Linux 练习六 (IPC 管道)
创始人
2024-05-30 09:54:25
文章目录
- 1 标准管道流
- 2 无名管道(PIPE)
- 3 命名管道(FIFO)
- 3.1 创建删除管道文件
- 3.2 打开和关闭FIFO文件
- 3.3 管道案例:基于管道的客服端服务器程序
使用环境:Ubuntu18.04
使用工具:VMWare workstations ,xshell
作者在学习Linux的过程中对常用的命令进行记录,通过思维导图的方式梳理知识点,并且通过xshell连接vmware中ubuntu虚拟机进行操作,并将练习的截图注解,每句话对应相应的命令,读者可以无障碍跟练。第六次练习的重点在于Linux的管道,这次是进程间的管道通信不同于练习四中介绍的管道文件。
1 标准管道流
- 和文件操作的io流一样,管道也支持文件流模式。通过打开和关闭管道流的函数是popen和pclose。
#include
FILE* popen(const char* command, const char* open_ mode);
int pclose(FILE* fp);
- 函数popen:允许一个程序将另一个程序作为新的进程启动,并可以传递数据给它或者通过它接收数据。command字符串就是要运行的程序名。open_mode必须是“r”或者“w”,如果是“r“被调用程序的输出就可以被调用程序使用,调用程序使用返回的FILE* 文件流指针,就可以通过调用stdio函数库中的fread来读取被调用程序的输出。如果是“w”,则可以调用fwrite向被调用程序发送数据,而被调用程序可以在自己的标准输入上读取这些数据。
- 函数pclose:关闭相关联的文件流。
//读取当前目录下file的内容
#include
int main()
{FILE* fp = open("./file","r");char buf[128] = {0};while(fgets(buf,sizeof(buf),fp)){puts(buf);}pclose(fp);return 0;
}
//写一串字符串到标准管道流,统计buf单词数量(被调用程序必须阻塞等待标准输入)
#include
int main()
{char buf[128] = {"apple orign banana man fale"};FILE* fp = popen("wc -w","w");//wc -w功能是统计字符串中单词的个数fwrite(buf,sizeof(buf),1,fp);//向被调用的wc -w命令所启动的程序发送buf内容pclose(fp);return 0;
}
2 无名管道(PIPE)
管道通信是linux进程通信的一种方式,例如可以使用ps -elf|grep ntp查询和ntp相关的管道
无名管道的特点:
- 只能在亲缘关系进程间通信(父子进程或者兄弟进程)
- 半双工通信
- 管道是特殊文件可以使用read、write,只能存在内存中
#include
int pipe(int fds[2]);
- 管道在程序中使用一对文件描述符表示,其中一个文件描述符有可读属性,一个有可写属性。fds[0]是可读,fds[1]是可写。函数pipe用于创建一个无名管道,如果成功,fds[0]中存放文件描述符,fds[1]存放可写文件描述符,并且函数返回0,否则返回-1。
- 通过调用pipe获取这对打开的文件描述符后,一个进程就可以从fds[0]中读数据,而另一个进程就可以向fds[1]中写数据。两进程必须有几成关系,才能继承这对打开的文件描述符。
- 管道文件不是真正的物理文件,存活在内存中不持久。当两进程都终止后,管道就自动消失。
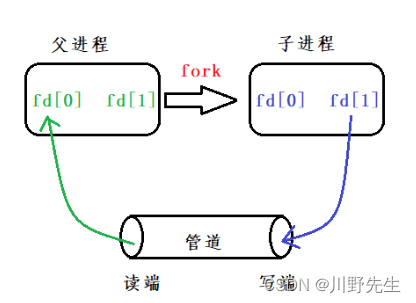
//创建父子进程,创建无名管道,父进程写数据,子进程读数据
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include int main()
{ int fds[2]; //设置读和写两个文件描述符pipe(fds); //使用pipe函数创建进程,并且将两个文件描述符传入参数printf("fds[0] = %d,fds[1] = %d\n",fds[0],fds[1]);char buf[32] = {'\0'};if(fork() == 0){ //表示子进程close(fds[1]); //子进程关闭写操作sleep(2); //确保父进程有时间关闭读操作,并且向管道中写内容if(read(fds[0],buf,sizeof(buf))){ //将管道中的内容读到buf缓冲区中puts(buf);close(fds[0]); //关闭子进程的读端exit(0); //结束子进程}}else{ //表示父进程close(fds[0]); //父进程关闭读write(fds[1],"hello",6); //从fds[1]向管道中写入hellowaitpid(-1,NULL,0); //等待子进程关闭//wait(NULL); //和waitpid同等效果//write(fds[1],"world",6); //此时会出现断开的管道因为子进程的读已经关闭了close(fds[1]); //父进程关闭写exit(0);}return 0;
}
