHN_NORMAL);int result;// 1. 检查NVME_CTRL_RESETTING标志,来确保nvme_reset_work不会被重复进入.if (dev->ctrl.state != NVME_CTRL_RESETTING) {dev_warn(dev->ctrl.device, "ctrl state %d is not RESETTING\n",dev->ctrl.state);return;}/** If we're called to reset a live controller first shut it down before* moving on.*/if (dev->ctrl.ctrl_config & NVME_CC_ENABLE)nvme_dev_disable(dev, false);nvme_sync_queues(&dev->ctrl);mutex_lock(&dev->shutdown_lock);// 2. result = nvme_pci_enable(dev);if (result)goto out_unlock;// 3. nvme_unquiesce_admin_queue(&dev->ctrl);mutex_unlock(&dev->shutdown_lock);/** Introduce CONNECTING state from nvme-fc/rdma transports to mark the* initializing procedure here.*/if (!nvme_change_ctrl_state(&dev->ctrl, NVME_CTRL_CONNECTING)) {dev_warn(dev->ctrl.device,"failed to mark controller CONNECTING\n");result = -EBUSY;goto out;}result = nvme_init_ctrl_finish(&dev->ctrl, was_suspend);if (result)goto out;nvme_dbbuf_dma_alloc(dev);result = nvme_setup_host_mem(dev);if (result < 0)goto out;result = nvme_setup_io_queues(dev);if (result)goto out;/** Freeze and update the number of I/O queues as thos might have* changed. If there are no I/O queues left after this reset, keep the* controller around but remove all namespaces.*/if (dev->online_queues > 1) {nvme_unquiesce_io_queues(&dev->ctrl);nvme_wait_freeze(&dev->ctrl);nvme_pci_update_nr_queues(dev);nvme_dbbuf_set(dev);nvme_unfreeze(&dev->ctrl);} else {dev_warn(dev->ctrl.device, "IO queues lost\n");nvme_mark_namespaces_dead(&dev->ctrl);nvme_unquiesce_io_queues(&dev->ctrl);nvme_remove_namespaces(&dev->ctrl);nvme_free_tagset(dev);}/** If only admin queue live, keep it to do further investigation or* recovery.*/if (!nvme_change_ctrl_state(&dev->ctrl, NVME_CTRL_LIVE)) {dev_warn(dev->ctrl.device,"failed to mark controller live state\n");result = -ENODEV;goto out;}nvme_start_ctrl(&dev->ctrl);return;out_unlock:mutex_unlock(&dev->shutdown_lock);out:/** Set state to deleting now to avoid blocking nvme_wait_reset(), which* may be holding this pci_dev's device lock.*/dev_warn(dev->ctrl.device, "Disabling device after reset failure: %d\n",result);nvme_change_ctrl_state(&dev->ctrl, NVME_CTRL_DELETING);nvme_dev_disable(dev, true);nvme_mark_namespaces_dead(&dev->ctrl);nvme_change_ctrl_state(&dev->ctrl, NVME_CTRL_DEAD);
}
nvme_pci_enable
在 nvme_reset_work 中有调用 nvme_pci_enable,其定义如下:
static int nvme_pci_enable(struct nvme_dev *dev)
{int result = -ENOMEM;struct pci_dev *pdev = to_pci_dev(dev->dev);int dma_address_bits = 64;// 1. 使能nvme设备的内存空间iomem,也就是之前映射的bar空间。if (pci_enable_device_mem(pdev))return result;// 设置设备具有获得总线的能力,即调用这个函数,使设备具备申请使用PCI总线的能力。pci_set_master(pdev);if (dev->ctrl.quirks & NVME_QUIRK_DMA_ADDRESS_BITS_48)dma_address_bits = 48;// 设定这个nvme设备的DMA区域大小,64 bits或者48 bitsif (dma_set_mask_and_coherent(dev->dev, DMA_BIT_MASK(dma_address_bits)))goto disable;// 读取Controller寄存器NVME_REG_CSTS,判断Controller的状态if (readl(dev->bar + NVME_REG_CSTS) == -1) {result = -ENODEV;goto disable;}/** Some devices and/or platforms don't advertise or work with INTx* interrupts. Pre-enable a single MSIX or MSI vec for setup. We'll* adjust this later.*/// 为设备分配中断请求。nvme设备支持三种中断模式:INITx/MSI/MSI-X.result = pci_alloc_irq_vectors(pdev, 1, 1, PCI_IRQ_ALL_TYPES);if (result < 0)goto disable;// 获取设备64位的Controller Capabilities(CAP)dev->ctrl.cap = lo_hi_readq(dev->bar + NVME_REG_CAP);dev->q_depth = min_t(u32, NVME_CAP_MQES(dev->ctrl.cap) + 1,io_queue_depth);dev->db_stride = 1 << NVME_CAP_STRIDE(dev->ctrl.cap);// 设置Doorbell地址,这里的4096来自SQ Tail DB的起始地址0x1000dev->dbs = dev->bar + 4096;/** Some Apple controllers require a non-standard SQE size.* Interestingly they also seem to ignore the CC:IOSQES register* so we don't bother updating it here.*/if (dev->ctrl.quirks & NVME_QUIRK_128_BYTES_SQES)dev->io_sqes = 7;elsedev->io_sqes = NVME_NVM_IOSQES;/** Temporary fix for the Apple controller found in the MacBook8,1 and* some MacBook7,1 to avoid controller resets and data loss.