《C++ Primer Plus》(第6版)第10章编程练习
《C++ Primer Plus》(第6版)第10章编程练习
- 《C++ Primer Plus》(第6版)第10章编程练习
- 1. 银行账户
- 2. Person类
- 3. golf类
- 4. Sales类
- 5. costom
- 6. Move类
- 7. Plorg类
- 8. List类
《C++ Primer Plus》(第6版)第10章编程练习
1. 银行账户
定义一个类来表示银行账户。数据成员包括储户姓名、账号(使用字符串)和存款。成员函数执行如下操作:
- 创建一个对象并将其初始化
- 显示储户姓名、账号和存款
- 存入参数指定的存款
- 取出参数指定的款项
代码:
bankAccount.h:
#ifndef BANKACCOUNT_H
#define BANKACCOUNT_H
#include
using namespace std;class BankAccount
{
private:string name;string account;double money;public:BankAccount();BankAccount(const string &n, const string &a, double m = 0.0);void show() const;void deposit(double cash);void withdraw(double cash);
};
#endif
bankAccount.cpp:
#include "bankAccount.h"
#include
using namespace std;BankAccount::BankAccount()
{name = "None";account = "None";money = 0.0;
}BankAccount::BankAccount(const string &n, const string &a, double m)
{name = n;account = a;money = m;
}void BankAccount::show() const
{cout << "Account Name:" << name << endl;cout << "Account Number:" << account << endl;cout << "Account Money:" << money << endl;
}void BankAccount::deposit(double cash)
{if (cash < 0){cout << "Error!Please enter a positive number.\n";return;}money += cash;
}void BankAccount::withdraw(double cash)
{if (money < cash){cout << "Insufficient balance.\n";return;}money -= cash;
} main.cpp:
#include "bankAccount.h"
#include
using namespace std;
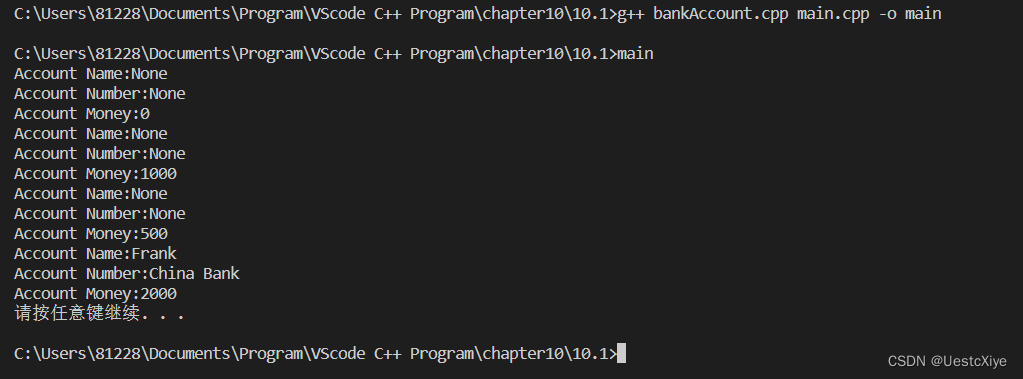
int main()
{BankAccount ba1;BankAccount ba2("Frank", "China Bank", 2000.0);ba1.show();ba1.deposit(1000.0);ba1.show();ba1.withdraw(500.0);ba1.show();ba2.show();system("pause");return 0;
}
运行结果:
2. Person类
下面是一个非常简单的类定义:
class Person
{
private:static const int LIMIT = 25;string lname; // Person’s last namechar fname[LIMIT]; // Person’s first name
public:Person() {lname = ""; fname[0] = '\0';}; // #1Person(const string & ln, const char * fn = "Heyyou"); // #2// the following methods display lname and fnamevoid Show() const; // firstname lastname formatvoid FormalShow() const; // lastname, firstname format
};
它使用了一个string对象和一个字符数组,让您能够比较它们的用法。请提供未定义的方法的代码,以完成这个类的实现。
再编写一个使用这个类的程序,它使用了三种可能的构造函数的调用(没有参数、一个参数和两个参数)以及两种显示方法。
下面是一个使用这些构造函数和方法的例子:
Person one; // use default constructor