- 管道两端的关闭是有先后顺序的,如果先关闭写端从另一端读取数据时,read函数会返回0,表示管道已经关闭。但是如果先关闭读端从另一端写入数据时,则会将写数据的进程接收到 SIGPIPE 信号,如果写的进程不对此信号处理,导致写进程终止。如果写进程处理了此信号,则写数据的write函数返回一个负值,表示管道已经关闭。看如下代码:
#include
#include
#include
#include int main()
{int fds[2];pipe(fds);//注释掉这部分将导致写进程被信号SIGPIPE终止,目的是屏蔽SIGPIPE信号,使进程不被终止sigset_t setSig; //设置信号集sigemptyset(&setSig); //将信号集清空,初始化信号集sigaddset(&setSig,SIGPIPE); //将SIGPIPE信号添加到信号集sigprocmask(SIG_BLOCK,&setSig,NULL); //将setSig信号集中的信号加入信号掩码中,作为新的信号屏蔽字char szBuf[10] = {0};if(fork() == 0){ //子进程close(fds[1]); //子进程关闭写sleep(2); //确保父关闭读的时间,并且写入管道中if(read(fds[0], szBuf, sizeof(szBuf))) //读取管道中的内容puts(szBuf);close(fds[0]); //子进程关闭读}else{close(fds[0]);//父进程关闭读write(fds[1], "hello", 6); //父进程通过fds[1]向管道中写入hellowait(NULL); //等待子进程结束write(fds[1], "world", 6); //子进程已经关闭了,父进程读不到东西了close(fds[1]); //父进程关闭读}return 0;
}
3 命名管道(FIFO)
- 上一节讲了无名管道只能在亲缘关系的进程中通信,很大程度上限制了管道的使用。命名管道可以突破这个限制,通过指定管道文件的路径实现不相关进程之间的通信。实际上,使用管道通信的操作,在Linux 练习四 (目录操作函数 + 文件操作函数)中就有提及,还实现了进程通信的功能。
3.1 创建删除管道文件
创建FIFO文件的方式和创建普通文件的方式一样,其函数名和 Linux下创建FIFO的命令名一样。
删除FIFO文件和 Linux下命令也一样。
#include
#include
int mkfifo(const char *pathname, mode_t mode); //创建管道文件
int unlink(const char *pathname); //删除管道文件
参数 pathname 为要创建的 FIFO 文件的全路径名;
参数 mode为文件的访问权限
如果创建成功,则返回 0,否则-1。
#include
#include
#include
#include
int main(int argc,char *argv[])//演示通过命令行传递参数
{if(argc != 2){ //检查参数数量puts("Usage: MkFifo.exe {filename}");return -1;}if(mkfifo(argv[1], 0666) == -1){ //创建一个管道文件perror("mkfifo fail");return -2;}//删除管道文件unlink(argv[1]);return 0;
}
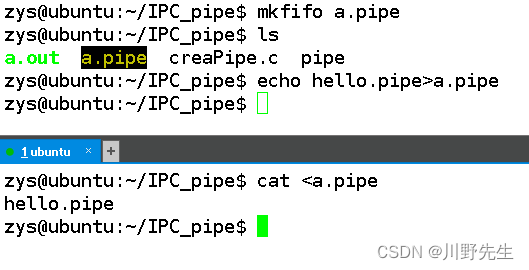
还可以使用命令创建和删除FIFO文件使用两个终端完成,必须一边读一边写,否则会卡住。
- 使用命令mkfifo创建管道文件,不能重复创建同一个管道文件
- 可以使用unlink删除管道文件
- 通过cat命令和echo命令和输入输出指向>和<来读写管道文件的案例,注意不要使用vim打开管道文件。
3.2 打开和关闭FIFO文件
- 对 FIFO 类型的文件的打开/关闭跟普通文件一样,都是使用 open 和 close 函数。如果打开时使用O_WRONLY 选项,则打开 FIFO 的写入端,如果使用 O_RDONLY 选项,则打开FIFO 的读取端,写入端和读取端都可以被几个进程同时打开。在Linux 练习四 (目录操作函数 + 文件操作函数)中2.10 管道中有提及。
- 如果以读取方式打开 FIFO,并且还没有其它进程以写入方式打开 FIFO,open 函数将被阻塞;同样,如果以写入方式打开 FIFO,并且还没其它进程以读取方式 FIFO,open 函数也将被阻塞。
- 与 PIPE 相同,关闭 FIFO 时,如果先关读取端,将导致继续往 FIFO 中写数据的进程接收 SIGPIPE 的信号
3.3 管道案例:基于管道的客服端服务器程序
- 服务器端:
维护服务器管道,接受来自客户端发来的字符串,将小写字母转换为大写字母,然后通过每个客户端维护的管道发给客户端。
//客户端代码
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
//定义客户端数据结构体
typedef struct tagmag
{int client_pid;char my_data[512];
}MSG;int main()