*/if (pdev->vendor == PCI_VENDOR_ID_APPLE && pdev->device == 0x2001) {dev->q_depth = 2;dev_warn(dev->ctrl.device, "detected Apple NVMe controller, ""set queue depth=%u to work around controller resets\n",dev->q_depth);} else if (pdev->vendor == PCI_VENDOR_ID_SAMSUNG &&(pdev->device == 0xa821 || pdev->device == 0xa822) &&NVME_CAP_MQES(dev->ctrl.cap) == 0) {dev->q_depth = 64;dev_err(dev->ctrl.device, "detected PM1725 NVMe controller, ""set queue depth=%u\n", dev->q_depth);}/** Controllers with the shared tags quirk need the IO queue to be* big enough so that we get 32 tags for the admin queue*/if ((dev->ctrl.quirks & NVME_QUIRK_SHARED_TAGS) &&(dev->q_depth < (NVME_AQ_DEPTH + 2))) {dev->q_depth = NVME_AQ_DEPTH + 2;dev_warn(dev->ctrl.device, "IO queue depth clamped to %d\n",dev->q_depth);}dev->ctrl.sqsize = dev->q_depth - 1; /* 0's based queue depth */nvme_map_cmb(dev);// 错误处理pci_enable_pcie_error_reporting(pdev);// Suspend之前保存设备当下的状态pci_save_state(pdev);result = nvme_pci_configure_admin_queue(dev);if (result)goto free_irq;return result;free_irq:pci_free_irq_vectors(pdev);disable:pci_disable_device(pdev);return result;
}
pci_alloc_irq_vectors
在 nvme_pci_enable 中有调用 pci_alloc_irq_vectors,其定义如下:
/*** pci_alloc_irq_vectors() - Allocate multiple device interrupt vectors* @dev: the PCI device to operate on* @min_vecs: minimum required number of vectors (must be >= 1)* @max_vecs: maximum desired number of vectors* @flags: One or more of:** * %PCI_IRQ_MSIX Allow trying MSI-X vector allocations* * %PCI_IRQ_MSI Allow trying MSI vector allocations** * %PCI_IRQ_LEGACY Allow trying legacy INTx interrupts, if* and only if @min_vecs == 1** * %PCI_IRQ_AFFINITY Auto-manage IRQs affinity by spreading* the vectors around available CPUs** Allocate up to @max_vecs interrupt vectors on device. MSI-X irq* vector allocation has a higher precedence over plain MSI, which has a* higher precedence over legacy INTx emulation.** Upon a successful allocation, the caller should use pci_irq_vector()* to get the Linux IRQ number to be passed to request_threaded_irq().* The driver must call pci_free_irq_vectors() on cleanup.** Return: number of allocated vectors (which might be smaller than* @max_vecs), -ENOSPC if less than @min_vecs interrupt vectors are* available, other errnos otherwise.*/
int pci_alloc_irq_vectors(struct pci_dev *dev, unsigned int min_vecs,unsigned int max_vecs, unsigned int flags)
{return pci_alloc_irq_vectors_affinity(dev, min_vecs, max_vecs,flags, NULL);
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(pci_alloc_irq_vectors);
pci_alloc_irq_vectors_affinity
/*** pci_alloc_irq_vectors_affinity() - Allocate multiple device interrupt* vectors with affinity requirements* @dev: the PCI device to operate on* @min_vecs: minimum required number of vectors (must be >= 1)* @max_vecs: maximum desired number of vectors* @flags: allocation flags, as in pci_alloc_irq_vectors()* @affd: affinity requirements (can be %NULL).** Same as pci_alloc_irq_vectors(), but with the extra @affd parameter.* Check that function docs, and &struct irq_affinity, for more details.*/
int pci_alloc_irq_vectors_affinity(struct pci_dev *dev, unsigned int min_vecs,unsigned int max_vecs, unsigned int flags,struct irq_affinity *affd)
{struct irq_affinity msi_default_affd = {0};int nvecs = -ENOSPC;// 当IRQ为Affinity自动分配时,IRQ中断会分配给所有CPUs。// 在nvme_pci_enable过程中调用时,*affd=NULLif (flags & PCI_IRQ_AFFINITY) {if (!affd)affd = &msi_default_affd;} else {if (WARN_ON(affd))affd = NULL;}// 分配MSI-X中断,配置MSI-X capability structureif (flags & PCI_IRQ_MSIX) {nvecs = __pci_enable_msix_range(dev, NULL, min_vecs, max_vecs,affd, flags);if (nvecs > 0)return nvecs;}// 分配MSI中断,配置MSI capability structureif (flags & PCI_IRQ_MSI) {nvecs = __pci_enable_msi_range(dev, min_vecs, max_vecs, affd);if (nvecs > 0)return nvecs;}/* use legacy IRQ if allowed */// 分配INITx中断if (flags & PCI_IRQ_LEGACY) {if (min_vecs == 1 && dev->irq) {/** Invoke the affinity spreading logic to ensure that* the device driver can adjust queue configuration* for the single interrupt case.*/if (affd)irq_create_affinity_masks(1, affd);pci_intx(dev, 1);return 1;}}return nvecs;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(pci_alloc_irq_vectors_affinity);
这三种中断不能同时 enable,比如要采用 MSI-X 中断,那就必须把 INITx 和 MSI 中断 disable。
nvme_pci_configure_admin_queue