Person two("Smythecraft"); // use #2 with one default argument
Person three("Dimwiddy", "Sam"); // use #2, no defaults one.Show();
cout << endl;
one.FormalShow();
// etc. for two and three
代码:
person.h:
#ifndef PERSON_H
#define PERSON_H
#include
#include
using namespace std;class Person
{
private:static const int LIMIT = 25;string lname;char fname[LIMIT];public:Person(){lname = "";fname[0] = '\0';};Person(const string &ln, const char *fn = "Heyyou");void Show() const;void FormalShow() const;
};
#endif person.cpp:
#include "person.h"
#include
#include
using namespace std;Person::Person(const string &ln, const char *fn)
{lname = ln;strcpy_s(fname, LIMIT, fn);
}void Person::Show() const
{cout << fname << " " << lname << endl;
}void Person::FormalShow() const
{cout << lname << " , " << fname << endl;
}
main.cpp:
#include "person.h"
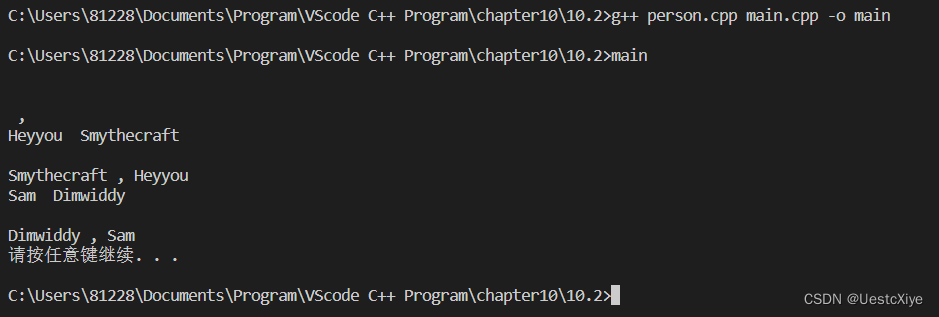
#include int main(void)
{Person one;Person two("Smythecraft");Person three("Dimwiddy", "Sam");one.Show();cout << endl;one.FormalShow();two.Show();cout << endl;two.FormalShow();three.Show();cout << endl;three.FormalShow();system("pause");return 0;
}
运行结果:
3. golf类
完成第9章的编程练习1,但要用正确的golf类声明替换那里的代码。用带合适参数的构造函数替换setgolf(golf&, const char*, int),以提供初始值。保留setgolf()的交互版本,但要用构造函数来实现它(例如,setgolf()的代码应该获得数据,将数据传递给构造函数来创建一个临时对象,并将其赋给调用对象,即*this)。
代码:
golf.h:
#ifndef GOLF_H
#define GOLF_H#include
using namespace std;class Golf
{
private:static const int Len = 40;char fullname[Len];int handicap;public:Golf();Golf(const char *fl, const int h = 0);void setHandicap(const int hc);void showgolf() const;
};
#endif
golf.cpp:
#include "golf.h"
#include
#include
using namespace std;Golf::Golf()
{char fn[Len];int h;cout << "Please enter the full name of player: ";cin.getline(fn, Len);cout << "Please enter the handicap of player: ";cin >> h;cin.get();*this = Golf(fn, h);
}Golf::Golf(const char *fl, const int h)
{strcpy_s(fullname, Len, fl);handicap = h;
}void Golf::setHandicap(const int hc)
{handicap = hc;
}void Golf::showgolf() const
{cout << "Information:\n";cout << "Full name: " << fullname << endl;cout << "Handicap: " << handicap << endl;
}
main.cpp:
#include "golf.h"
#include
