【Alamofire】【Swift】属性包装器注解@propertyWrapper
Alamofire 中的源码例子
import Foundationprivate protocol Lock {func lock()func unlock()
}extension Lock {/// Executes a closure returning a value while acquiring the lock.////// - Parameter closure: The closure to run.////// - Returns: The value the closure generated.func around(_ closure: () throws -> T) rethrows -> T {lock(); defer { unlock() }return try closure()}/// Execute a closure while acquiring the lock.////// - Parameter closure: The closure to run.func around(_ closure: () throws -> Void) rethrows {lock(); defer { unlock() }try closure()}
}#if os(Linux) || os(Windows)extension NSLock: Lock {}#endif#if os(macOS) || os(iOS) || os(watchOS) || os(tvOS)
/// An `os_unfair_lock` wrapper.
final class UnfairLock: Lock {private let unfairLock: os_unfair_lock_tinit() {unfairLock = .allocate(capacity: 1)unfairLock.initialize(to: os_unfair_lock())}deinit {unfairLock.deinitialize(count: 1)unfairLock.deallocate()}fileprivate func lock() {os_unfair_lock_lock(unfairLock)}fileprivate func unlock() {os_unfair_lock_unlock(unfairLock)}
}
#endif/// A thread-safe wrapper around a value.
@propertyWrapper
@dynamicMemberLookup
final class Protected {#if os(macOS) || os(iOS) || os(watchOS) || os(tvOS)private let lock = UnfairLock()#elseif os(Linux) || os(Windows)private let lock = NSLock()#endifprivate var value: Tinit(_ value: T) {self.value = value}/// The contained value. Unsafe for anything more than direct read or write.var wrappedValue: T {get { lock.around { value } }set { lock.around { value = newValue } }}var projectedValue: Protected { self }init(wrappedValue: T) {value = wrappedValue}/// Synchronously read or transform the contained value.////// - Parameter closure: The closure to execute.////// - Returns: The return value of the closure passed.func read(_ closure: (T) throws -> U) rethrows -> U {try lock.around { try closure(self.value) }}/// Synchronously modify the protected value.////// - Parameter closure: The closure to execute.////// - Returns: The modified value.@discardableResultfunc write(_ closure: (inout T) throws -> U) rethrows -> U {try lock.around { try closure(&self.value) }}subscript(dynamicMember keyPath: WritableKeyPath) -> Property {get { lock.around { value[keyPath: keyPath] } }set { lock.around { value[keyPath: keyPath] = newValue } }}subscript(dynamicMember keyPath: KeyPath) -> Property {lock.around { value[keyPath: keyPath] }}
}extension Protected where T == Request.MutableState {/// Attempts to transition to the passed `State`.////// - Parameter state: The `State` to attempt transition to.////// - Returns: Whether the transition occurred.func attemptToTransitionTo(_ state: Request.State) -> Bool {lock.around {guard value.state.canTransitionTo(state) else { return false }value.state = statereturn true}}/// Perform a closure while locked with the provided `Request.State`.////// - Parameter perform: The closure to perform while locked.func withState(perform: (Request.State) -> Void) {lock.around { perform(value.state) }}
}
/// A thread-safe wrapper around a value.