在 nvme_pci_enable 中有调用 nvme_pci_configure_admin_queue,其定义如下:
static int nvme_pci_configure_admin_queue(struct nvme_dev *dev)
{int result;u32 aqa;struct nvme_queue *nvmeq;result = nvme_remap_bar(dev, db_bar_size(dev, 0));if (result < 0)return result;// 1. 从CAP寄存器中判断对Subsystem Reset的支持情况dev->subsystem = readl(dev->bar + NVME_REG_VS) >= NVME_VS(1, 1, 0) ?NVME_CAP_NSSRC(dev->ctrl.cap) : 0;if (dev->subsystem &&(readl(dev->bar + NVME_REG_CSTS) & NVME_CSTS_NSSRO))writel(NVME_CSTS_NSSRO, dev->bar + NVME_REG_CSTS);/** If the device has been passed off to us in an enabled state, just* clear the enabled bit. The spec says we should set the 'shutdown* notification bits', but doing so may cause the device to complete* commands to the admin queue ... and we don't know what memory that* might be pointing at!*/// 2. 调用nvme_disable_ctrlresult = nvme_disable_ctrl(&dev->ctrl, false);if (result < 0)return result;// 3. 调用nvme_alloc_queue// 设备disable之后第一次调用nvmeq, 此时值为Null。这时需要调用nvme_alloc_queue分配NVMe queue.result = nvme_alloc_queue(dev, 0, NVME_AQ_DEPTH);if (result)return result;dev->ctrl.numa_node = dev_to_node(dev->dev);nvmeq = &dev->queues[0];aqa = nvmeq->q_depth - 1;aqa |= aqa << 16;// 4. nvme_alloc_queue分配NVMe queue后,就要将nvme admin queue的属性以及已经分配的admin SQ/CQ内存地址写入寄存器。writel(aqa, dev->bar + NVME_REG_AQA);lo_hi_writeq(nvmeq->sq_dma_addr, dev->bar + NVME_REG_ASQ);lo_hi_writeq(nvmeq->cq_dma_addr, dev->bar + NVME_REG_ACQ);// 5. 对admin queue分配内存之后,调用nvme_enable_ctrl将设备enable。这个函数与nvme_disable_ctrl函数类似,只是过程相反。result = nvme_enable_ctrl(&dev->ctrl);if (result)return result;// 6. 对之前申请的queue进行初始化操作nvmeq->cq_vector = 0;nvme_init_queue(nvmeq, 0);// 7. 调用queue_request_irq申请中断。这个函数主要的工作是设置中断处理函数,默认情况下不使用线程化的中断处理,而是使用中断上下文的中断处理。result = queue_request_irq(nvmeq);if (result) {dev->online_queues--;return result;}set_bit(NVMEQ_ENABLED, &nvmeq->flags);return result;
}
从上面的代码,我们可以了解到 nvme_pci_configure_admin_queue 中大致的步骤如下:
-
- 从
CAP寄存器中判断对Subsystem Reset的支持情况;
- 从
-
- 调用
nvme_disable_ctrl;
- 调用
-
- 调用
nvme_alloc_queue;
- 调用
-
- 调用
lo_hi_writeq;
- 调用
-
- 调用
nvme_enable_ctrl;
- 调用
-
- 调用
nvme_init_queue;
- 调用
-
- 调用
queue_request_irq;
- 调用
对于上面的步骤,挨个逐步分析:
1. 读取 NVM Subsystem Reset 寄存器
Controller 的 CAP 寄存器 bit[36] 定义了对 NVM subsystem reset 是否支持,如下图:
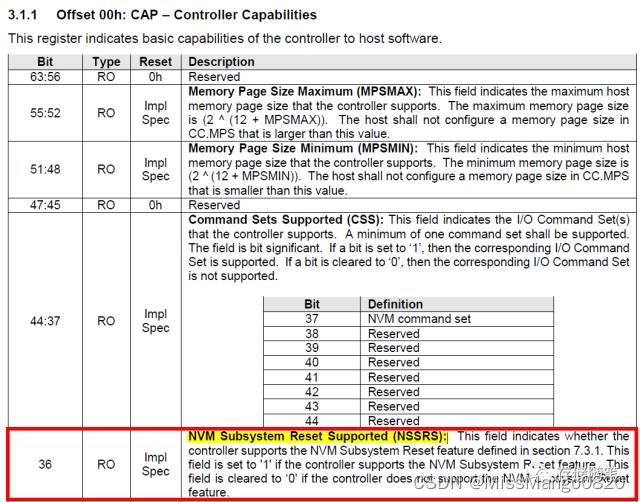
一般情况下,NVM subsystem 就是一块 SSD 了,由 Controller、NAND 以及接口组成一个 NVM subsystem。
NVM Subsystem Reset 是 Controller Level Reset 的一种。
2&5. nvme_disable_ctrl / nvme_enable_ctrl
在对 NVMe controller 进行操作时需要通过 nvme_disable_ctrl 将设备 disable,完成后再调用 nvme_enable_ctrl 将设备 enable。
int nvme_disable_ctrl(struct nvme_ctrl *ctrl, bool shutdown)
{int ret;ctrl->ctrl_config &= ~NVME_CC_SHN_MASK;if (shutdown)ctrl->ctrl_config |= NVME_CC_SHN_NORMAL;elsectrl->ctrl_config &= ~NVME_CC_ENABLE;// 这里的ctrl->ops就是之前nvme_probe函数中nvme_init_ctrl时传进去的nvme_pci_ctrl_ops// reg_write32通过NVME_REG_CC寄存器disable设备。ret = ctrl->ops->reg_write32(ctrl, NVME_REG_CC, ctrl->ctrl_config);if (ret)return ret;if (shutdown) {return nvme_wait_ready(ctrl, NVME_CSTS_SHST_MASK,NVME_CSTS_SHST_CMPLT,ctrl->shutdown_timeout, "shutdown");}if (ctrl->quirks & NVME_QUIRK_DELAY_BEFORE_CHK_RDY)msleep(NVME_QUIRK_DELAY_AMOUNT);// 在函数最后,通过读取状态寄存器NVME_REG_CSTS来等待设备真正停止。// 超时上限是根据CAP寄存器Bit[31:24]的Timeout域来计算出来的,每个单位代表500ms。return nvme_wait_ready(ctrl, NVME_CSTS_RDY, 0,(NVME_CAP_TIMEOUT(ctrl->cap) + 1) / 2, "reset");
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(nvme_disable_ctrl);
// 通过读取状态寄存器NVME_REG_CSTS来等待设备真正停止。超时上限是根据CAP寄存器Bit[31:24]的Timeout域来计算出来的,每个单位代表500ms。
#define NVME_CAP_TIMEOUT(cap) (((cap) >> 24) & 0xff)

nvme_wait_ready
static int nvme_wait_ready(struct nvme_ctrl *ctrl, u32 mask, u32 val,u32 timeout, const char *op)
{unsigned long timeout_jiffies = jiffies + timeout * HZ;u32 csts;int ret;while ((ret = ctrl->ops->reg_read32(ctrl, NVME_REG_CSTS, &csts)) == 0) {if (csts == ~0)return -ENODEV;if ((csts & mask) == val)break;usleep_range(1000, 2000);if (fatal_signal_pending(current))return -EINTR;if (time_after(jiffies, timeout_jiffies)) {dev_err(ctrl->device,"Device not ready; aborting %s, CSTS=0x%x\n",op, csts);return -ENODEV;}}return ret;
}
// 同 nvme_disable_ctrl 的过程基本相反
int nvme_enable_ctrl(struct nvme_ctrl *ctrl)
