Linux 练习七 (IPC 共享内存)
创始人
2024-06-01 01:44:09
文章目录
- System V 共享内存机制:shmget shmat shmdt shmctl
- 案例一:有亲缘关系的进程通信
- 案例二:非亲缘关系的进程通信
- 内存写端write1.c
- 内存读端read1.c
- 案例三:不同程序之间的进程通信
- 程序一,写者shmwr.c
- 程序二,读者shmre.c
使用环境:Ubuntu18.04
使用工具:VMWare workstations ,xshell
作者在学习Linux的过程中对常用的命令进行记录,通过思维导图的方式梳理知识点,并且通过xshell连接vmware中ubuntu虚拟机进行操作,并将练习的截图注解,每句话对应相应的命令,读者可以无障碍跟练。第七次练习的重点在于Linux的进程通信之共享内存。
System V 共享内存机制:shmget shmat shmdt shmctl
- 内存共享的原理及实现:
共享内存本质是一段特殊的内存区域,进程间需要共享的数据被存放在该共享内存区域中,所有需要访问该共享区域的进程都要把共享区域映射 到本进程的地址空间去,不是拷贝。这样一个使用共享内存的进程可以将信息写入空间,而另一个今后才能可以通过对映射地址进行读内存获取刚刚写入的信息,完成进程间通信。 - 共享内存允许一个或多个进程通过同时出现在它们的虚拟地址空间的内存进行通信,而这块虚拟内存的页面被每个共享内存的页表条目所引用,同时并不需要在所有进程的虚拟内存中都有相同的地址。进程对象对于共享内存的访问通过key键值来控制,同时通过key键值来进行访问权限检查。
#include
#include
#include
key_t ftok(const char *pathname, int proj_id);
int shmget(key_t key, int size, int shmflg);
void *shmat(int shmid, const void *shmaddr, int shmflg);
int shmdt(const void *shmaddr);
int shmctl(int shmid, int cmd, struct shmid_ds *buf);
- 函数
ftok(const char *pathname, int proj_id);用于创建一个关键字,可以用此key关联一个共享内存段
- 参数pathname为一个全路径文件名,此文件必须可访问。
- 参数proj_jd通常传入一非0字符
- 通过pathname和proj_id组合可以创建唯一的key
- 如果调用成功,返回一个关键字key,否则返回-1
- 函数
shmget(key_t key, int size, int shmflg);用于创建或打开一共享内存段,该内存段由函数的第一个参数唯一创建。
- 创建成功返回唯一的共享内存标识号(类似于进程号),否则返回-1
- 参数key是一个共享内存关联的关键字,如果该key已经关联共享内存,则返回内存段标志,表示打开了此内存段。如果该key不存在,则创建一个新的共享内存段。key 的值既可以用 ftok 函数产生,也可以是 IPC_PRIVATE(用于创建一个只属于创建进程的共享内存,主要用于父子通信),表示总是创建新的共享内存段。
- 参数size指定共享内存段的大小,以字节为单位。
- 参数shmflg是掩码合成纸,可以是访问权限值与(IPC_CREAT 或 IPC_EXCL)的合成。IPC_CREAT 表示如果内存段不存在就创建。IPC_EXCL 表示如果该内存段存在,则函数返回失败结果(-1)。如果调用成功,返回内存段标识,否则返回-1
- 函数
*shmat(int shmid, const void *shmaddr, int shmflg);将共享内存段映射到进程空间的某一地址。
- 参数shmid是共享内存段的标识,通常应该是shmget的成功返回值,即共享内存标识号
- 参数shmaddr制定的是共享内存连接到当前进程汇总的地址位置。通常是是NULL,表示让系统来选择共享内存出现的地址。
- 参数shmflg是一组位标识,指定 shmget 函数的动作,比如传入 IPC_CREAT 表示要创建新的共享内存,通常为0。
- 如果函数调用成功,返回映射后的进程空间的首地址,否则返回(char *)-1。
- 函数
shmdt(const void *shmaddr);用于将共享内存段与进程空间分离。
- 参数shmaddr通常为shmat的成功返回值,即映射后的进程空间首址。
- 函数成功后返回0,失败后返回-1。
- 将共享内存分离并不是真的删除,只是使得该共享内存对当前进程不可再用。
- 函数
shmctl(int shmid, int cmd, struct shmid_ds *buf是共享内存的控制函数,可以用来删除共享内存段。
- 参数shmid是共享内存段标识,通常是shmget的成功返回值。
- 参数cmd是对共享内存段的操作方式,可选为可选为 IPC_STAT,IPC_SET,IPC_RMID。通常为 IPC_RMID,表示删除共享内存段。
- 参数buf是表示共享内存段的信息结构体数据,通常为NULL。
- 有进程连接,执行返回0,标记删除成功,但是直到最后一个进程结束连接后,共享内存真正被删除。
- 结构体shmid_ds
struct shmid_ds {struct ipc_perm shm_perm; /* Ownership and permissions */size_t shm_segsz; /* Size of segment (bytes) */time_t shm_atime; /* Last attach time */time_t shm_dtime; /* Last detach time */time_t shm_ctime; /* Last change time */pid_t shm_cpid; /* PID of creator */pid_t shm_lpid; /* PID of last shmat(2)/shmdt(2) */shmatt_t shm_nattch; /* No. of current attaches */...