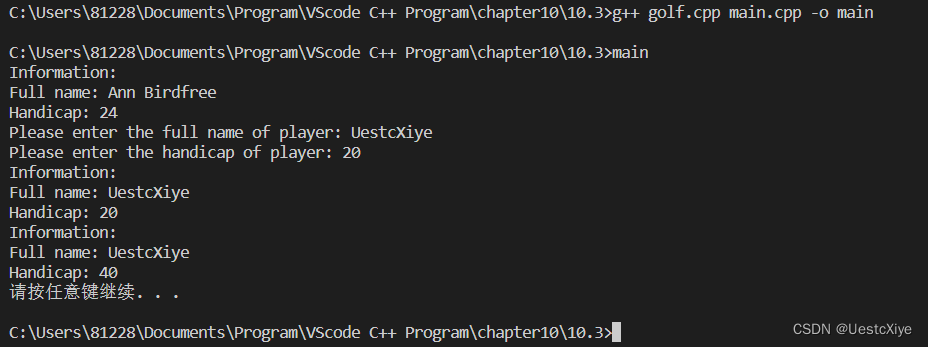
using namespace std;int main()
{Golf ann("Ann Birdfree", 24);ann.showgolf();Golf andy;andy.showgolf();andy.setHandicap(40);andy.showgolf();system("pause");return 0;
}
运行结果:
4. Sales类
代码:
sales.h:
#ifndef SALES_H
#define SALES_Hnamespace SALES
{class Sales{private:static const int QUARTERS = 4;double sales[QUARTERS];double average;double max;double min;public:Sales();Sales(const double ar[], const int n);void showSales() const;};
}#endif
sales.cpp:
#include "sales.h"
#include
using namespace std;
namespace SALES
{Sales::Sales(const double ar[], const int n) // 非交互式版本{if (n < 4){for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)sales[i] = ar[i];for (int j = n; j < 4; j++)sales[j] = 0;}else{for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)sales[i] = ar[i];}average = (sales[0] + sales[1] + sales[2] + sales[3]) / 4;double t_max = 0.0;double t_min = 1000000;for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++){if (sales[i] > t_max)t_max = sales[i];if (sales[i] < t_min)t_min = sales[i];}max = t_max;min = t_min;}Sales::Sales() // 交互式版本{cout << "Enter sales:\n";for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++){cout << "The #" << i + 1 << " quarter is: ";cin >> sales[i];}average = (sales[0] + sales[1] + sales[2] + sales[3]) / 4;double t_max = 0.0;double t_min = 1000000;for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++){if (sales[i] > t_max)t_max = sales[i];if (sales[i] < t_min)t_min = sales[i];}max = t_max;min = t_min;}void Sales::showSales() const{cout << "The sales of 4 quarters are $" << sales[0] << ", $" << sales[1] << ", $" << sales[2] << ", $" << sales[3] << endl;cout << "Average:" << average << endl;cout << "Max:" << max << endl;cout << "Min:" << min << endl;}
}
main.cpp:
#include "sales.h"
#include
using namespace SALES;
using namespace std;int main()
{Sales s1;double ar[3] = {10, 20, 30};Sales s2(ar, 3);cout << "#1:" << endl;s1.showSales();cout << "--------------------------------------------------" << endl;cout << "#2:" << endl;s2.showSales();system("pause");return 0;
}
运行结果:
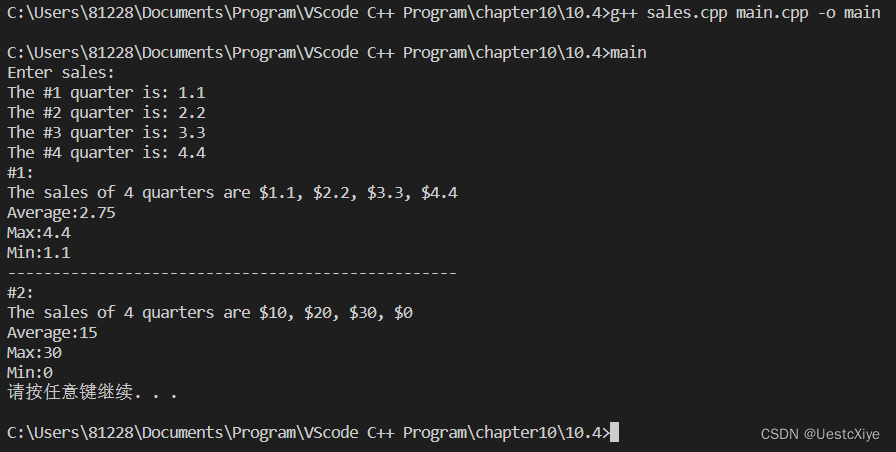
5. costom
考虑下面的结构声明:
struct customer{char fullname[35];double payment;
};