{unsigned dev_page_min;u32 timeout;int ret;ret = ctrl->ops->reg_read64(ctrl, NVME_REG_CAP, &ctrl->cap);if (ret) {dev_err(ctrl->device, "Reading CAP failed (%d)\n", ret);return ret;}dev_page_min = NVME_CAP_MPSMIN(ctrl->cap) + 12;if (NVME_CTRL_PAGE_SHIFT < dev_page_min) {dev_err(ctrl->device,"Minimum device page size %u too large for host (%u)\n",1 << dev_page_min, 1 << NVME_CTRL_PAGE_SHIFT);return -ENODEV;}if (NVME_CAP_CSS(ctrl->cap) & NVME_CAP_CSS_CSI)ctrl->ctrl_config = NVME_CC_CSS_CSI;elsectrl->ctrl_config = NVME_CC_CSS_NVM;if (ctrl->cap & NVME_CAP_CRMS_CRWMS) {u32 crto;ret = ctrl->ops->reg_read32(ctrl, NVME_REG_CRTO, &crto);if (ret) {dev_err(ctrl->device, "Reading CRTO failed (%d)\n",ret);return ret;}if (ctrl->cap & NVME_CAP_CRMS_CRIMS) {ctrl->ctrl_config |= NVME_CC_CRIME;timeout = NVME_CRTO_CRIMT(crto);} else {timeout = NVME_CRTO_CRWMT(crto);}} else {timeout = NVME_CAP_TIMEOUT(ctrl->cap);}ctrl->ctrl_config |= (NVME_CTRL_PAGE_SHIFT - 12) << NVME_CC_MPS_SHIFT;ctrl->ctrl_config |= NVME_CC_AMS_RR | NVME_CC_SHN_NONE;ctrl->ctrl_config |= NVME_CC_IOSQES | NVME_CC_IOCQES;// 这里的ctrl->ops就是之前nvme_probe函数中nvme_init_ctrl时传进去的nvme_pci_ctrl_ops// reg_write32通过NVME_REG_CC寄存器disable设备ret = ctrl->ops->reg_write32(ctrl, NVME_REG_CC, ctrl->ctrl_config);if (ret)return ret;/* Flush write to device (required if transport is PCI) */ret = ctrl->ops->reg_read32(ctrl, NVME_REG_CC, &ctrl->ctrl_config);if (ret)return ret;ctrl->ctrl_config |= NVME_CC_ENABLE;ret = ctrl->ops->reg_write32(ctrl, NVME_REG_CC, ctrl->ctrl_config);if (ret)return ret;return nvme_wait_ready(ctrl, NVME_CSTS_RDY, NVME_CSTS_RDY,(timeout + 1) / 2, "initialisation");
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(nvme_enable_ctrl);
3. nvme_alloc_queue
设备 disable 之后需要调用 nvme_alloc_queue 分配 NVMe queue。
static int nvme_alloc_queue(struct nvme_dev *dev, int qid, int depth)
{struct nvme_queue *nvmeq = &dev->queues[qid];if (dev->ctrl.queue_count > qid)return 0;nvmeq->sqes = qid ? dev->io_sqes : NVME_ADM_SQES;nvmeq->q_depth = depth;// 1. 调用 dma_alloc_coherent 为 completion queue 分配内存以供 DMA 使用。nvmeq->cqes为申请到的内存的虚拟地址,供内核使用。// 而nvmeq->cq_dma_addr就是这块内存的物理地址,供DMA控制器使用。nvmeq->cqes = dma_alloc_coherent(dev->dev, CQ_SIZE(nvmeq),&nvmeq->cq_dma_addr, GFP_KERNEL);if (!nvmeq->cqes)goto free_nvmeq;// 2. 调用 nvme_alloc_sq_cmds 来处理 submission queue,假如nvme版本是1.2或者以上的,并且cmb支持 submission queue,那就使用 cmb。// 否则的话,和 completion queue 一样使用dma_alloc_coherent来分配内存。if (nvme_alloc_sq_cmds(dev, nvmeq, qid))goto free_cqdma;nvmeq->dev = dev;spin_lock_init(&nvmeq->sq_lock);spin_lock_init(&nvmeq->cq_poll_lock);nvmeq->cq_head = 0;nvmeq->cq_phase = 1;nvmeq->q_db = &dev->dbs[qid * 2 * dev->db_stride];nvmeq->qid = qid;dev->ctrl.queue_count++;return 0;free_cqdma:dma_free_coherent(dev->dev, CQ_SIZE(nvmeq), (void *)nvmeq->cqes,nvmeq->cq_dma_addr);free_nvmeq:return -ENOMEM;
}
调用 nvme_alloc_queue,设备 disable 之后第一次调用 nvmeq,此时值为 Null。
这时需要调用 nvme_alloc_queue 分配 NVMe queue。
4. lo_hi_writeq
nvme_alloc_queue 分配 NVMe queue 后,就要将 nvme admin queue 的属性以及已经分配的admin SQ/CQ 内存地址写入寄存器。
static inline void lo_hi_writeq(__u64 val, volatile void __iomem *addr)
{writel(val, addr);writel(val >> 32, addr + 4);
}
6. nvme_init_queue
static void nvme_init_queue(struct nvme_queue *nvmeq, u16 qid)
{struct nvme_dev *dev = nvmeq->dev;nvmeq->sq_tail = 0;nvmeq->last_sq_tail = 0;nvmeq->cq_head = 0;nvmeq->cq_phase = 1;nvmeq->q_db = &dev->dbs[qid * 2 * dev->db_stride];memset((void *)nvmeq->cqes, 0, CQ_SIZE(nvmeq));nvme_dbbuf_init(dev, nvmeq, qid);dev->online_queues++;wmb(); /* ensure the first interrupt sees the initialization */
}
在这个过程中,对 SQ Tail,CQ Head 以及 CQ phase 等变量进行初始化赋值,然后通过 q_db 指向 Doorbell 寄存器。
7. queue_request_irq
static int queue_request_irq(struct nvme_queue *nvmeq)
{struct pci_dev *pdev = to_pci_dev(nvmeq->dev->dev);int nr = nvmeq->dev->ctrl.instance;if (use_threaded_interrupts) {return pci_request_irq(pdev, nvmeq->cq_vector, nvme_irq_check,nvme_irq, nvmeq, "nvme%dq%d", nr, nvmeq->qid);} else {return pci_request_irq(pdev, nvmeq->cq_vector, nvme_irq,NULL, nvmeq, "nvme%dq%d", nr, nvmeq->qid);}
}
调用 queue_request_irq 申请中断。
默认情况下不使用线程化的中断处理,而是使用中断上下文的中断处理。
线程化与中断上下文的概念:
中断线程化是实现
Linux实时性的一个重要步骤,在linux标准内核中,中断是最高优先级的执行单元,不管内核当时处理什么,只要有中断事件,系统将立即响应该事件并执行相应的中断处理代码,除非当时中断关闭。因此,如果系统有严重的网络或I/O负载,中断将非常频繁,后发生的实时任务将很难有机会运行,也就是说,毫无实时性可言。
中断线程化之后,中断将作为内核线程运行而且赋予不同的实时优先级,实时任务可以有比中断线程更高的优先级,这样,实时任务就可以作为最高优先级的执行单元来运行,即使在严重负载下仍有实时性保证。内核空间和用户空间是操作系统理论的基础之一,即内核功能模块运行在内核空间,而应用程序运行在用户空间。现代的
CPU都具有不同的操作模式,代表不同的级别,不同的级别具有不同的功能,在较低的级别中将禁止某些操作。
Linux系统设计时利用了这种硬件特性,使用了两个级别,最高级别和最低级别,内核运行在最高级别(内核态),这个级别可以进行所有操作,而应用程序运行在较低级别(用户态),在这个级别,处理器控制着对硬件的直接访问以及对内存的非授权访问。
内核态和用户态有自己的内存映射,即自己的地址空间。
正是有了不同运行状态的划分,才有了上下文的概念。用户空间的应用程序,如果想要请求系统服务,比如操作一个物理设备,或者映射一段设备空间的地址到用户空间,就必须通过系统调用来(操作系统提供给用户空间的接口函数)实现。通过系统调用,用户空间的应用程序就会进入内核空间,由内核代表该进程运行于内核空间,这就涉及到上下文的切换,用户空间和内核空间具有不同的地址映射,通用或专用的寄存器组。而用户空间的进程要传递很多变量、参数给内核,内核也要保存用户进程的一些寄存器、变量等,以便系统调用结束后回到用户空间继续执行。所谓的进程上下文,就是一个进程在执行的时候,CPU的所有寄存器中的值、进程的状态以及堆栈中的内容,当内核需要切换到另一个进程时,它需要保存当前进程的所有状态,即保存当前进程的进程上下文,以便再次执行该进程时,能够恢复切换时的状态,继续执行。
同理,硬件通过触发信号,导致内核调用中断处理程序,进入内核空间。这个过程中,硬件的一些变量和参数也要传递给内核,内核通过这些参数进行中断处理,中断上下文就可以理解为硬件传递过来的这些参数和内核需要保存的一些环境,主要是被中断的进程的环境。
nvme_init_ctrl
在 nvme_pci_alloc_dev 中有调用 nvme_init_ctrl,再看一下其定义,如下:
/** Initialize a NVMe controller structures. This needs to be called during* earliest initialization so that we have the initialized structured around* during probing.*/
int nvme_init_ctrl(struct nvme_ctrl *ctrl, struct device *dev,const struct nvme_ctrl_ops *ops, unsigned long quirks)
{int ret;ctrl->state = NVME_CTRL_NEW;clear_bit(NVME_CTRL_FAILFAST_EXPIRED, &ctrl->flags);spin_lock_init(&ctrl->lock);mutex_init(&ctrl->scan_lock);INIT_LIST_HEAD(&ctrl->namespaces);xa_init(&ctrl->cels);init_rwsem(&ctrl->namespaces_rwsem);ctrl->dev = dev;ctrl->ops = ops;ctrl->quirks = quirks;ctrl->numa_node = NUMA_NO_NODE;INIT_WORK(&ctrl->scan_work, nvme_scan_work);INIT_WORK(&ctrl->async_event_work, nvme_async_event_work);INIT_WORK(&ctrl->fw_act_work, nvme_fw_act_work);INIT_WORK(&ctrl->delete_work, nvme_delete_ctrl_work);init_waitqueue_head(&ctrl->state_wq);INIT_DELAYED_WORK(&ctrl->ka_work, nvme_keep_alive_work);INIT_DELAYED_WORK(&ctrl->failfast_work, nvme_failfast_work);memset(&ctrl->ka_cmd, 0, sizeof(ctrl->ka_cmd));ctrl->ka_cmd.common.opcode = nvme_admin_keep_alive;BUILD_BUG_ON(NVME_DSM_MAX_RANGES * sizeof(struct nvme_dsm_range) >PAGE_SIZE);ctrl->discard_page = alloc_page(GFP_KERNEL);if (!ctrl->discard_page) {ret = -ENOMEM;goto out;}ret = ida_alloc(&nvme_instance_ida, GFP_KERNEL);if (ret < 0)goto out;ctrl->instance = ret;device_initialize(&ctrl->ctrl_device);ctrl->device = &ctrl->ctrl_device;ctrl->device->devt = MKDEV(MAJOR(nvme_ctrl_base_chr_devt),ctrl->instance);ctrl->device->class = nvme_class;ctrl->device->parent = ctrl->dev;if (ops->dev_attr_groups)ctrl->device->groups = ops->dev_attr_groups;elsectrl->device->groups = nvme_dev_attr_groups;ctrl->device->release = nvme_free_ctrl;dev_set_drvdata(ctrl->device, ctrl);// 1. set device name with nvme%dret = dev_set_name(ctrl->device, "nvme%d", ctrl->instance);if (ret)goto out_release_instance;nvme_get_ctrl(ctrl);cdev_init(&ctrl->cdev, &nvme_dev_fops);ctrl->cdev.owner = ops->module;ret = cdev_device_add(&ctrl->cdev, ctrl->device);if (ret)goto out_free_name;/** Initialize latency tolerance controls. The sysfs files won't* be visible to userspace unless the device actually supports APST.*/ctrl->device->power.set_latency_tolerance = nvme_set_latency_tolerance;dev_pm_qos_update_user_latency_tolerance(ctrl->device,min(default_ps_max_latency_us, (unsigned long)S32_MAX));nvme_fault_inject_init(&ctrl->fault_inject, dev_name(ctrl->device));nvme_mpath_init_ctrl(ctrl);ret = nvme_auth_init_ctrl(ctrl);if (ret)goto out_free_cdev;return 0;
out_free_cdev:cdev_device_del(&ctrl->cdev, ctrl->device);
out_free_name:nvme_put_ctrl(ctrl);kfree_const(ctrl->device->kobj.name);
out_release_instance:ida_free(&nvme_instance_ida, ctrl->instance);
out:if (ctrl->discard_page)__free_page(ctrl->discard_page);return ret;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(nvme_init_ctrl);
dev_set_name
在 nvme_init_ctrl 中有调用 dev_set_name 以创建一个名字叫 nvmex 的字符设备,其定义如下:
/*** dev_set_name - set a device name* @dev: device* @fmt: format string for the device's name*/
int dev_set_name(struct device *dev, const char *fmt, ...)