};
struct ipc_perm {key_t __key; /* Key supplied to shmget(2) */uid_t uid; /* Effective UID of owner */gid_t gid; /* Effective GID of owner */uid_t cuid; /* Effective UID of creator */gid_t cgid; /* Effective GID of creator */unsigned short mode; /* Permissions + SHM_DEST andSHM_LOCKED flags */unsigned short __seq; /* Sequence number */
};
案例一:有亲缘关系的进程通信
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#define PERM S_IRUSR | S_IWUSR //表示用户可读可写 即 0600int main(int argc,char** argv)
{int shmid = shmget(IPC_PRIVATE,1024,PERM);//只有IPC_PRIVATE情况可以不设置IPC_CREAT,让操作系统来开辟空间if(shmid == -1) {//如果返回的共享内存标识号不为-1,即创建共享内存失败,错误处理fprintf(stderr,"Create Share Memory Error:%s\n\a",strerror(errno));exit(1);} if(fork() > 0){ //父进程代码char *p_addr = (char*)shmat(shmid,NULL,0); //将共享内存段地址映射到父进程的进程空间中memset(p_addr,'\0',1024); //设置这段地址空间初始化为0strncpy(p_addr,"share memory", 1024);//将字符串写入内存printf("父进程id:%d,写入缓冲区:%s\n",getpid(),p_addr);sleep(2);wait(NULL); //处理结束的进程,防止僵尸进程shmctl(shmid,IPC_RMID,0);//通过唯一的共享内存标识号,删除共享内存exit(0);}else{ //子进程代码sleep(5); //给父进程留足写数据的时间char* c_addr = (char*)shmat(shmid,NULL,0); //将共享内存段地址映射到子进程的进程空间中,可以读取其中内容printf("子进程id:%d,进程标识号:%d 读缓冲区内容: %s\n",getpid(),shmid,c_addr);exit(0);}return 0;
} 运行结果:

案例二:非亲缘关系的进程通信
内存写端write1.c
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#includeint main()
{key_t key = ftok("./file1",1); //1 写端使用ftok函数获取此文件的唯一关键字if(key == -1){ //获取失败的处理perror("fotk");exit(-1);}int shmid = shmget(key,512,IPC_CREAT|0666); //2 按照key创建512B大小的共享内存段,返回该共享内存段的标识符if(shmid == -1){ //创建失败的处理perror("shmget");exit(-1);}char *pMap = (char *)shmat(shmid,NULL,0); //3 获得共享内存段的首地址memset(pMap,'\0',512);strcpy(pMap,"hello world"); //4 想共享内存段中写入内容if(shmdt(pMap) == -1){ //5 关闭共享内存段perror("shmdt");exit(-1);} return 0;
} 内存读端read1.c
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
int main()
{key_t key = ftok("./file1",1); //1 读端使用ftok函数获取此文件的唯一关键字if(key == -1){ //获取失败的处理perror("fotk");exit(-1);}int shmid = shmget(key,512,0666|IPC_CREAT); //2 按照key创建4096大小的共享内存段,权限设可读,返回该共享内存段的标识符if(shmid == -1){ //创建失败的处理perror("shmid");exit(-1);}char* pMap = shmat(shmid,NULL,0); //3 获取共享内存段的首地址printf("读到的内容:%s\n",pMap); //4 读取共享内存段的内容if(shmctl(shmid,IPC_RMID,0) == -1){ //5 删除共享内存段,注意和shmdt作区分 perror("shmctl");exit(-1);}return 0;