编写一个程序,它从栈中添加和删除customer结构(栈用Stack类声明表示)。每次customer结构被删除时,其payment的值都将被加入到总数中,并报告总数。
注意:应该可以直接使用Stack类而不作修改;只需修改typedef声明,使Item的类型为customer,而不是unsigned long即可。
代码:
stack.h:
#ifndef STACK10_H_
#define STACK10_H_
#include
struct customer
{char fullname[35];double payment;
};
typedef customer Item;
class Stack
{
private:enum{MAX = 10};Item items[MAX];int top;
public:Stack();bool isempty() const;bool isfull() const;bool push(const Item& item);bool pop(Item& item);
};
#endif // !STACK_H_ stack.cpp:
#include "stack10.h"
Stack::Stack()
{top = 0;
}
bool Stack::isempty() const
{return top == 0;
}
bool Stack::isfull() const
{return top == MAX;
}bool Stack::push(const Item& item)
{if (top < MAX){items[top++] = item;return true;}elsereturn false;
}bool Stack::pop(Item& item)
{if (top > 0){item = items[--top];return true;}elsereturn false;
}
main.cpp:
#include "stack.h"
#include
#include
using namespace std;int main()
{Stack st;char ch;customer po;double total_payment = 0.0;cout << "Please enter A to add a purchase order,\n";cout << "P to process a PO, or Q to quit.\n";while (cin >> ch && toupper(ch) != 'Q'){while (cin.get() != '\n')continue;if (!isalpha(ch)){cout << "\a";continue;}switch (ch){case 'A':case 'a':cout << "Enter the name of customer: ";cin.getline(po.fullname, 30);cout << "Enter the payment: ";cin >> po.payment;cin.get();if (st.isfull())cout << "Stack already full.\n";elsest.push(po);break;case 'P':case 'p':if (st.isempty())cout << "stack already empty.\n";else{total_payment += po.payment;st.pop(po);cout << "PO {" << po.fullname << ", " << po.payment << "} popped.\n";}break;}cout << "Please enter A to add a purchase order,\n";cout << "P to Process a PO, or Q to quit.\n";}cout << "Bye!\n";system("pause");return 0;
}
运行结果:
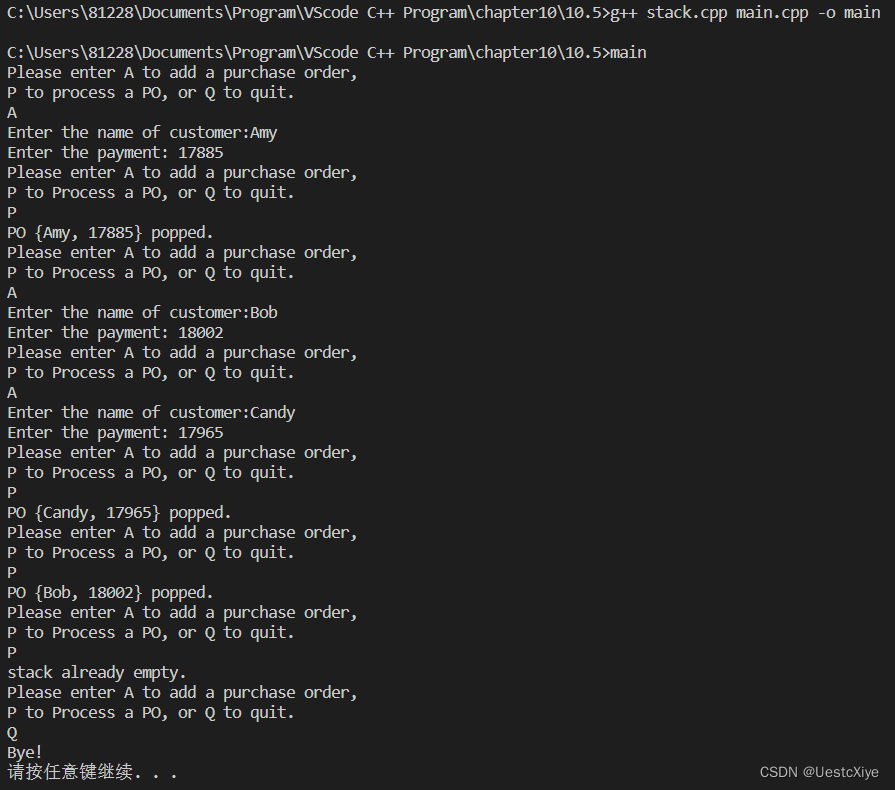
6. Move类
下面是一个类声明:
class Move
{
private:double x;double y;
public:Move(double a = 0, double b = 0); // sets x, y to a, bshowmove() const; // shows current x,y valuesMove add(const Move & m) const;
// this function adds x of m to x of invoking object to get new x,
// adds y of m to y of invoking object to get new y, creates a new
// move object initialized to new x, y values and returns it