{va_list vargs;int err;va_start(vargs, fmt);err = kobject_set_name_vargs(&dev->kobj, fmt, vargs);va_end(vargs);return err;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(dev_set_name);
这个 nvmex 中的 x 是通过 kobject_set_name_vargs 获得唯一的索引值。
kobject_set_name_vargs
在 dev_set_name 中有调用 kobject_set_name_vargs,其定义如下:
/*** kobject_set_name_vargs() - Set the name of a kobject.* @kobj: struct kobject to set the name of* @fmt: format string used to build the name* @vargs: vargs to format the string.*/
int kobject_set_name_vargs(struct kobject *kobj, const char *fmt,va_list vargs)
{const char *s;if (kobj->name && !fmt)return 0;s = kvasprintf_const(GFP_KERNEL, fmt, vargs);if (!s)return -ENOMEM;/** ewww... some of these buggers have '/' in the name ... If* that's the case, we need to make sure we have an actual* allocated copy to modify, since kvasprintf_const may have* returned something from .rodata.*/if (strchr(s, '/')) {char *t;t = kstrdup(s, GFP_KERNEL);kfree_const(s);if (!t)return -ENOMEM;strreplace(t, '/', '!');s = t;}kfree_const(kobj->name);kobj->name = s;return 0;
}
nvme_dev_map
先看它的定义,如下:
static int nvme_dev_map(struct nvme_dev *dev)
{struct pci_dev *pdev = to_pci_dev(dev->dev);if (pci_request_mem_regions(pdev, "nvme"))return -ENODEV;# NVME_REG_DBS = 0x1000, /* SQ 0 Tail Doorbell */if (nvme_remap_bar(dev, NVME_REG_DBS + 4096))goto release;return 0;release:pci_release_mem_regions(pdev);return -ENODEV;
}
pci_request_mem_regions
在 nvme_dev_map 中有调用 pci_request_mem_regions,其定义如下:
static inline int
pci_request_mem_regions(struct pci_dev *pdev, const char *name)
{return pci_request_selected_regions(pdev,pci_select_bars(pdev, IORESOURCE_MEM), name);
}
pci_select_bars
在 pci_request_mem_regions 中有调用 pci_select_bars,其定义如下:
/*** pci_select_bars - Make BAR mask from the type of resource* @dev: the PCI device for which BAR mask is made* @flags: resource type mask to be selected** This helper routine makes bar mask from the type of resource.*/
int pci_select_bars(struct pci_dev *dev, unsigned long flags)
{int i, bars = 0;for (i = 0; i < PCI_NUM_RESOURCES; i++)if (pci_resource_flags(dev, i) & flags)bars |= (1 << i);return bars;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(pci_select_bars);
调用 pci_select_bars,其返回值为 mask。因为 pci 设备的 header 配置空间有 6 个 32 位的Bar 寄存器,所以 mark 中的每一位的值就代表其中一个 Bar 是否被置起:
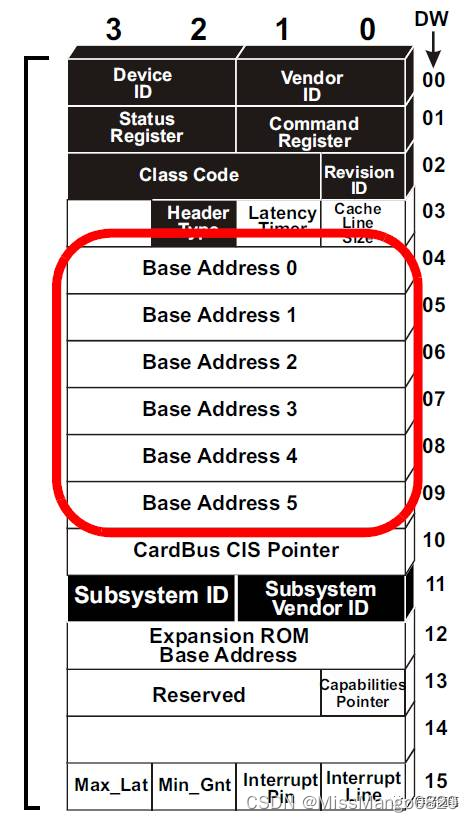
pci_request_selected_regions
在 pci_request_mem_regions 中有调用 pci_request_selected_regions,其定义如下:
/*** pci_request_selected_regions - Reserve selected PCI I/O and memory resources* @pdev: PCI device whose resources are to be reserved* @bars: Bitmask of BARs to be requested* @res_name: Name to be associated with resource*/
int pci_request_selected_regions(struct pci_dev *pdev, int bars,const char *res_name)
{return __pci_request_selected_regions(pdev, bars, res_name, 0);
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(pci_request_selected_regions);
调用 pci_request_selected_regions,这个函数的一个参数就是之前调用 pci_select_bars 返回的mask 值,作用就是把对应的这个几个 bar 保留起来,不让别人使用。
nvme_remap_bar
在 nvme_dev_map 中有调用 nvme_remap_bar,其定义如下:
static int nvme_remap_bar(struct nvme_dev *dev, unsigned long size)
{struct pci_dev *pdev = to_pci_dev(dev->dev);if (size <= dev->bar_mapped_size)return 0;if (size > pci_resource_len(pdev, 0))return -ENOMEM;if (dev->bar)iounmap(dev->bar);// 将一个IO地址空间映射到内核的虚拟地址空间上去dev->bar = ioremap(pci_resource_start(pdev, 0), size);if (!dev->bar) {dev->bar_mapped_size = 0;return -ENOMEM;}dev->bar_mapped_size = size;dev->dbs = dev->bar + NVME_REG_DBS;return 0;
}
调用 ioremap,在 linux 中我们无法直接访问物理地址,需要映射到虚拟地址,ioremap 就是这个作用。
映射完后,我们访问 dev->bar 就可以直接操作 nvme 设备上的寄存器了。但是代码中,并没有根据 pci_select_bars 的返回值来决定映射哪个 bar,而是直接映射 bar0,原因是 nvme 协议中强制规定了 bar0 就是内存映射的基址。
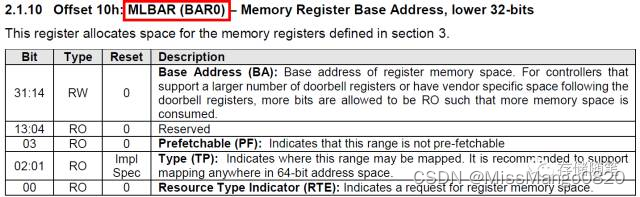
nvme_setup_prp_pools
static int nvme_setup_prp_pools(struct nvme_dev *dev)
{dev->prp_page_pool = dma_pool_create("prp list page", dev->dev,NVME_CTRL_PAGE_SIZE,NVME_CTRL_PAGE_SIZE, 0);if (!dev->prp_page_pool)return -ENOMEM;/* Optimisation for I/Os between 4k and 128k */dev->prp_small_pool = dma_pool_create("prp list 256", dev->dev,256, 256, 0);if (!dev->prp_small_pool) {dma_pool_destroy(dev->prp_page_pool);return -ENOMEM;}return 0;