} **注意:**如果运行时出错,再运行会出现“错误的参数”、“段错误”等,需要检查共享内存段是否关闭了,可以按如下操作,有可能会出现程序创建了共享内存段,然后没删除的情况,导致想再次运行报错。
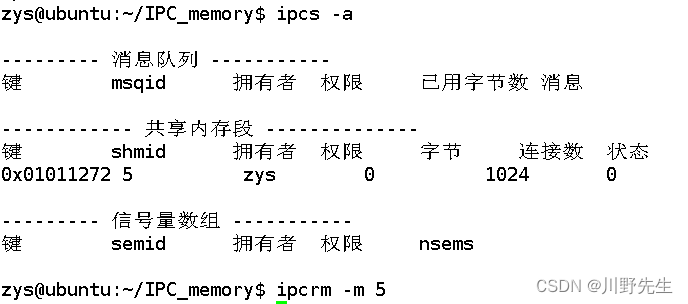
再次运行调试就ok了

案例三:不同程序之间的进程通信
程序一,写者shmwr.c
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
struct text
{int useful; //是否可用的标志char buf[1024];
};int main()
{int shmid = shmget((key_t)5080,sizeof(struct text),0600|IPC_CREAT);//创建唯一key,大小为text的共享内存段,返回唯一内存标识号if(shmid == -1){ //创建失败的处理perror("shmget");exit(-1);}struct text* ptext = (struct text*)shmat(shmid,NULL,0);//获得shmid共享内存段的首地址ptext->useful = 0;while(1){if(ptext->useful == 0){ //判断此内存段是否被用int iret = read(STDIN_FILENO,ptext->buf,1024); //从标准输入到buf缓冲中,如果read函数不输入会阻塞ptext->useful = 1; //将缓冲区改为占用状态if(strncmp("end",ptext->buf,3) == 0){ //如果输入的end,则结束break;}ptext->useful = 0; //将缓冲区改为未占用状态,新一次传输}sleep(1);}shmdt((void*)ptext); //将此进程和共享内存段分离return 0;
}
程序二,读者shmre.c
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
struct text
{int useful; //是否可用的标志char buf[1024];
};int main()
{int shmid = shmget((key_t)5080,sizeof(struct text),0600|IPC_CREAT);//创建唯一key,大小为text的共享内存段,返回唯一内存标识号if(shmid == -1){ //创建失败的处理perror("shmget");exit(-1);}struct text* ptext = (struct text*)shmat(shmid,NULL,0);//获得shmid共享内存段的首地址ptext->useful = 0;while(1){if(ptext->useful == 1){write(STDOUT_FILENO,ptext->buf,strlen(ptext->buf));//将缓冲区中的内容打印到标准输出窗口中,如果没有内容write会阻塞ptext->useful = 0;if(strncmp("end",ptext->buf,3) == 0){ //输入end退出循环break;}}sleep(1);}shmdt((void*)ptext); //将此进程和共享内存段分离shmctl(shmid,IPC_RMID,0); //清除该进程空间return 0;
} 演示结果,读者结合代码自行体会,end覆盖了内存空间的起始字符,如何修改可以不覆盖呢?

上一篇:Nginx服务优化与防盗链
下一篇:STL中的函数对象
相关内容
热门资讯
苗族的传统节日 贵州苗族节日有...
【岜沙苗族芦笙节】岜沙,苗语叫“分送”,距从江县城7.5公里,是世界上最崇拜树木并以树为神的枪手部落...
应用未安装解决办法 平板应用未...
---IT小技术,每天Get一个小技能!一、前言描述苹果IPad2居然不能安装怎么办?与此IPad不...
脚上的穴位图 脚面经络图对应的...
人体穴位作用图解大全更清晰直观的标注了各个人体穴位的作用,包括头部穴位图、胸部穴位图、背部穴位图、胳...
阿西吧是什么意思 阿西吧相当于...
即使你没有受到过任何外语培训,你也懂四国语言。汉语:你好英语:Shit韩语:阿西吧(아,씨발! )日...