//此函数将m的x加到调用对象的x以获取新的x,将m的y添加到调用对象的y中以获得新的y,
//创建一个新的对象,并将对象初始化为新的x,y值并返回它reset(double a = 0, double b = 0); // resets x,y to a, b
};
请提供成员函数的定义和测试这个类的程序。
代码:
move.h:
#ifndef MOVE_H
#define MOVE_Hclass Move
{
private:double x;double y;public:Move(double a = 0, double b = 0);void showmove() const;Move add(const Move &m) const;void reset(double a = 0, double b = 0);
};#endif
move.cpp:
#include "move.h"
#include Move::Move(double a, double b)
{x = a;y = b;
}void Move::showmove() const
{using std::cout;using std::endl;cout << "x:" << x << endl;cout << "y:" << y << endl;
}Move Move::add(const Move &m) const
{return Move(x + m.x, y + m.y);
}void Move::reset(double a, double b)
{x = a;y = b;
} main.cpp:
#include "move.h"
#include
using namespace std;int main()
{Move a(1, 1);Move b(2.3, 3.4);a.showmove();b.showmove();Move c = a.add(b);c.showmove();system("pause");return 0;
}
运行结果:
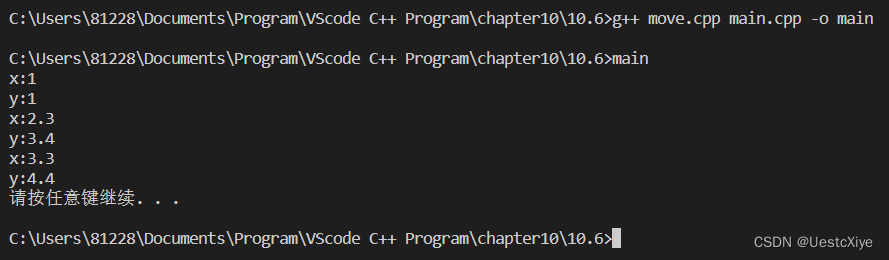
7. Plorg类
Betelgeusean plorg有这些特征。
数据:
- plorg的名称不超过19个字符
- plorg的满意指数(CI),这是一个整数
操作:
- 新的plorg将有名称,其CI值为50
- plorg的CI可以修改
- plorg可以报告其名称和CI
请编写一个Plorg类声明(包括数据成员和成员函数原型)来表示plorg,并编写成员函数的函数定义。然后编写一个小程序,以演示Plorg类的所有特性。
代码:
plorg.h:
#ifndef PLORG_H
#define PLORG_H#include
class Plorg
{
private:static const int LEN = 19;char name[LEN];int ci;public:Plorg();Plorg(const char *str,const int c_i=50);void setCI(const int c_i);void show()const;};
#endif
plorg.cpp:
#include "plorg.h"
#include
#include Plorg::Plorg()
{strcpy_s(name, LEN, "Plorga");ci = 0;
}Plorg::Plorg(const char *str, const int c_i)
{strcpy_s(name, LEN, str);ci = c_i;
}void Plorg::setCI(const int c_i)
{ci = c_i;
}void Plorg::show() const
{using std::cout;using std::endl;cout << "Name:" << name << endl;cout << "CI:" << ci << endl;
} main.cpp:
#include "plorg.h"
#include
using namespace std;int main()
{Plorg p1;p1.show();p1.setCI(100);p1.show();Plorg p2("Amazon", 10);p2.show();system("pause");return 0;
}
运行结果:
8. List类
可以将简单列表描述成下面这样:
- 可存储0或多个某种类型的列表;
- 可创建空列表;
- 可在列表中添加数据项;
- 可确定列表是否为空;
- 可确定列表是否为满;
- 可访问列表中的每一个数据项,并对它执行某种操作。
可以看到,这个列表确实很简单,例如,它不允许插入或删除数据项。
请设计一个List类来表示这种抽象类型。您应提供头文件list.h和实现文件list.cpp,前者包含类定义,后者包含类方法的实现。您还应该创建一个简短的程序来使用这个类。