}
nvme_setup_prp_pools 主要是创建了两个 dma pool,后面就可以通过其他 dma 函数从 dma pool 中获得 memory 了。
prp_page_pool提供的是块大小为Page_Size(格式化时确定,例如4KB) 的内存,主要是为了对于不一样长度的prp list来做优化。prp_small_pool里提供的是块大小为256字节的内存。
nvme_alloc_admin_tag_set
在 nvme_probe 中使用 nvme_mq_admin_ops 对 nvme_alloc_admin_tag_set 进行初始化。
static const struct blk_mq_ops nvme_mq_admin_ops = {.queue_rq = nvme_queue_rq,.complete = nvme_pci_complete_rq,.init_hctx = nvme_admin_init_hctx,.init_request = nvme_pci_init_request,.timeout = nvme_timeout,
};
再回归到 nvme_alloc_admin_tag_set,如下:
int nvme_alloc_admin_tag_set(struct nvme_ctrl *ctrl, struct blk_mq_tag_set *set,const struct blk_mq_ops *ops, unsigned int cmd_size)
{int ret;memset(set, 0, sizeof(*set));set->ops = ops;set->queue_depth = NVME_AQ_MQ_TAG_DEPTH;if (ctrl->ops->flags & NVME_F_FABRICS)set->reserved_tags = NVMF_RESERVED_TAGS;set->numa_node = ctrl->numa_node;set->flags = BLK_MQ_F_NO_SCHED;if (ctrl->ops->flags & NVME_F_BLOCKING)set->flags |= BLK_MQ_F_BLOCKING;set->cmd_size = cmd_size;set->driver_data = ctrl;set->nr_hw_queues = 1;set->timeout = NVME_ADMIN_TIMEOUT;// 1. 分配tag set并与request queue关联ret = blk_mq_alloc_tag_set(set);if (ret)return ret;// 2. 对hardware queue和software queues进行初始化,并配置两者之间的mapping关系,最后将返回值传递给dev->ctrl.admin_q。ctrl->admin_q = blk_mq_init_queue(set);if (IS_ERR(ctrl->admin_q)) {ret = PTR_ERR(ctrl->admin_q);goto out_free_tagset;}if (ctrl->ops->flags & NVME_F_FABRICS) {ctrl->fabrics_q = blk_mq_init_queue(set);if (IS_ERR(ctrl->fabrics_q)) {ret = PTR_ERR(ctrl->fabrics_q);goto out_cleanup_admin_q;}}ctrl->admin_tagset = set;return 0;out_cleanup_admin_q:blk_mq_destroy_queue(ctrl->admin_q);blk_put_queue(ctrl->admin_q);
out_free_tagset:blk_mq_free_tag_set(set);ctrl->admin_q = NULL;ctrl->fabrics_q = NULL;return ret;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(nvme_alloc_admin_tag_set);
这个函数是 NVMe 设备采用 Multi-Queue( MQ )的核心函数,所以在展开解析这个函数之前,我们先聊聊 Linux Multi-Queue Block Layer。
多队列、原生异步、无锁是 NVMe 的最大特色,这些为高性能而生的设计迫使 Linux Kernel 在3.19 抛弃了老的单队列 Block Layer 而转向 Multi-Queue Block Layer。
这个 Multi-Queue Block Layer 的架构直接对应于 NVMe 的多队列设计,如下图:
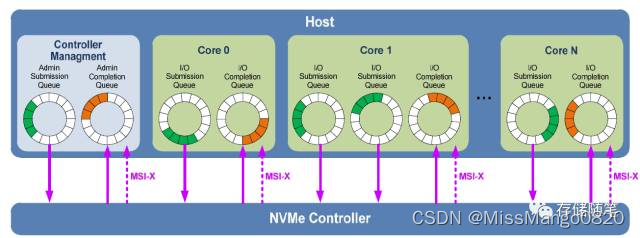
所谓的 Multi-Queue 机制就是在多核 CPU 的情况下,将不同的 block 层提交队列分配到不同的CPU 核上,以更好的平衡 IO 的工作负载,大幅提高 SSD 等存储设备的 IO 效率。
Multi-Queue Block Layer 长啥样子呢?如下图所示:
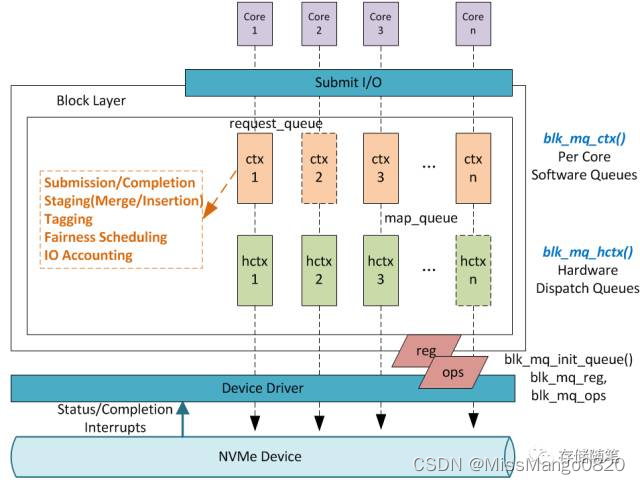
Multi-Queue Block Layer 分为两层,Software Queues 和 Hardware Dispatch Queues。
Softeware Queues 是 per core 的,Queue 的数目与协议有关系,比如 NVMe 协议,可以有最多64K 对 IO SQ/CQ。Software Queues 层做的事情如上图标识部分。
Hardware Queues 数目由底层设备驱动决定,可以 1 个或者多个。最大支持数目一般会与 MSI-X 中断最大数目一样,支持 2K。设备驱动通过 map_queue 维护 Software Queues 和 Hardware Queues 之间的对接关系。
需要强调一点,Hardware Queues 与 Software Queues 的数目不一定相等,上图 1:1 Mapping 的情况属于最理想的情况。
到这里,Multi-Queue Block Layer 基本理论我们就算回顾完毕了,再回头看看nvme_alloc_admin_tag_set 这个函数。
nvme_alloc_admin_tag_set
在 nvme_alloc_admin_tag_set 中使用 blk_mq_alloc_tag_set,
/** Alloc a tag set to be associated with one or more request queues.* May fail with EINVAL for various error conditions. May adjust the* requested depth down, if it's too large. In that case, the set* value will be stored in set->queue_depth.*/
int blk_mq_alloc_tag_set(struct blk_mq_tag_set *set)
{int i, ret;BUILD_BUG_ON(BLK_MQ_MAX_DEPTH > 1 << BLK_MQ_UNIQUE_TAG_BITS);if (!set->nr_hw_queues)return -EINVAL;if (!set->queue_depth)return -EINVAL;if (set->queue_depth < set->reserved_tags + BLK_MQ_TAG_MIN)return -EINVAL;if (!set->ops->queue_rq)return -EINVAL;if (!set->ops->get_budget ^ !set->ops->put_budget)return -EINVAL;if (set->queue_depth > BLK_MQ_MAX_DEPTH) {pr_info("blk-mq: reduced tag depth to %u\n",BLK_MQ_MAX_DEPTH);set->queue_depth = BLK_MQ_MAX_DEPTH;}if (!set->nr_maps)set->nr_maps = 1;else if (set->nr_maps > HCTX_MAX_TYPES)return -EINVAL;/** If a crashdump is active, then we are potentially in a very* memory constrained environment. Limit us to 1 queue and* 64 tags to prevent using too much memory.