{int server_fifo_fd,client_fifo_fd; //定义客户端管道描述符和用户端管道描述符char client_fifo[256]; //设置客户端缓冲区MSG my_msg; char* pstr;memset(&my_msg,0,sizeof(MSG)); //清空my_msgmkfifo("SERVER_FIFO",0777); //新建一个管道文件,权限是0777server_fifo_fd = open("./SERVER_FIFO",O_RDONLY); //以只读的方式打开管道文件if(server_fifo_fd == -1){ //打开失败的处理perror("server_fifo_fd");exit(-1);}int iret;//读取管道文件不为空的情况,将管道内容读到结构体的my_data中while((iret = read(server_fifo_fd,&my_msg.my_data,sizeof(MSG))>0)){ pstr = my_msg.my_data; printf("%s\n",my_msg.my_data); //打印客户端数据while(*pstr!='\0'){ //将所有字符转为大写字符*pstr = toupper(*pstr);pstr++; }memset(client_fifo,0,256); //清空管道文件sprintf(client_fifo,"CLIENT_FIFO_%d",my_msg.client_pid);//客户端pid格式化写入client_fifo中client_fifo_fd = open(client_fifo,O_WRONLY);//客户端以只写的方式打开client_fifo命名的文件客户管道if(client_fifo_fd == -1){perror("client_fifo_fd");exit(-1);}write(client_fifo_fd,&my_msg,sizeof(MSG)); //将结构体写入管道内容printf("%s\n",my_msg.my_data);printf("OVER!\n");close(client_fifo_fd);}return 0;
}
- 客户端:
想服务器端发送数据,然后从自己的客户端管道中接受服务器返回的数据。
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
//定义客户端数据结构体
typedef struct tagmag
{int client_pid;char my_data[512];
}MSG;int main()
{int server_fifo_fd,client_fifo_fd;char client_fifo[256] = {0};sprintf(client_fifo,"CLIENT_FIFO_%d",getpid());//将客户端id写入client_fifo字符串中MSG my_msg;memset(&my_msg,0,sizeof(MSG)); //清空结构体my_msg.client_pid = getpid(); //获取客户端的进程idserver_fifo_fd = open("./SERVER_FIFO_NAME",O_WRONLY); //以只写的方式打开服务端管道文件,并获取文件描述符mkfifo(client_fifo,0777); //以client_fifo的内容,创建属于该进程的管道文件while(1){int n = read(STDIN_FILENO,my_msg.my_data,512);//从标准输入读入字符串到my_datamy_msg.my_data[n] = '\0';write(server_fifo_fd,&my_msg,sizeof(MSG));//将结构体内容写入服务器管道文件中client_fifo_fd = open(client_fifo,O_RDONLY);//以只读的方式打开客户端管道文件,并且获取文件描述符n = read(client_fifo_fd,&my_msg,sizeof(MSG));//将结构体读入客户端管道文件中my_msg.my_data[n] = 0; write(STDOUT_FILENO,my_msg.my_data,strlen(my_msg.my_data));//将my_data内容写入标准输入输出中close(client_fifo_fd);//关闭客户端}unlink(client_fifo);//删除客户端管道文件return 0;
} 相关内容
热门资讯
苗族的传统节日 贵州苗族节日有...
【岜沙苗族芦笙节】岜沙,苗语叫“分送”,距从江县城7.5公里,是世界上最崇拜树木并以树为神的枪手部落...
北京的名胜古迹 北京最著名的景...
北京从元代开始,逐渐走上帝国首都的道路,先是成为大辽朝五大首都之一的南京城,随着金灭辽,金代从海陵王...
世界上最漂亮的人 世界上最漂亮...
此前在某网上,选出了全球265万颜值姣好的女性。从这些数量庞大的女性群体中,人们投票选出了心目中最美...
长白山自助游攻略 吉林长白山游...
昨天介绍了西坡的景点详细请看链接:一个人的旅行,据说能看到长白山天池全凭运气,您的运气如何?今日介绍...
猫咪吃了塑料袋怎么办 猫咪误食...
你知道吗?塑料袋放久了会长猫哦!要说猫咪对塑料袋的喜爱程度完完全全可以媲美纸箱家里只要一有塑料袋的响...