@propertyWrapper
@dynamicMemberLookup
final class Protected {}
使用:
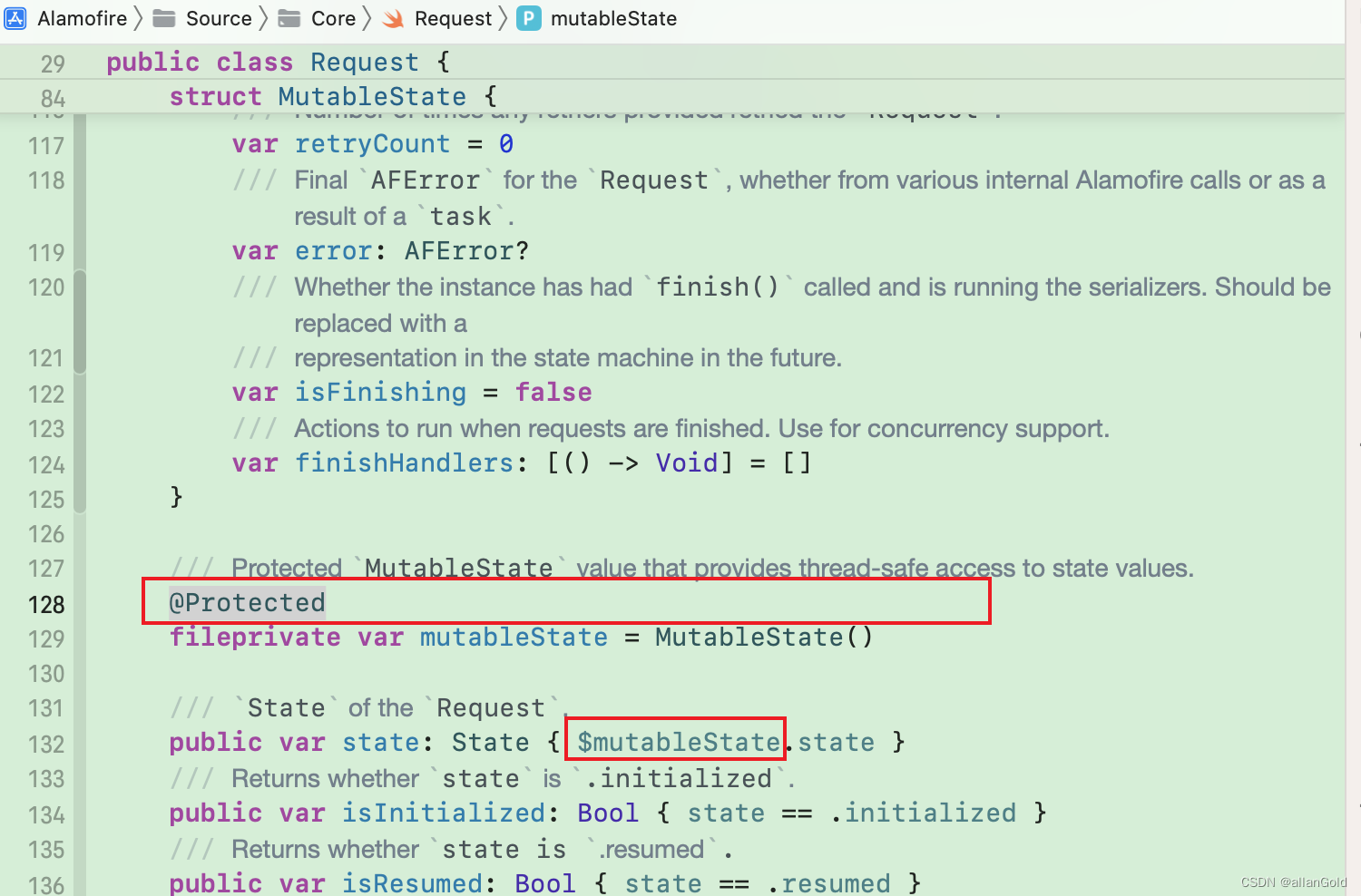
参考:链接
属性包装器(Property Wrappers)
A property wrapper adds a layer of separation between code that manages how a property is stored and the code that defines a property.
属性包装器,用来修饰属性,它可以抽取关于属性重复的逻辑来达到简化代码的目的
For example, if you have properties that provide thread-safety checks or store their underlying data in a database, you have to write that code on every property. When you use a property wrapper, you write the management code once when you define the wrapper, and then reuse that management code by applying it to multiple properties.
比如:如果你有属性提供了线程安全检查或将数据存到数据库功能,那么你将需要为每个属性编写类似代码。有了属性包装器,我们就可以避免类似重复代码
如何使用属性包装器
To define a property wrapper, you make a
structure, enumeration, or classthat defines a wrappedValue property.
我们通过 @propertyWrapper 来标识structure, enumeration, or class来实现属性包装,有两个要求
- 必须使用属性
@propertyWrapper进行定义。 - 它必须具有
wrappedValue属性。
简单使用
使用@propertyWrapper创建一个 TwelveOrLess结构体,该结构体保证被封装的值number小于等于12,如果我们存储的值大于12,那么属性返回12
@propertyWrapper
struct TwelveOrLess {private var number: Intinit() {self.number = 0}var wrappedValue: Int {get {number}set {number = min(newValue, 12)}}
}
在 SmallRectangle 结构体上使用TwelveOrLess,使用包装属性通过@开始拼接包装类TwelveOrLess,放置在属性之前即可。如:@TwelveOrLess
struct SmallRectangle {@TwelveOrLess var height: Int @TwelveOrLess var width: Int
}var rectangle = SmallRectangle()
print(rectangle.height)
// Prints "0"rectangle.height = 10
print(rectangle.height)
// Prints "10"rectangle.height = 24
print(rectangle.height)
// Prints "12"
通过上面的代码可以看出:
- width和height初始值为0
- 设置height为10,其值有效,满足条件,number将会被设置为10,所以打印为10
- 设置height为24,超过最大值12,所以number将会被设置为12,打印为12
使用 @TwelveOrLess 修饰的属性可以自动将值限制在 12 及以下。那么,当使用属性包装时,实际发生了什么呢?在通过对属性包装时编译器会自动转为下面的代码:
struct SmallRectangle {private var _height = TwelveOrLess()private var _width = TwelveOrLess()var height: Int {get { return _height.wrappedValue }set { _height.wrappedValue = newValue }}var width: Int {get { return _width.wrappedValue }set { _width.wrappedValue = newValue }}
}
也就是rectangle.height = 24 这句代码的调用路径:
- 调用
SmallRectangle height的set函数 - 调用
TwelveOrLess wrappedValue的set函数 - 调用
number = min(newValue, 12)来保证新设置的值小于等于 12
注意:当没有给
@TwelveOrLess修饰的变量赋初始值时,默认使用init()初始化。
struct ZeroRectangle {@TwelveOrLess var height: Int@TwelveOrLess var width: Int
}var zeroRectangle = ZeroRectangle()
print(zeroRectangle.height, zeroRectangle.width)
// Prints "0 0"
设置初始值(Setting Initial Values for Wrapped Properties)
将上面的 SmallRectangle 改写为下面的代码你会发现报错 :
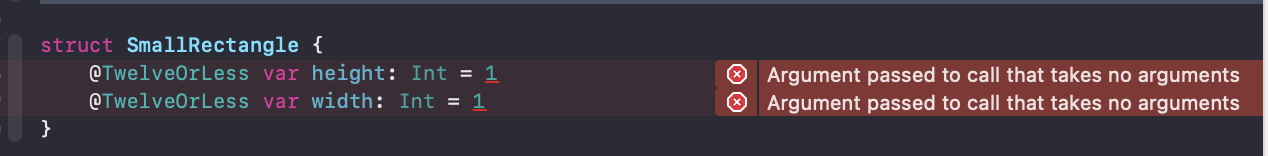
截屏2021-12-28 上午11.28.07.png
这是因为我们的 TwelveOrLess 并没有提供有参的初始化函数。只需要在 TwelveOrLess 添加初始化函数即可解决:
@propertyWrapper
struct SmallNumber {private var maximum: Int // 最大值private var number: Intvar wrappedValue: Int {get { return number }set { number = min(newValue, maximum) }}init() {maximum = 12number = 0}init(wrappedValue: Int) {maximum = 12number = min(wrappedValue, maximum)}init(wrappedValue: Int, maximum: Int) {self.maximum = maximumnumber = min(wrappedValue, maximum)}
}
为属性直接设置值,将使用init(wrappedValue:)初始化
struct UnitRectangle {@SmallNumber var height: Int = 1@SmallNumber var width: Int = 1
}var unitRectangle = UnitRectangle()
print(unitRectangle.height, unitRectangle.width)
// Prints "1 1"
属性包装器拥有参数,将使用init(wrappedValue:maximum:)进行初始化
struct NarrowRectangle {@SmallNumber(wrappedValue: 2, maximum: 5) var height: Int@SmallNumber(wrappedValue: 3, maximum: 4) var width: Int
}var narrowRectangle = NarrowRectangle()
print(narrowRectangle.height, narrowRectangle.width)
// Prints "2 3"narrowRectangle.height = 100
narrowRectangle.width = 100
print(narrowRectangle.height, narrowRectangle.width)
// Prints "5 4"
直接赋值和属性包装器初始化组合使用
struct MixedRectangle {@SmallNumber var height: Int = 1@SmallNumber(maximum: 9) var width: Int = 2
}var mixedRectangle = MixedRectangle()
print(mixedRectangle.height)
// Prints "1"mixedRectangle.height = 20
print(mixedRectangle.height)
// Prints "12"
直接赋值操作作为wrappedValue值,所以设置height为1,即相当于调用SmallNumber(wrappedValue: 1),对于width而言,相当于调用SmallNumber(wrappedValue: 2, maximum: 9)
Projecting a Value From a Property Wrapper
除了wrappedValue值,属性包装器还能通过projectedValue 用来获取你定义逻辑的一些额外状态值。比如在上面的例子中,你想获取你设置的值是否超过了限定的最大值,这个就可以用 projectedValue 来获取。
@propertyWrapper
struct SmallNumber {private var number: Intprivate(set) var projectedValue: Boolvar wrappedValue: Int {get { return number }set {if newValue > 12 {number = 12projectedValue = true} else {number = newValueprojectedValue = false}}}init() {self.number = 0self.projectedValue = false}
}
获取状态值:
struct SomeStructure {@SmallNumber var someNumber: Int
}
var someStructure = SomeStructure()someStructure.someNumber = 4
print(someStructure.$someNumber)
// Prints "false"someStructure.someNumber = 55
print(someStructure.$someNumber)
// Prints "true"
通过 $+属性名的方式来获取 projectedValue。当设值为 4 的时候,没有大于 12,没有触发条件,所以 $someNumber 为 false;当设值为 55 的时候,大于 12,触发了条件,所以 $someNumber 为 true。
使用场景
字符串首字母大写
@propertyWrapper struct Capitalized {var wrappedValue: String {didSet { wrappedValue = wrappedValue.capitalized }}init(wrappedValue: String) {self.wrappedValue = wrappedValue.capitalized}
}
定义User,并使用Capitalized
struct User {@Capitalized var firstName: String@Capitalized var lastName: String
}let user = User(firstName: "jack", lastName: "long")
print(user.firstName, user.lastName) // Jack Long
属性加锁使用
@propertyWrapper
class LockAtomic {private var value: Tprivate let lock = NSLock()public init(wrappedValue value: T) {self.value = value}public var wrappedValue: T {get { getValue() }set { setValue(newValue: newValue) }}// 加锁处理获取数据func getValue() -> T {lock.lock()defer { lock.unlock() }return value}// 设置数据加锁func setValue(newValue: T) {lock.lock()defer { lock.unlock() }value = newValue}
}
使用LockAtomic
@LockAtomic
var json: [String: String]?json = ["a": "1"]
print(json) // Optional(["a": "1"])
参考
- Property Wrappers
- Property wrappers in Swift
- Swift Property Wrappers