*/if (is_kdump_kernel()) {set->nr_hw_queues = 1;set->nr_maps = 1;set->queue_depth = min(64U, set->queue_depth);}/** There is no use for more h/w queues than cpus if we just have* a single map*/if (set->nr_maps == 1 && set->nr_hw_queues > nr_cpu_ids)set->nr_hw_queues = nr_cpu_ids;if (set->flags & BLK_MQ_F_BLOCKING) {set->srcu = kmalloc(sizeof(*set->srcu), GFP_KERNEL);if (!set->srcu)return -ENOMEM;ret = init_srcu_struct(set->srcu);if (ret)goto out_free_srcu;}ret = -ENOMEM;set->tags = kcalloc_node(set->nr_hw_queues,sizeof(struct blk_mq_tags *), GFP_KERNEL,set->numa_node);if (!set->tags)goto out_cleanup_srcu;for (i = 0; i < set->nr_maps; i++) {set->map[i].mq_map = kcalloc_node(nr_cpu_ids,sizeof(set->map[i].mq_map[0]),GFP_KERNEL, set->numa_node);if (!set->map[i].mq_map)goto out_free_mq_map;set->map[i].nr_queues = is_kdump_kernel() ? 1 : set->nr_hw_queues;}blk_mq_update_queue_map(set);ret = blk_mq_alloc_set_map_and_rqs(set);if (ret)goto out_free_mq_map;mutex_init(&set->tag_list_lock);INIT_LIST_HEAD(&set->tag_list);return 0;out_free_mq_map:for (i = 0; i < set->nr_maps; i++) {kfree(set->map[i].mq_map);set->map[i].mq_map = NULL;}kfree(set->tags);set->tags = NULL;
out_cleanup_srcu:if (set->flags & BLK_MQ_F_BLOCKING)cleanup_srcu_struct(set->srcu);
out_free_srcu:if (set->flags & BLK_MQ_F_BLOCKING)kfree(set->srcu);return ret;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(blk_mq_alloc_tag_set);
nvme_alloc_admin_tag_set
在 nvme_alloc_admin_tag_set 中使用 blk_mq_init_queue,
static struct request_queue *blk_mq_init_queue_data(struct blk_mq_tag_set *set,void *queuedata)
{struct request_queue *q;int ret;q = blk_alloc_queue(set->numa_node);if (!q)return ERR_PTR(-ENOMEM);q->queuedata = queuedata;ret = blk_mq_init_allocated_queue(set, q);if (ret) {blk_put_queue(q);return ERR_PTR(ret);}return q;
}struct request_queue *blk_mq_init_queue(struct blk_mq_tag_set *set)
{return blk_mq_init_queue_data(set, NULL);
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(blk_mq_init_queue);
int blk_mq_init_allocated_queue(struct blk_mq_tag_set *set,struct request_queue *q)
{/* mark the queue as mq asap */q->mq_ops = set->ops;q->poll_cb = blk_stat_alloc_callback(blk_mq_poll_stats_fn,blk_mq_poll_stats_bkt,BLK_MQ_POLL_STATS_BKTS, q);if (!q->poll_cb)goto err_exit;if (blk_mq_alloc_ctxs(q))goto err_poll;/* init q->mq_kobj and sw queues' kobjects */blk_mq_sysfs_init(q);INIT_LIST_HEAD(&q->unused_hctx_list);spin_lock_init(&q->unused_hctx_lock);xa_init(&q->hctx_table);blk_mq_realloc_hw_ctxs(set, q);if (!q->nr_hw_queues)goto err_hctxs;INIT_WORK(&q->timeout_work, blk_mq_timeout_work);blk_queue_rq_timeout(q, set->timeout ? set->timeout : 30 * HZ);q->tag_set = set;q->queue_flags |= QUEUE_FLAG_MQ_DEFAULT;blk_mq_update_poll_flag(q);INIT_DELAYED_WORK(&q->requeue_work, blk_mq_requeue_work);INIT_LIST_HEAD(&q->requeue_list);spin_lock_init(&q->requeue_lock);q->nr_requests = set->queue_depth;/** Default to classic polling*/q->poll_nsec = BLK_MQ_POLL_CLASSIC;blk_mq_init_cpu_queues(q, set->nr_hw_queues);blk_mq_add_queue_tag_set(set, q);blk_mq_map_swqueue(q);return 0;err_hctxs:blk_mq_release(q);
err_poll:blk_stat_free_callback(q->poll_cb);q->poll_cb = NULL;
err_exit:q->mq_ops = NULL;return -ENOMEM;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(blk_mq_init_allocated_queue);
static void blk_mq_realloc_hw_ctxs(struct blk_mq_tag_set *set,struct request_queue *q)
{struct blk_mq_hw_ctx *hctx;unsigned long i, j;/* protect against switching io scheduler */mutex_lock(&q->sysfs_lock);for (i = 0; i < set->nr_hw_queues; i++) {int old_node;int node = blk_mq_get_hctx_node(set, i);struct blk_mq_hw_ctx *old_hctx = xa_load(&q->hctx_table, i);if (old_hctx) {old_node = old_hctx->numa_node;blk_mq_exit_hctx(q, set, old_hctx, i);}if (!blk_mq_alloc_and_init_hctx(set, q, i, node)) {if (!old_hctx)break;pr_warn("Allocate new hctx on node %d fails, fallback to previous one on node %d\n",node, old_node);hctx = blk_mq_alloc_and_init_hctx(set, q, i, old_node);WARN_ON_ONCE(!hctx);}}/** Increasing nr_hw_queues fails. Free the newly allocated* hctxs and keep the previous q->nr_hw_queues.*/if (i != set->nr_hw_queues) {j = q->nr_hw_queues;} else {j = i;q->nr_hw_queues = set->nr_hw_queues;}xa_for_each_start(&q->hctx_table, j, hctx, j)blk_mq_exit_hctx(q, set, hctx, j);mutex_unlock(&q->sysfs_lock);
}