该列表的规范很简单,这个主要旨在简化这个编程练习。可以选择使用数组或链表来实现该列表,但公有接口不应依赖于所做的选择。也就是说,公有接口不应有数组索引、节点指针等。应使用通用概念来表达创建列表、在列表中添加数据项等操作。对于访问数据项以及执行操作,通常应使用将函数指针作为参数的函数来处理:
void visit(void (*pf)(Item &));
其中,pf指向一个将Item引用作为参数的函数(而不是成员函数),Item是列表中数据项的类型。visit()函数将该函数用于列表中的每个数据项。
代码:
list.h:
#ifndef LIST_H
#define LIST_H#include
#include
using namespace std;struct customer
{string name;double consumption;
};
typedef customer Item;
class List
{
private:static const int LEN = 20;Item items[LEN];int top = 0;public:List();bool isEmpty() const;bool isFull() const;bool add(const Item &item);void visit(void (*pf)(Item &item));void show() const;
};
void total(Item &item); // 计算总营业额(列表中所有顾客消费额相加)
#endif list.cpp:
#include "list.h"
#include
#include
using namespace std;double sum = 0.0;List::List()
{top = 0;
}bool List::isEmpty() const
{return top == 0;
}bool List::isFull() const
{return top == Len;
}bool List::add(const Item &item)
{if (top < Len){items[top++] = item;return true;}elsereturn false;
}void List::show() const
{for (int i = 0; i < top; i++){cout << "#" << i + 1 << ":" << endl;cout << "Name: " << items[i].name << endl;cout << "Consumption: " << items[i].consumption << endl;}
}void List::visit(void (*pf)(Item &item))
{for (int i = 0; i < top; i++){pf(items[i]);}
}void total(Item &item)
{sum += item.consumption;
} main.cpp:
#include "list.h"
#include
using namespace std;extern double sum;int main()
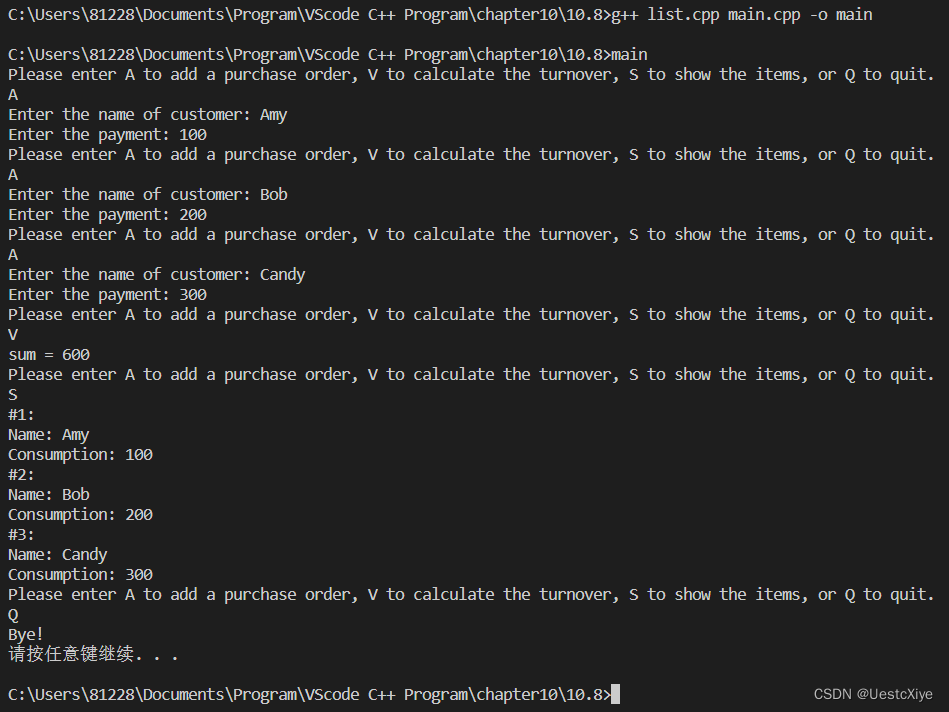
{List st;char ch;customer po;cout << "Please enter A to add a purchase order, V to calculate the turnover, S to show the items, or Q to quit.\n";while (cin >> ch && toupper(ch) != 'Q'){while (cin.get() != '\n')continue;if (!isalpha(ch)){cout << "\a";continue;}switch (ch){case 'A':case 'a':cout << "Enter the name of customer: ";getline(cin, po.name);cout << "Enter the payment: ";cin >> po.consumption;cin.get();if (st.isFull())cout << "List already full.\n";elsest.add(po);break;case 'S':case 's':st.show();break;case 'V':case 'v':if (st.isEmpty()){cout << "List is empty.\n";}else{st.visit(total);cout << "sum = " << sum << endl;}}cout << "Please enter A to add a purchase order, V to calculate the turnover, S to show the items, or Q to quit.\n";}cout << "Bye!\n";system("pause");return 0;
}
运行结果: