数据结构笔记
文章目录
- 第一章:数据结构与算法
- 第二章:稀疏数组和队列
- 一 、稀疏sparsearray 数组
- (一)案例需求
- (二)稀疏数组介绍
- (三)应用实列
- (四)代码实现
- 二、队列
- (一)数组模拟队列
- 代码实现
- (二)数组模拟环形队列
- 第三章:链表
- 一、链表
- (一)链表介绍
- 单链表的应用实例
- 代码实现
- 修改数据
- 删除节点
- 完整代码
- (二)面试题
- 二、双链表
- (一)、双向链表的介绍
- (二) 、应用案例
- 三、单向环形链表应用场景
- (一)约瑟夫问题
- (二) 代码实现
- 第四章:栈
- (一)、栈介绍
- (二)数组模拟栈的思路分析
- (三)练习:使用链表来模拟栈
- 版本一:双链表实现栈
- 版本二:双链表实现栈
- 版本三:单链表实现
- 版本四:单链表实现 ,改变测试环境(推荐)
- (四)栈实现综合案例——计算器
- (五)栈的三种表达式
- 1、前缀表达式
- 2、后缀表达式
- (六)逆波兰计算器
- **方法一**:通过系统提供的栈stack来实现
- **方法二**:编写一个数组栈
- 版本一:中缀表达式转为后缀表达式
- 版本二:功能完整实现
- 第五章:递归
- (一)递归介绍
- (二)迷宫回溯问题分析与实现
- (三)八皇后问题(回溯问题)
- 1、介绍
- 2、代码实现
- 第六章:排序算法
- 一、排序算法
- 二、算法的时间复杂度
- (一)算法的评判方法
- (二)时间复杂度
- 1、时间频度
- 2 、时间复杂度
- (三)平均时间复杂度
- 1、平均时间复杂度
- 2、最坏时间复杂度
- (四)空间复杂度——空间换时间
- 三、冒泡排序算法(bubble sorting)
- (一)代码实现
- 四、选择排序算法
- (一)选举排序介绍
- (二)代码实现
- 五、插入排序算法
- (一)介绍
- (二)代码实现
- 六、希尔排序算法(shell)
- (一)希尔排序算法介绍
- (二)代码实现
- 方法一:交换法
- 方法二:移动法——插入法
- 七、快排算法——Quicksort
- (一)快排算法介绍
- (二)代码实现
- 八、归并排算法
- (一)介绍
- (二)代码实现
- 九、基数排序
- (一)基础知识
- (二)代码实现
- 十、排序总结
第一章:数据结构与算法
一、数据结构概述
数据结构包括:
- 线性结构:数据元素之间存在的一对一的线性关系
- 两种不同存储结构:
- 顺序存储结构 (使用顺序表,顺序表中存储的元素是连续的,即存储的位置是连续的)
- 链式存储结构(使用链式表,存储数据不一定是连续的,好处:利用磁盘的碎片化的空间)
- 常见结构:数组、队列、链表和栈
- 两种不同存储结构:
- 非线性结构:数据元素之间不一定是一对一的关系
- 常用:二位数组、多维数组、广义表、树结构、图结构
第二章:稀疏数组和队列
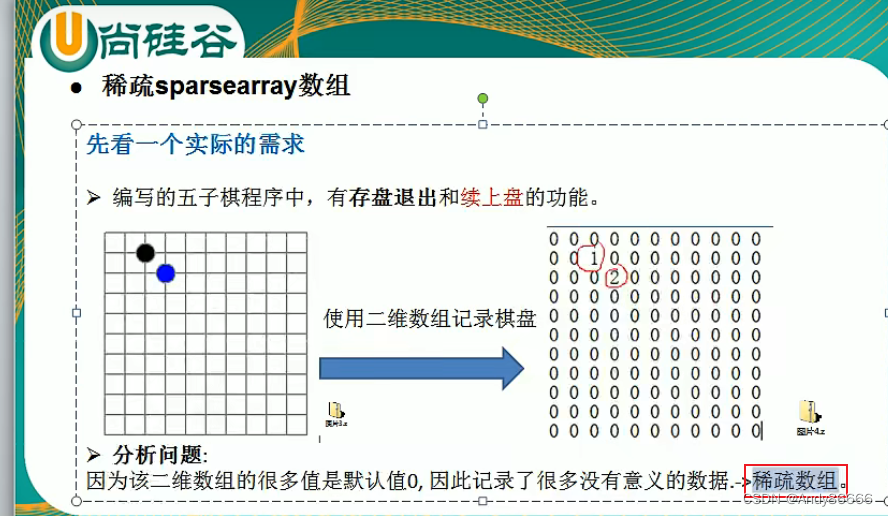
一 、稀疏sparsearray 数组
(一)案例需求
案例:五子棋的数据的存盘和继续上次棋盘
- 主要解决:其盘数据的存放问题
如果用二维数组进行连续存储数据,会记录很多无意义的数据
- 解决办法:稀疏数组,来压缩二维数组
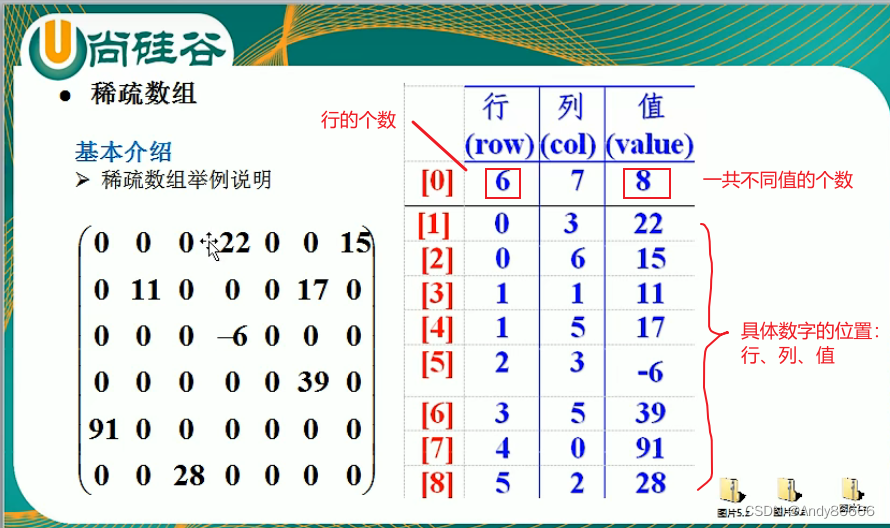
(二)稀疏数组介绍
稀疏数组适用范围:
- 数组中大部分的元素为0
- 元素为同一个值
稀疏数组处理方法:
- 记录数组一共几列几行、不同值的个数
- 不同的元素的行、列、值记录在稀疏数组中
(三)应用实列
稀疏数组,可以用来保存二维数组(eg:棋盘、地图等)
二维数组转稀疏数组的思路:
-
遍历二维数组,得到有效数据的个数 sum (即:知道列的个数,而行的个数是固定的3)
-
根据sum就可以创建稀疏数组spareseArr int
[sum+1][3] -
将二维数组的有效数据存入到稀疏数组
(第一行数据为:行个数、列个数、数据个数)
稀疏数组的形状:[数据个数+1,3]
稀疏数组转二维数组的思路:
- 先读取稀疏数组中第一行数据,来创建原始的二维数组
- 在读取稀疏数组中后几行的数据,并将值赋给二维数组中
(四)代码实现
创建DataStructures,创建package :com.lcj.sparseArray,创建类:SparseArray

package com.lcj.sparseArray;
/*
* 编写时间:202208014
* 编写人员:lcj
* 编写目的:联系稀疏数组
* */
public class SparseAarray {public static void main(String[] args){// 1. 创建11*11的二维数组(棋盘)// 0 表示没有棋子,1表示黑棋,2表示蓝棋int chessArr1[][] = new int[11][11];chessArr1[1][2] = 1;chessArr1[2][3] = 2;// 输出原始棋盘的数据for (int[] row:chessArr1){for (int data:row){System.out.printf("%d\t",data);}System.out.println();}
// __________________________________________________________________//(一):二维数组转为稀疏数组// 1.先遍历二维数组,得到数据的个数 (稀疏数组 形状:[个数+1,3])int count = 0;for(int i = 0;i < chessArr1.length;i++){for (int j=0;j < chessArr1[1].length;j++){if(chessArr1[i][j] != 0)count++;}}System.out.println("数值的个数:"+count);// 2.创建稀疏数组int sparseArray[][] = new int[count+1][3];// 第一行的数据sparseArray[0][0] = chessArr1.length;sparseArray[0][1] = chessArr1[1].length;sparseArray[0][2] = count;// 3.添加数值int a = 0; // 作用:统计不为零的数值的个数来确定,稀疏数组的行下标for(int i = 0;i < chessArr1.length;i++){for (int j=0;j < chessArr1[1].length;j++){if(chessArr1[i][j] != 0) {a++;sparseArray[a][0] = i; // 数据的行sparseArray[a][1] = j; // 数据的列sparseArray[a][2] = chessArr1[i][j]; // 数据值}}}// 4.输出稀疏数组for (int[] row : sparseArray) {for (int data : row) {System.out.printf("%d\t",data);}System.out.println();}// _____________________________________________________________________//(二):稀疏数组转换为二维数组// 1.创建二维数组int chessArr2[][] = new int[sparseArray[0][0]][sparseArray[0][1]];//2.添加数值到二维数组中for (int i =1 ;i< sparseArray.length; i++){chessArr2[sparseArray[i][0]][sparseArray[i][1]] = sparseArray[i][2];}// 3.输出二维数组for (int[] row : chessArr2) {for (int data : row) {System.out.printf("%d\t",data);}System.out.println();}}
}课后练习题:
-
在前面的基础上,将稀疏数组保存到磁盘中,eg:map.data
-
恢复原来的数组时,读取map.data进行恢复
二、队列
队列的特点:先进先出
实现方法:数组和链表
(一)数组模拟队列
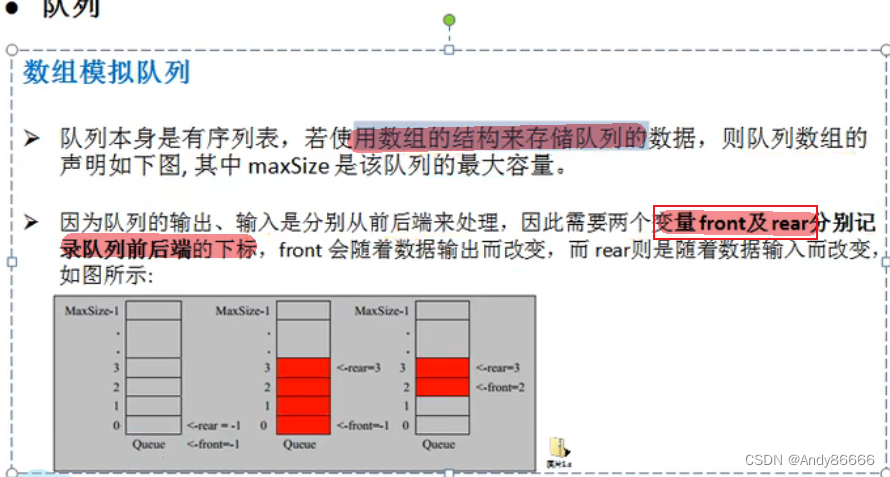
加入数据【addQueue】的思路:
- 将尾指针往后移:rear+1,当front==rear [空]
- 若尾指针rear小于队列的最大值
maxsize-1,可以将数据存入到队列中,如果等于maxsize-1,则无法进行存储数据
注意:
- rear 指向队列中最后一个元素
- front指向队列中第一个元素中前一个位置
代码实现
创建package:com.lcj.queue,创建类名:ArrayQueueDamon
package com.lcj.queue;import java.util.Scanner;/** 编写时间:20220814* 编写人员:lcj* 编写目的:数组模拟队列* */
public class ArrayQueueDamon {public static void main(String[] args) {// 代码测试//创建对象arrayQueue Queue = new arrayQueue(3); //最大值为3char key = ' ';//接收用户输入Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);boolean loop = true; //创建循环条件// 输出一个菜单while(loop){ // 创建死循环System.out.println("s(show):显示队列");System.out.println("e(exit):退出队列");System.out.println("a(add):添加数据到队列");System.out.println("g(get):从队列中取数据");System.out.println("h(head):查队列中头部数据");key = scanner.next().charAt(0); //获取单个字符switch (key){case 's':Queue.showQueue();break;case 'a':System.out.println("请输入一个数据:");int value = scanner.nextInt();Queue.addQueue(value);break;case 'g':try {int res = Queue.getQueu();System.out.printf("取出数据:%d\n",res);}catch (Exception e){System.out.println(e.getMessage());}break;case 'h':try {int res = Queue.headQueue();System.out.printf("输入数据队列头部数据:%d\n",res);}catch (Exception e){System.out.println(e.getMessage());}break;case 'e':scanner.close(); // 关闭scannerloop = false;break;default:break;}}System.out.println("退出成功");}
}// 使用数组来模拟队列
class arrayQueue{private int maxsize; // 最大值private int rear; // 队列的尾指针,private int front; // 队列的头指针,private int[] arr; // 存放数据// 创建队列的构造器public arrayQueue(int MaxSize){maxsize = MaxSize; // 最大值arr = new int[maxsize];rear = -1; // 指向队列尾部的数据,包含尾部数据front = -1; // 指向队列的头部的前一个位置,不包含尾部数据}// 判断队列是否满,满就不能插入数据,满就可以读取数据public boolean isFull(){return rear == maxsize-1;}// 判断队列是否为空,空就不能读取数据,空就能插入数据public boolean isEmpty(){return rear == front;}// 添加数据到队列public void addQueue(int n){// 判断队列是否满了if(isFull()){System.out.println("队列已经满了,不能添加数据");return;}rear++; // rear需要往后移动arr[rear] = n; //添加数据}// 获取队列的数据 (出队列)public int getQueu(){// 判断数据是否为空if(isEmpty()){
// System.out.println("队列数据为空");
// return 0;throw new RuntimeException("队列数据为空");}front++; //front数据后移return arr[front];}// 显示队列的所有数据public void showQueue(){// 判断队列是否为空if (isEmpty()){
// throw new RuntimeException("队列数据为空,不能展示数据");System.out.println("队列数据为空,不能展示数据");return;}for (int i= front+1; i<=rear; i++){System.out.printf("arr[%d]=%d\n",i,arr[i]);}}//显示队列的头数据,注意不是取出数据public int headQueue(){//判断数据是否为空if (isEmpty()){throw new RuntimeException("数据为空");}return arr[front+1];}
}注意:需要测试一下代码
问题:
- 当前这种形式的队列数据有问题,front往后移动后,front前面的数据虽然是无效数据,但是想要添加数据是无法再添加数据的,这导致资源的浪费了
- 队列不能重复使用,没有达到复用的效果
解决办法:
- 环形队列
(二)数组模拟环形队列

注意:
- rear 变量的含义发生了变换,和数组模拟队列的不一样了,现在是指向最后一个元素的后一个位置
- front 变量的含义也发生了变化,指向了队列的第一个元素,也就是说==
arr[front]的第一个元素位置==,原来是第一个元素前一个位置。 - 队列满的条件:
(rear+1)%maxsize = front - 队列为空:rear =front
- 队列中有效个数:
(rear+maxsize-front)%maxsize
代码实现:
创建类:CircleArrayQueueDaemon
package com.lcj.queue;import jdk.nashorn.internal.ir.CallNode;import java.util.Scanner;/*
* 编写人:lcj
* 编写时间:20220815
* 编写目的:学习环形队列
* */
public class CircleArrayQueueDaemon {public static void main(String[] args){//测试思考//创建对象CircleArray circleArray = new CircleArray(3);char key = ' ';Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);boolean loop = true;while (loop){System.out.println("s(show):显示对列");System.out.println("e(exit):退出");System.out.println("a(add):添加对列");System.out.println("g(get):获取对列数据");System.out.println("h(head):队列头部数据");System.out.println("n(num):队列有效数据");key = scanner.next().charAt(0);switch (key){case 's':System.out.println("展示队列数据");circleArray.showQueue();break;case 'a':System.out.println("添加数据,请输入数据");int value = scanner.nextInt();circleArray.addQueu(value);break;case 'e':System.out.println("退出程序");loop = false; // 跳出循环break;case 'g':try {System.out.println("获取队列的数据");int num = circleArray.getQueue();System.out.println("值:"+num);}catch (Exception e){e.getMessage();}break;case 'h':System.out.print("获取队列的头部数据:");System.out.println(circleArray.getHead());break;case 'n':System.out.println("查看队列的有效数据" );int size = circleArray.size();System.out.println("有效数据为:"+size);break;default:System.out.println("数据输入有误请重新输入");break;}}System.out.println("程序已经退出成功");}
}
class CircleArray{private int maxsize; // 队列长度private int front; // 队列的头private int rear; // 队列的尾private int[] arr; // 队列的数组// 创建构造器public CircleArray(int maxsize) {this.maxsize = maxsize;front = 0; // 指向元素第一位置rear = 0; // 指向元素的第二个位置,即 尾部序号+1arr = new int[maxsize];}// 判断是否满了public boolean isFull(){return (rear+1)%maxsize == front;}// 判断是否为空public boolean isEmpty(){return rear==front;}//添加数据,会不会添加数据导致覆盖原来的数据public void addQueu(int n){// 判断是否满if(isFull() && size()System.out.println("队列已满,不能添加数据");return;}arr[rear] = n;
// rear++; // rear往后移动数据 erro:不能实现环形队列rear=(rear+1)%maxsize;// 注意:这里rear+1 == rear++}//取出数据public int getQueue(){//判断数据是否为空if(isEmpty()){throw new RuntimeException("数据为空,不能取数");}// 取出数据后,front需要往后移动,需要一个值来保存数据//方法一:int value = arr[front];
// front++;front = (front+1)%maxsize; //front+1 = front++return value;//方法二:
// front = (front+1)%maxsize;
// return arr[(front-1)%maxsize];}// 获取数据头部public int getHead(){return arr[front];}// 显示所有的数据public void showQueue(){//判断队列是否为空if(isEmpty()){System.out.println("队列为空");return;}//遍历数据,front+(rear-front+maxsize)%maxsizefor (int i=front;i < front+(rear-front+maxsize)%maxsize;i++){ // (rear-front+maxsize)%maxsize 有效数据System.out.printf("arr[%d]=%d\n",i%maxsize,arr[i%maxsize]);}}// 数据有效个数public int size(){return (rear+maxsize-front)%maxsize;}} 第三章:链表
一、链表
(一)链表介绍
链表是有序的列表
data域:数据
next域:地址
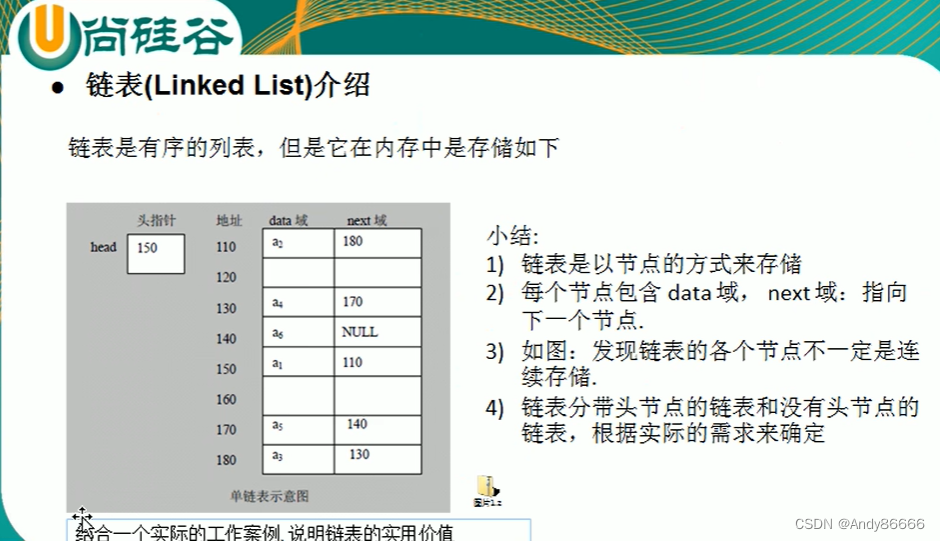
特点:
- 链表是
以节点的方式来存储数据 - 每一个节点包含data域,next域 (指向下一个节点)
- 链表中的数据并不一定是连续存放的
- 链表分为:
- 带头节点的链表 (head节点:不存放具体的数据)
- 没有带头节点的链表
单链表的应用实例
eg:单链表来管理水浒传的人物图
实现:代头节点的单向链表
代码实现
创建package:linkedlist,创建类:SingleLinkedListDemo
要求一:添加英雄,直接添加到链表的尾部中
package com.lcj.linkedlist;public class SignalLinkedList {public static void main(String[] args) {// 测试数据HeroNode hero1 = new HeroNode(1,"宋江","及时雨");HeroNode hero2 = new HeroNode(2,"宋江","及时雨");HeroNode hero3 = new HeroNode(3,"宋江","及时雨");// 创建链表管理器LinkedManager linkedManager = new LinkedManager();// 添加数据linkedManager.add(hero1);linkedManager.add(hero2);linkedManager.add(hero3);// 展示数据linkedManager.list();}}// 管理节点数据
class LinkedManager {//先创建一个头节点数据,但是并不存放数据private HeroNode head = new HeroNode(0, "", "");//添加节点到单链表中,但是数据需要添加到节点中的最后一个数据的Next为(Null)// 不考虑数据的编号public void add(HeroNode Node) {// 创建一个辅助指针来判断数据是否到达尾部HeroNode tmp = head;// 遍历循环while (true) {// 找最后节点数据if (tmp.next == null) {break;}// 如果没有找到最后一个节点,需要往后移动tmp = tmp.next;}// 退出循环的时候,就是指向最后节点,现在需要添加新的节点tmp.next = Node;}// 显示数据(遍历数据)public void list(){//判断链表是否为空,没有指向其他的节点if(head.next == null){System.out.println("链表为空");return;}//头节点不能动,需要创建辅助节点遍历数据HeroNode tmp = head.next;while(true){//判断是否到达最后if(tmp == null){
// System.out.println("最后的");break;}// 数据节点信息System.out.println(tmp);// 将tmp往后移动tmp = tmp.next;}}
}
// 创建节点数据
class HeroNode{public int no; // 创建序号public String name;//英雄名字public String nickname; // 昵称public HeroNode next; //指向下一个节点 ,值为java的引用,类似于c语言的指针//创建构造器public HeroNode(int no, String name, String nickname) {this.no = no;this.name = name;this.nickname = nickname;}
// 数据进行格式,便于后期数据的展示@Overridepublic String toString() {return "HeroNode{" +"no=" + no +", name='" + name + '\'' +", nickname='" + nickname + '\'' +'}';}
}
要求二:根据英雄的编号进行数据排序、修改节点值
添加数据
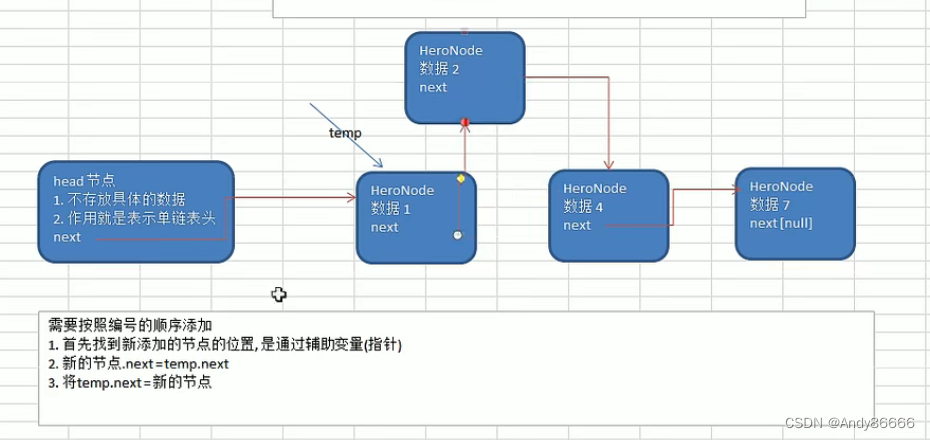
需要按照编号的顺序添加
- 首先找到新添加的节点位置
- 新的节点数据.next = tmp.next
- tmp.next = 新节点
思路:
- 找到序号前一个位置
- 插入数据
//按照数据序号顺序进行添加数据public void addByOrder(HeroNode node){HeroNode tmp = head;// 查找序号位置时,tmp要指向插入数据的前一个位置,不是能插入数据boolean flag = false; // 判断需要的编号是否存在,存在就不能添加while(true){if(tmp.next == null){//找到数据链尾了break;}if (tmp.next.no > node.no){ //判断位置,成功就位置在tmp处break;}else if (tmp.next.no == node.no){ //说明编号存在flag = true;break;}tmp = tmp.next;}// 判断flagif(flag){System.out.println("序号存在,请重新输入数据");}else{node.next = tmp.next; //新节点的后序是tmp的后序tmp.next = node; // 旧节点的后序等于新节点}}
修改数据
// 修改节点的信息,根据no编号来修改,即no编号不能改// 根据node的no序号来进行修改public void update(HeroNode node){if(head.next == null){System.out.println("链表为空");return;}//找需要修改的序号,因此需要进行遍历数据/* 版本一boolean flage = true;HeroNode tmp = head.next; // 创建临时的引用来遍历数据while (flage){if(tmp == null){ //到达链尾break;}if (tmp.no == node.no){tmp.name = node.name;tmp.nickname = node.nickname;break;}else{tmp = tmp.next;}}*/// 版本二boolean flage = false;HeroNode tmp = head.next; // 创建临时的引用来遍历数据while (true){if(tmp == null){ //到达链尾break;}if (tmp.no == node.no){flage = true;break;}else{tmp = tmp.next;}}// flage 为true会执行文件if(flage){tmp.name = node.name;tmp.nickname = node.nickname;}else{System.out.println("该节点数据没有找到");}}删除节点
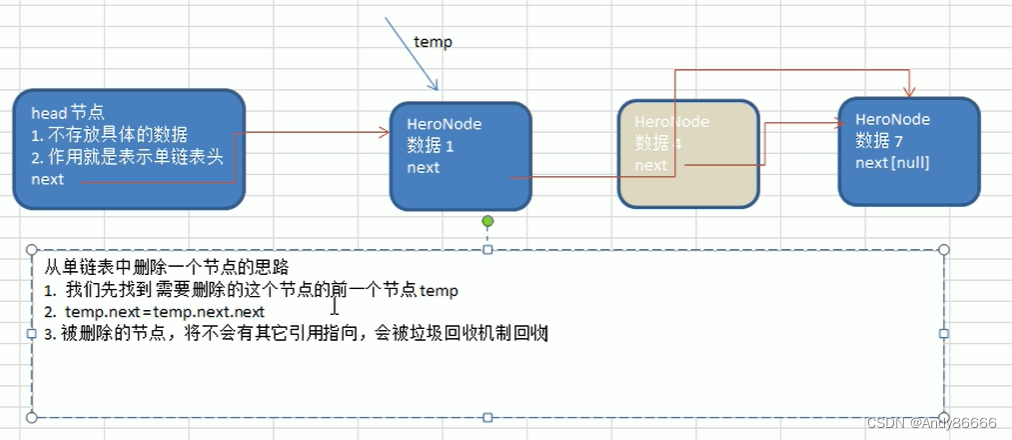
- 找到需要删除点的前一个点 tmp
- tmp.next = tmp.next.next
- 被删除的节点,将不会有其引用指向,会被垃圾回收机制回收
// 删除节点//思路:找到需要删除点的前一个点 tmp;public void del(int no){HeroNode tmp = head;boolean flag = false; // 标志是否找到待删除节点while(true){if(tmp.next == null){ // 位置处于数据的链尾break;}if(tmp.next.no == no){ //找到待删除节点的前一个节点的tmpflag = true;break;}tmp = tmp.next; //tmp后移,遍历}//判断flagif (flag){tmp.next = tmp.next.next;}else{System.out.println("该节点不存在");}}
完整代码
完整代码:添加数据(有序添加、排序添加)、修改数据、删除数据、
package com.lcj.linkedlist;public class SignalLinkedList {public static void main(String[] args) {// 测试数据HeroNode hero1 = new HeroNode(1,"宋江","及时雨");HeroNode hero2 = new HeroNode(2,"宋江","及时雨");HeroNode hero3 = new HeroNode(3,"宋江","及时雨");// 创建链表管理器LinkedManager linkedManager = new LinkedManager();// 添加数据
// linkedManager.add(hero1);
// linkedManager.add(hero2);
// linkedManager.add(hero3);//顺序添加数据linkedManager.addByOrder(hero3);linkedManager.addByOrder(hero2);linkedManager.addByOrder(hero1);// 展示数据linkedManager.list();System.out.println("======================================");// 修改节点数据HeroNode hero4 = new HeroNode(3,"法外张三","罗翔");linkedManager.update(hero4);linkedManager.list();// 展示数据// 删除节点linkedManager.del(1);System.out.println("==========删除数据后=========");linkedManager.list();}
}// 管理节点数据
class LinkedManager {//先创建一个头节点数据,但是并不存放数据private HeroNode head = new HeroNode(0, "", "");//添加节点到单链表中,但是数据需要添加到节点中的最后一个数据的Next为(Null)// 不考虑数据的编号public void add(HeroNode Node) {// 创建一个辅助指针来判断数据是否到达尾部HeroNode tmp = head;// 遍历循环while (true) {// 找最后节点数据if (tmp.next == null) {break;}// 如果没有找到最后一个节点,需要往后移动tmp = tmp.next;}// 退出循环的时候,就是指向最后节点,现在需要添加新的节点tmp.next = Node;}// 修改节点的信息,根据no编号来修改,即no编号不能改// 根据node的no序号来进行修改public void update(HeroNode node){if(head.next == null){System.out.println("链表为空");return;}//找需要修改的序号,因此需要进行遍历数据/* 版本一boolean flage = true;HeroNode tmp = head.next; // 创建临时的引用来遍历数据while (flage){if(tmp == null){ //到达链尾break;}if (tmp.no == node.no){tmp.name = node.name;tmp.nickname = node.nickname;break;}else{tmp = tmp.next;}}*/// 版本二boolean flage = false;HeroNode tmp = head.next; // 创建临时的引用来遍历数据while (true){if(tmp == null){ //到达链尾break;}if (tmp.no == node.no){flage = true;break;}else{tmp = tmp.next;}}// flage 为true会执行文件if(flage){tmp.name = node.name;tmp.nickname = node.nickname;}else{System.out.println("该节点数据没有找到");}}//按照数据序号顺序进行添加数据public void addByOrder(HeroNode node){HeroNode tmp = head;// 查找序号位置时,tmp要指向插入数据的前一个位置,不是能插入数据boolean flag = false; // 判断需要的编号是否存在,存在就不能添加while(true){if(tmp.next == null){//找到数据链尾了break;}if (tmp.next.no > node.no){ //判断位置,成功就位置在tmp处break;}else if (tmp.next.no == node.no){ //说明编号存在flag = true;break;}tmp = tmp.next;}// 判断flagif(flag){System.out.println("序号存在,请重新输入数据");}else{node.next = tmp.next; //新节点的后序是tmp的后序tmp.next = node; // 旧节点的后序等于新节点}}// 删除节点//思路:找到需要删除点的前一个点 tmp;public void del(int no){HeroNode tmp = head;boolean flag = false; // 标志是否找到待删除节点while(true){if(tmp.next == null){ // 位置处于数据的链尾break;}if(tmp.next.no == no){ //找到待删除节点的前一个节点的tmpflag = true;break;}tmp = tmp.next; //tmp后移,遍历}//判断flagif (flag){tmp.next = tmp.next.next;}else{System.out.println("该节点不存在");}}// 显示数据(遍历数据)public void list(){//判断链表是否为空,没有指向其他的节点if(head.next == null){System.out.println("链表为空");return;}//头节点不能动,需要创建辅助节点遍历数据HeroNode tmp = head.next;while(true){//判断是否到达最后if(tmp == null){
// System.out.println("最后的");break;}// 数据节点信息System.out.println(tmp);// 将tmp往后移动tmp = tmp.next;}}
}
// 创建节点数据
class HeroNode{public int no; // 创建序号public String name;//英雄名字public String nickname; // 昵称public HeroNode next; //指向下一个节点 ,值为java的引用,类似于c语言的指针//创建构造器public HeroNode(int no, String name, String nickname) {this.no = no;this.name = name;this.nickname = nickname;}
// 数据进行格式,便于后期数据的展示@Overridepublic String toString() {return "HeroNode{" +"no=" + no +", name='" + name + '\'' +", nickname='" + nickname + '\'' +'}';}
}
(二)面试题
- 求单链表中有效节点的个数
- 查找单链表中的倒数第K个节点——新浪面试
- 单链表的反转 ——腾讯面试
- 从尾到头打印单链表——百度:要求(1)反向遍历 (2)stack栈
- 合并两个有序的单链表,合并之后的链表依然有序
题一:求单链表中有效节点的个数
注意:不要将头节点也统计进去
public void nodeNum(){HeroNode temp = head.next;int count=0;while(true){//如果到达链尾if(temp == null){break;}temp = temp.next;count++;}System.out.println("节点个数为:"+count);}题目二:查找单链表中的倒数第K个节点——新浪面试
- 思路:
- 先遍历一下数据,统计数据的有效个数
- 有效个数 - k,得到需要找的
public void findLastIndex(int k){HeroNode temp = head.next;// 统计个数int count=0;while(true){//如果到达链尾if(temp == null){break;}temp = temp.next;count++;}// 判断k是否有效if(k > count|| k<=0){System.out.println("超出了链表范围");return;}else{ //读取第k个值的位置int flag = count - k;HeroNode temp1 = head.next;for(int i=0;itemp1 = temp1.next;}System.out.printf("序号:%d \t 名字:%s",temp1.no,temp1.name);} }
注意:if(k > count|| k<=0)我遗漏了k<=0的问题
题目三:单链表的反转 ——腾讯面试
-
思路:(头插入数据)
- 新建一个链表,用来存储数据
- 将旧链表中的节点数据移动到新节点中
- 新链表指向旧链表的头
public static void reversetList(HeroNode head){//判断链表是否为空,或者只有一个节点的,无需反转if (head.next == null || head.next.next ==null){return;}HeroNode tmp = head.next;HeroNode next = null; //用来指向tmp的下一个节点数据HeroNode reversetHead = new HeroNode(0,"",""); //新链表的头节点数// 遍历链表,将旧链表中的节点数据移动到新节点中while(tmp != null){next = tmp.next ; //用于保存当前节点下一个节点数据tmp.next = reversetHead.next;reversetHead.next = tmp;tmp = next; //往后移动}head.next = reversetHead.next;}核心代码:
next = tmp.next ; //用于保存当前节点下一个节点数据
tmp.next = reversetHead.next;
reversetHead.next = tmp;
tmp = next; //往后移动
题目四:从尾到头打印单链表——百度:要求(1)反向遍历 (2)stack栈
-
方法一:先将单链表进行反转操作,然后再遍历即可,但是不建议使用,破坏数据的原结构
-
方法二:利用栈将各个节点的数据压入到栈中,然后利用栈的先进后出特点
//利用栈将各个节点的数据压入到栈中,然后利用栈的==先进后出==特点public static void reserverPrinter(HeroNode head){if(head.next == null){return;}Stackstack = new Stack<>();HeroNode tmp = head.next;//数据入栈while (tmp != null){ //数据不能为空,为空代表到达链尾stack.push(tmp);//stack中添加数据pushtmp = tmp.next;}//数据出栈while(stack.size()>0){System.out.println(stack.pop()); //pop 将数据弹出}}
题目五:合并两个有序的单链表,合并之后的链表依然有序
二、双链表
(一)、双向链表的介绍

双向链表添加了pre,目的:用它来指向节点的前一个节点
双向节点删除数据:
-
可以指向待删除的节点 temp
-
temp.pre.next = temp.next
-
temp.next.pre = temp.pre
单链表存在的问题:
- 单向链表查找的方向只能是一个方向,而双向链表可以向前或者向后查找
- 单向链表不能自我删除,需要靠辅助节点,而双向链表可以自我删除
(二) 、应用案例
实现英雄的案列
创建类:DoubleLinkedListDamon
package com.lcj.linkedlist;public class DoubleLinkedListDaemon {public static void main(String[] args){HeroNode2 hero1 = new HeroNode2(1,"宋江","及时雨");HeroNode2 hero2 = new HeroNode2(8,"宋江","及时雨");HeroNode2 hero3 = new HeroNode2(3,"宋江","及时雨");//创建一个双向链表DoubleLinkedList doubleLinkedList = new DoubleLinkedList();doubleLinkedList.add(hero2);doubleLinkedList.add(hero1);doubleLinkedList.add(hero3);//数据展示doubleLinkedList.list();// 数据修改System.out.println("==========数据修改============");HeroNode2 hero4 = new HeroNode2(3,"张三","及时雨");doubleLinkedList.update(hero4);doubleLinkedList.list();//数据删除System.out.println("==========数据删除==========");doubleLinkedList.del(3);doubleLinkedList.list();//添加数据System.out.println("===========添加数据=========");HeroNode2 hero5 = new HeroNode2(5,"lisi","李四");doubleLinkedList.add(hero5);doubleLinkedList.list();}
}
// 管理双向链表
class DoubleLinkedList{private HeroNode2 head = new HeroNode2(0,"","");// 显示数据(遍历数据)public void list(){//判断链表是否为空,没有指向其他的节点if(head.next == null){System.out.println("链表为空");return;}//头节点不能动,需要创建辅助节点遍历数据HeroNode2 tmp = head.next;while(true){//判断是否到达最后if(tmp == null){
// System.out.println("最后的");break;}// 数据节点信息System.out.println(tmp);// 将tmp往后移动tmp = tmp.next;}}//添加数据到链表的末尾//思路:找到链表末尾public void add(HeroNode2 Node) {// 创建一个辅助指针来判断数据是否到达尾部HeroNode2 tmp = head;// 遍历循环while (true) {// 找最后节点数据if (tmp.next == null) {break;}// 如果没有找到最后一个节点,需要往后移动tmp = tmp.next;}// 退出循环的时候,就是指向最后节点,现在需要添加新的节点,形成双向链tmp.next = Node;Node.pre = tmp;}//添加数据 要求:按照序号进行添加数据public void addByOrder(HeroNode2 node){HeroNode2 tmp = head;// 查找序号位置时,tmp要指向插入数据的前一个位置,不是能插入数据boolean flag = false; // 判断需要的编号是否存在,存在就不能添加while(true){if(tmp.next == null){//找到数据链尾了break;}if (tmp.next.no > node.no){ //判断位置,成功就位置在tmp处break;}else if (tmp.next.no == node.no){ //说明编号存在flag = true;break;}tmp = tmp.next;}// 判断flagif(flag){System.out.println("序号存在,请重新输入数据");}else{node.next = tmp.next; //新节点的后序是tmp的后序tmp.next = node; // 旧节点的后序等于新节点}}//修改节点内容//思路:主要是找到节点的位置// 根据node的no序号来进行修改,public void update(HeroNode2 node){if(head.next == null){System.out.println("链表为空");return;}//找需要修改的序号,因此需要进行遍历数据/* 版本一boolean flage = true;HeroNode tmp = head.next; // 创建临时的引用来遍历数据while (flage){if(tmp == null){ //到达链尾break;}if (tmp.no == node.no){tmp.name = node.name;tmp.nickname = node.nickname;break;}else{tmp = tmp.next;}}*/// 版本二boolean flage = false;HeroNode2 tmp = head.next; // 创建临时的引用来遍历数据while (true){if(tmp == null){ //到达链尾break;}if (tmp.no == node.no){flage = true;break;}else{tmp = tmp.next;}}// flage 为true会执行文件if(flage){tmp.name = node.name;tmp.nickname = node.nickname;}else{System.out.println("该节点数据没有找到");}}//删除节点数// 只需要直接找到需要删除的节点,不需要像单链表一样找到前面的节点,再进行数据删除public void del(int no){//判断数据是否为空if(head.next == null){System.out.println("数据为空");return;}HeroNode2 tmp = head.next;boolean flag = false; // 标志是否找到待删除节点while(true){if(tmp == null){ // 位置处于数据的链尾break;}if(tmp.no == no){ //找到待删除节点的前一个节点的tmpflag = true;break;}tmp = tmp.next; //tmp后移,遍历}//判断flagif (flag){tmp.pre.next = tmp.next;// 如果是最后一个节点,不需要执行这个,否则会出现空指针的问题if(tmp.next !=null) {tmp.next.pre = tmp.pre;}}else{System.out.println("该节点不存在");
class HeroNode2{public int no;public String name;public String nickname;public HeroNode2 next; //指向下一个节点public HeroNode2 pre; // 指向前一个节点public HeroNode2(int no, String name, String nickname) {this.no = no;this.name = name;this.nickname = nickname;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "HeroNode2{" +"no=" + no +", name='" + name + '\'' +", nickname='" + nickname + '\'' +'}';}
三、单向环形链表应用场景
(一)约瑟夫问题

人数 n=5
开始序号: k= 1
取出数据间隔 m=2
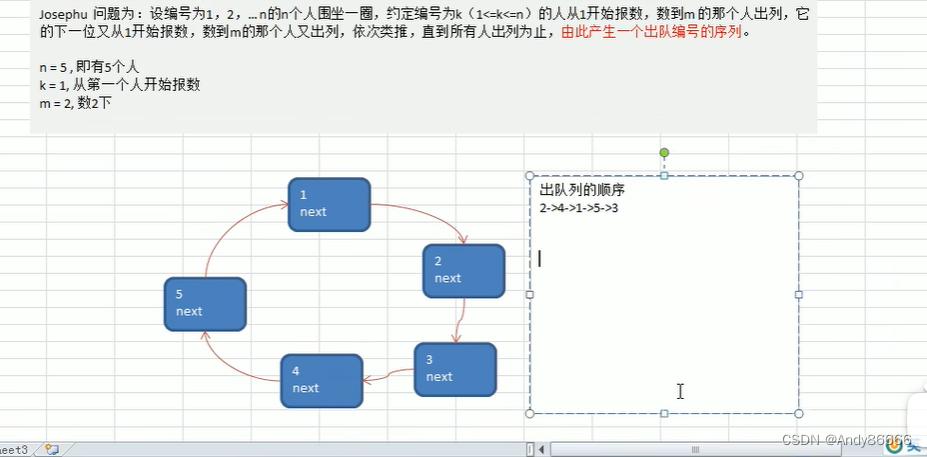
(二) 代码实现
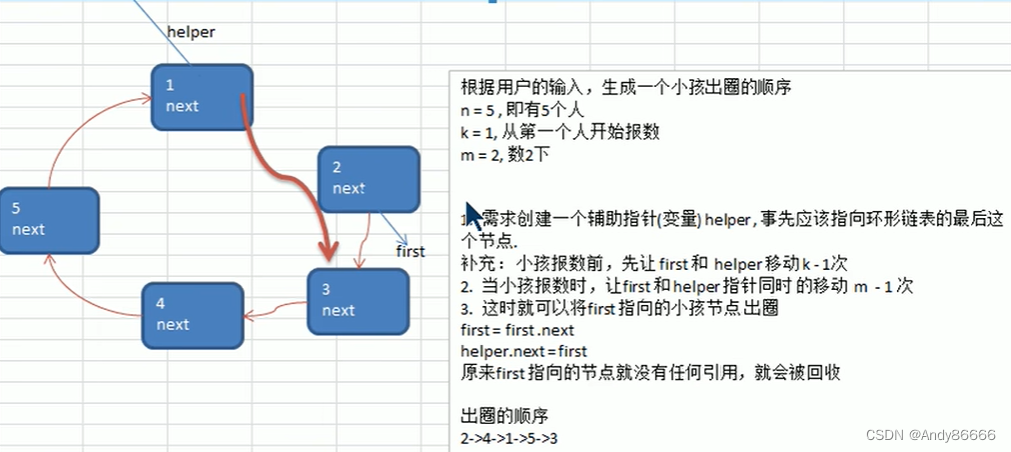
要求:
-
构建单向环形链表
- 创建第一个节点,通过first指向该节点,并形成环形
- 当每创建创建一个新的节点,将该节点加入到链表中
-
遍历环形链表
- 通过一个辅助指针 tmp ,指向first 节点
- 通过while循环进行统计,循环终止条件
tmp.next = first
-
创建出队列的编号序列
-
人数 n=5
开始序号: k= 1
取出数据间隔 m=2
-
创建辅助节点
helper,指向代删除的节点的前一个节点,注意起始位置位于环形列表的最后一个位置 ,报数自己也需要报一次补充:先将
first和helper需要移动到k-1的位置 -
报数时,让
first和helper移动m-1次 -
删除节点:
first = first.nextper.next =first
-
创建类:Josephu
package com.lcj.linkedlist;
/*
* 编写目的:学习约瑟夫问题,了解单向环形链表
* 类似于丢手绢的游戏,只是固定了次数
* */
public class Joseph {public static void main(String[] args){// 测试CircleSingleLinkedList circleSingleLinkedList = new CircleSingleLinkedList();
// circleSingleLinkedList.addBoy(5); // 创建5个节点
// circleSingleLinkedList.showBody();//出圈测试int startNum = 2;int countNum = 2;int nums = 10;circleSingleLinkedList.addBoy(nums);circleSingleLinkedList.showBody();circleSingleLinkedList.countBoy(startNum,countNum,nums);}
}//创建单向环形链表
class CircleSingleLinkedList{// 创建一个first节点,但是没有编号的private Boy first = null;//添加节点数据,构建成一个环形的链表// nums 的数量为 创建节点的个数public void addBoy(int nums){//判断nums 的个数if(nums < 1){System.out.println("输入nums的值不正确");return;}Boy curBoy = null; //辅助指针,帮助构建形式链表// 创建环形链表for (int i = 1; i <= nums ; i++) {Boy boy = new Boy(i);if (i==1){first = boy;first.setNext(first); // first 的后序是自己本身,这样才能构成环curBoy = first;}else{curBoy.setNext(boy); // 连接新的节boy.setNext(first); // 形成 环形curBoy = boy; // 将辅助节点往新的节点进行移动}}}// 遍历当前的环形链表public void showBody(){// 判断链表是否为空if(first == null){System.out.println("链表为空");return;}// 创建辅助节点Boy curBoy1 = first;while (true){System.out.printf("小朋友编号:%d\n", curBoy1.getNo());if (curBoy1.getNext() == first) {System.out.println("数据遍历完成");break;}curBoy1 = curBoy1.getNext(); //指针往后移动}}/*
* startNo 是从第几个小孩开始数数
* countNum 间隔的人数
* nums 小孩人数
* */public void countBoy(int startNo,int countNum,int nums){if(first ==null || startNo <1 || startNo > nums){System.out.println("参数输入有误");return;}//创建一个辅助节点数据Boy helper = first;//将helper指向链尾,即first的前一个节点上,目的是便于删除数据while(true){if(helper.getNext() == first){ //判断helper是否到达链尾,主要是为了删除数据时,指向删除点的前一个位置break;}helper = helper.getNext();}// 将frist和helper的移动startNo-1的位置for (int i = 0; i < startNo-1; i++) {helper = helper.getNext();first = first.getNext();}// 小孩子报数,让first和helper移动countNum -1次,然后出圈(删除)while(true){if(helper == first){ // 只有一个数据,helper是在first前面的break;}//first和helper移动countNum -1次for (int i = 0; i < countNum-1; i++) {helper = helper.getNext();first = first.getNext();}//first指向节点System.out.printf("小孩%d出圈\n",first.getNo());// 删除数据first = first.getNext();helper.setNext(first);}System.out.printf("最后的节点为%d\n",first.getNo());}
}//创建节点 ,名字为boy
class Boy{private int no; // 节点的编号private Boy next; // 指向下一个节点public Boy(int no){this.no = no;}public int getNo() {return no;}public void setNo(int no) {this.no = no;}public Boy getNext() {return next;}public void setNext(Boy next) {this.next = next;}
}注意:只有一个节点可以自己指向自己
第四章:栈
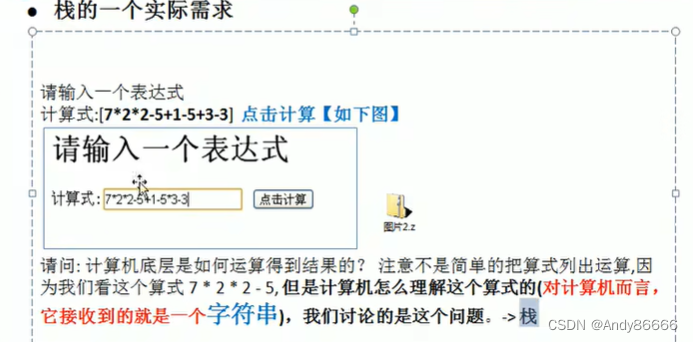
(一)、栈介绍
-
栈是一种先进先出(first in last out)的有效列表
-
允许插入和删除的一端,为变化的一端,称为
栈顶(Top),另一端固定为栈底(Bottom),
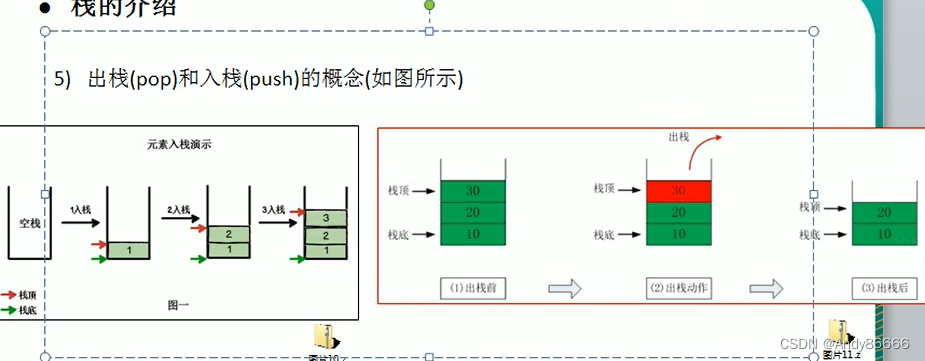
-
栈的应用

中缀表达式转后缀表达式是面试中常考的
(二)数组模拟栈的思路分析
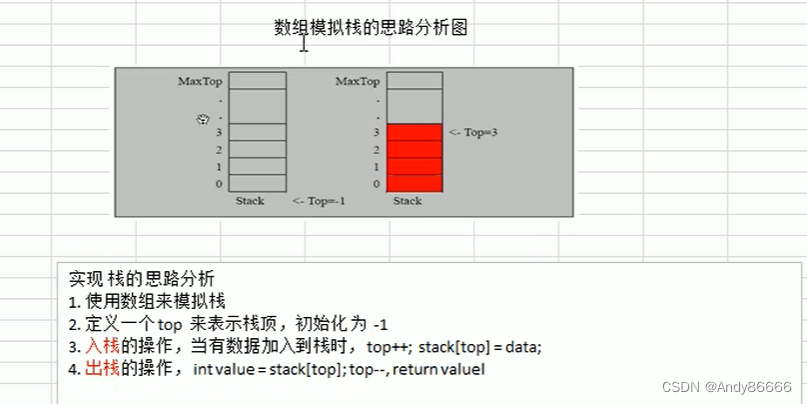
-
使用数组来模拟栈
-
定义一个top,来表示栈顶,初始化为-1
-
入栈的操作,当数据加入栈时,top++,stack[top]=data;
-
出栈的操作,int value = stack[top], top–
创建packe:com.lcj.Stack
创建class:ArrayStackDemo
package com.lcj.stack;import com.sun.imageio.plugins.wbmp.WBMPImageReader;import java.util.Scanner;// 数组栈的学习
public class ArrayStackDamon {public static void main(String[] args){//数组栈测试ArrayStack stack = new ArrayStack(4);String key = ""; //输入的数据boolean loop = true; //判断循环的条件Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);// 测试菜单while(loop){System.out.println("输入exit:退出");System.out.println("输入push数据入栈");System.out.println("输入pop数据出栈");System.out.println("输入show 显示栈");key = scanner.next();switch (key){case "show":stack.list();break;case "push":System.out.println("请输入需要插入的数据");int value = scanner.nextInt();stack.push(1);break;case "exit":System.out.println("退出");loop = false;break;case "pop":System.out.println("数据出栈");try{int v = stack.pop();System.out.println("出栈的数值为"+v);}catch(Exception e){System.out.println(e.getMessage());}default:break;}}System.out.println("退出成功");}
}//栈
class ArrayStack{private int top = -1; //标记栈顶的位置private int maxSize; //栈的最大长度private int stack[]; // 栈数组进行存储数据//构建器public ArrayStack(int maxSize){this.maxSize = maxSize;stack = new int[this.maxSize];}//判断是否为空public boolean isEmpty(){return top==-1;}//判断是否栈满,即达到maxsizepublic boolean isFull(){return top == maxSize-1 ;// 注意:这点是从0开始计算的}//数据入栈public void push(int value){//判断是否栈满if (isFull()){System.out.println("栈满");return;}top++; // top指向的是有数据的栈顶stack[top] = value;}//数据出栈public int pop(){//判断数据是否为空if (isEmpty()){throw new RuntimeException("栈为空"); // 因为这点数据结果有类型,需要使用运行异常来解决}int value = stack[top];top--;return value;}// 遍历数据public void list(){//判断数据是否为空if (isEmpty()) {System.out.println("栈为空");return;}for (int i = top; i >= 0 ; i--) {System.out.printf("stack[%d]=%d\n",i,stack[i]);}}
}
(三)练习:使用链表来模拟栈
思路一:双链表doubleLinked
- 创建双链表doubleLinked,两个指针 :next、pre,栈顶指针:top
- 入栈:节点tmp 添加到链尾,
前一个节点.next = tmp,前一个节点的.next.pre = tmp - 出栈:
tmp.pre.next = null ,tmp.pre = null, - 遍历数据
版本一:双链表实现栈
package com.lcj.stack;
/*
* 创建人:lcj
* 创建时间:2022年8月29
* 目的:用链表来实现栈
* */
public class LinkedStackDamon {public static void main(String[] args){//测试stack stack = new stack();
// System.out.println(stack.topSite()); //测试topSite是否运行正常doubleLinked node1 = new doubleLinked(2);doubleLinked node2 = new doubleLinked(3);doubleLinked node3 = new doubleLinked(4);stack.add(node1);stack.add(node2);stack.add(node3);stack.show();stack.pop();
// System.out.println(stack.topSite());stack.show();}
}//stack
class stack{//创建一个first的头节点doubleLinked head = new doubleLinked(1);//top 确定栈顶位置public doubleLinked topSite(){doubleLinked tmp = head; //创建一个辅助节点while (true){if(tmp.getNext() == null){// break;
// System.out.println("1");return tmp;}tmp = tmp.getNext(); //往后移动}}//添加数据public void add(doubleLinked node){doubleLinked tmp = topSite(); //创建一个辅助节点tmp.setNext(node); // 连接nexttmp.getNext().setPre(tmp); // 将新节点的pre连接到前一节点上
// System.out.println(tmp.getNext().getValue());}//展示数据public void show(){doubleLinked top = topSite();while(true){if (top.getPre()==null){ // 到达 head 之前break;}System.out.println(top.getValue());top = top.getPre(); //将辅助指针往前面进行移动}}//数据出栈public int pop(){doubleLinked top = topSite(); // 获得栈顶int value = top.getValue();top.getPre().setNext(null);top.setPre(null);System.out.println("删除");return value;}
}// 用双链表来实现
class doubleLinked{private int value; // 链表中保存的值private doubleLinked next; //指向后序private doubleLinked pre; //指向前序private doubleLinked top; // 栈顶//构建对象public doubleLinked(int value) {this.value = value;}public int getValue() {return value;}public void setValue(int value) {this.value = value;}public doubleLinked getNext() {return next;}public void setNext(doubleLinked next) {this.next = next;}public doubleLinked getPre() {return pre;}public void setPre(doubleLinked pre) {this.pre = pre;}public doubleLinked getTop() {return top;}public void setTop(doubleLinked top) {this.top = top;}
}
版本二:双链表实现栈
package com.lcj.stack;
/*
* 创建人:lcj
* 创建时间:2022年8月29
* 目的:用链表来实现栈
* */
public class LinkedStackDamon {public static void main(String[] args){//测试stack stack = new stack();
// System.out.println(stack.topSite()); //测试topSite是否运行正常doubleLinked node1 = new doubleLinked(2);doubleLinked node2 = new doubleLinked(3);doubleLinked node3 = new doubleLinked(4);stack.add(node1);stack.add(node2);stack.add(node3);stack.show();stack.pop();
// System.out.println(stack.topSite());stack.show();}
}//stack
class stack{//创建一个first的头节点doubleLinked head = new doubleLinked(1);//top 确定栈顶位置public doubleLinked topSite(){doubleLinked tmp = head; //创建一个辅助节点while (true){if(tmp.next == null){// break;
// System.out.println("top找到");return tmp;}tmp = tmp.next; //往后移动}}//添加数据public void add(doubleLinked node){doubleLinked tmp = topSite(); //创建一个辅助节点tmp.next = node; // 连接nexttmp.next.pre = tmp; // 将新节点的pre连接到前一节点上}//展示数据public void show(){doubleLinked top = topSite();while(true){if (top.pre==null){ // 到达 head 之前break;}System.out.println(top.getValue());top = top.pre; //将辅助指针往前面进行移动}}//数据出栈public int pop(){doubleLinked top = topSite(); // 获得栈顶int value = top.getValue();top.pre.next = null;top.pre = null;System.out.println("删除");return value;}}// 用双链表来实现
class doubleLinked{public int value; // 链表中保存的值public doubleLinked next; //指向后序public doubleLinked pre; //指向前序public doubleLinked top; // 栈顶//构建对象public doubleLinked(int value) {this.value = value;}public int getValue() {return value;}public void setValue(int value) {this.value = value;}
}
思想二:创建一个单链表
-
创建一个
singalLinked -
添加链表的数据tmp :
前一节点.next = tmp -
数据出栈:
- 方法一:遍历数据,找到最后一个数据,缺点时间过长
- 方法二:将链表的反转,将数据出栈后,由反转回去
-
数据入栈:
- 思路一:直接找到链尾进行插入数据
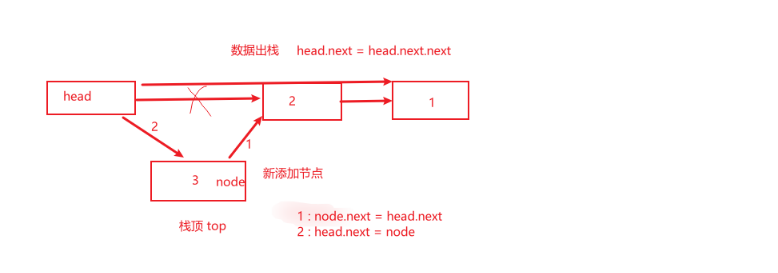
注意:添加数据和数据出栈都需要,注意后面节点是否存在
版本三:单链表实现
package com.lcj.stack;
/** 创建人:lcj* 创建时间:2022年8月29* 目的:用单链表来实现栈* */
public class SingalLinkedStackDaemon {public static void main(String[] args){// 测试StackLinked stack1 = new StackLinked();//添加数据singalLinked Linked1 = new singalLinked(1);singalLinked Linked2 = new singalLinked(2);singalLinked Linked3 = new singalLinked(3);singalLinked Linked4 = new singalLinked(4);stack1.push(Linked1);stack1.push(Linked2);stack1.push(Linked3);stack1.push(Linked4);// 展示数据System.out.println("展示数据");stack1.show();//数据出栈System.out.println("数据出栈");try {stack1.pop();stack1.pop();}catch (Exception e){System.out.println(e.getMessage());}stack1.show();}
}// 创建栈
class StackLinked{singalLinked head = new singalLinked(1); // 栈的头节点,需要保持不动//添加数据和数据出栈都需要,注意后面节点是否存在,即栈是否空的情况public boolean isEmpty(){return head.next == null;}//数据入栈public void push(singalLinked node){//判断链表是否空if (isEmpty()){head.next = node; //直接将数据连接到node上,不需要连接后面的return;}// 链表为不空时node.next = head.next; // 将后面连接head.next = node; //将前面head连接}//数据出栈public int pop(){// 栈是否为空if (isEmpty()){throw new RuntimeException("栈表为空");}// 栈只存在一个节点if (head.next.next == null ){head.next = null;return head.next.getValue(); // 返回被删除的值}int value = head.next.getValue();head.next = head.next.next; // 将head连接删除的节点的后面一个return value; // 返回被删除的值}//展示数据public void show(){singalLinked tmp = head;//判断是否空if (isEmpty()){System.out.println("栈为空");return; //退出}while(true){//判断数据是否到达链尾if(tmp.next == null){break;}tmp = tmp.next; //往后移动System.out.printf("%d\n",tmp.getValue());}}
}//创建单链表
class singalLinked{public int value; // value 是指栈中的值public singalLinked next;public singalLinked(int value) {this.value = value;}public int getValue() {return value;}public void setValue(int value) {this.value = value;}
}
版本四:单链表实现 ,改变测试环境(推荐)
package com.lcj.stack;import java.util.Scanner;/** 创建人:lcj* 创建时间:2022年8月29* 目的:用单链表来实现栈* */
public class SingalLinkedStackDaemon {public static void main(String[] args){/* 测一// 测试StackLinked stack1 = new StackLinked();//添加数据singalLinked Linked1 = new singalLinked(1);singalLinked Linked2 = new singalLinked(2);singalLinked Linked3 = new singalLinked(3);singalLinked Linked4 = new singalLinked(4);stack1.push(Linked1);stack1.push(Linked2);stack1.push(Linked3);stack1.push(Linked4);// 展示数据System.out.println("展示数据");stack1.show();//数据出栈System.out.println("数据出栈");try {stack1.pop();stack1.pop();}catch (Exception e){System.out.println(e.getMessage());}stack1.show();*///测试二StackLinked stack1 = new StackLinked();boolean loop = true ; // 循环跳出的条件Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);String key = ""; // 输入的关键字while(loop){System.out.println("输入exit退出");System.out.println("输入push数据入栈");System.out.println("输入pop数据出栈");System.out.println("输入show展示数据");key = scanner.next();switch (key){case "exit":System.out.println("退出");loop = false;break;case "push":System.out.println("数据入栈");System.out.println("请输入节点数据:");int index = scanner.nextInt();
// singalLinked Linked = new singalLinked(index);stack1.push(new singalLinked(index));break;case "pop":System.out.println("数据出栈");int a = stack1.pop();System.out.println("删除的值为:"+a);break;case "show":System.out.println("展示数据");stack1.show();break;default:System.out.println("输入有误");break;}}System.out.println("退出成功");}
}// 创建栈
class StackLinked{singalLinked head = new singalLinked(1); // 栈的头节点,需要保持不动//添加数据和数据出栈都需要,注意后面节点是否存在,即栈是否空的情况public boolean isEmpty(){return head.next == null;}//数据入栈public void push(singalLinked node){//判断链表是否空if (isEmpty()){head.next = node; //直接将数据连接到node上,不需要连接后面的return;}// 链表为不空时node.next = head.next; // 将后面连接head.next = node; //将前面head连接}//数据出栈public int pop(){// 栈是否为空if (isEmpty()){throw new RuntimeException("栈表为空");}// 栈只存在一个节点if (head.next.next == null ){head.next = null;return head.next.getValue(); // 返回被删除的值}int value = head.next.getValue();head.next = head.next.next; // 将head连接删除的节点的后面一个return value; // 返回被删除的值}//展示数据public void show(){singalLinked tmp = head;//判断是否空if (isEmpty()){System.out.println("栈为空");return; //退出}while(true){//判断数据是否到达链尾if(tmp.next == null){break;}tmp = tmp.next; //往后移动System.out.printf("%d\n",tmp.getValue());}}
}//创建单链表
class singalLinked{public int value; // value 是指栈中的值public singalLinked next;public singalLinked(int value) {this.value = value;}public int getValue() {return value;}public void setValue(int value) {this.value = value;}
}(四)栈实现综合案例——计算器

思路:创建两个栈,一个数栈 numStack(用于存储数值) ,一个符号栈 operStack(存储符号)
-
通过一个
index来判断计算表达式中数值和符号 -
发现数值直接入数据栈
-
如果发现是符号,需要分两种情况:
3.1符号栈为空,直接添加到符号栈中
3.2符号栈已经存在了,需要判断待添加的符号和符号栈中栈顶的符号,比较优先级
3.2.1如果待入栈的符号大于栈顶的,则直接入栈
3.2.2如果待入栈的符号小于、等于栈顶的,则需要
pop 两个数栈中的,与pop符号栈的中的符号进行计算,并将运算结果和待入栈的符号分别入栈 -
当计算表达式扫描完成后,就顺序从数据栈中和符号栈中pop出两个数值和符合,并将结果放进数据栈中
-
最后在数栈只有一个数字,即表达式的结果
注意:符号栈是更加栈顶特点:先进后出,因此将优先级高的后出。
创建class:calculatot
package com.lcj.stack;import com.sun.deploy.security.SelectableSecurityManager;
import sun.font.DelegatingShape;public class Calculator {public static void main(String[] args) {String expression = "3+2*6-2";//创建两个栈ArrayStack1 numStack = new ArrayStack1(20); //数栈ArrayStack1 operStack = new ArrayStack1(20); //符号栈//定义需要的相关变量int index = 0; //用于扫描,表达式的int num1 = 0;int num2 = 0;int res = 0;int oper = 0;char ch = ' '; //符号保存到这里面的//通过while循环进行扫描表达式while (true){//依次得到expression的每一个字符ch = expression.substring(index,index+1).charAt(0);// substring(开始,结束)//判断ch的类型进行下一步的操作if(operStack.isOper(ch)){ //如果是运算符//1. 判断当前的符号栈是否为空,为空直接入栈if (!operStack.isEmpty()){//2 如果待入栈的符号大于栈顶的,则直接入栈//3 如果待入栈的符号小于、等于栈顶的if (operStack.priority(ch) <= operStack.priority(operStack.peek())){num1 = numStack.pop();num2 = numStack.pop();oper = operStack.pop();res = numStack.cal(num1,num2,oper);//将结果入数栈numStack.push(res);//将符号入栈operStack.push(ch);} else {operStack.push(ch);}}else{ // 不为空operStack.push(ch);}}else{ //数字直接入栈numStack.push(ch - 48); //注意:ch是字符串,在ASCII码中需要 - 48}//判断是否扫描完index++;if(expression.length() <= index){break;}}//当计算表达式扫描完成后,就**顺序从数据栈中和符号栈中pop出两个数值和符合**,并将结果放进数据栈中while (true){//判断是否计算完if(operStack.isEmpty()){break;}num1 = numStack.pop();num2 = numStack.pop();oper = operStack.pop();res = numStack.cal(num1,num2,oper);numStack.push(res);}System.out.println("结果为:"+numStack.pop());}
}
//栈
class ArrayStack1{private int top = -1; //标记栈顶的位置private int maxSize; //栈的最大长度private int stack[]; // 栈数组进行存储数据//构建器public ArrayStack1(int maxSize){this.maxSize = maxSize;stack = new int[this.maxSize];}//判断是否为空public boolean isEmpty(){return top==-1;} // top的初始位置为-1//判断是否栈满,即达到maxsizepublic boolean isFull(){return top == maxSize-1 ;// 注意:这点是从0开始计算的}//数据入栈public void push(int value){//判断是否栈满if (isFull()){System.out.println("栈满");return;}top++; // top指向的是有数据的栈顶stack[top] = value;}//数据出栈public int pop(){//判断数据是否为空if (isEmpty()){throw new RuntimeException("栈为空"); // 因为这点数据结果有类型,需要使用运行异常来解决}int value = stack[top];top--;return value;}// 遍历数据public void list(){//判断数据是否为空if (isEmpty()) {System.out.println("栈为空");return;}for (int i = top; i >= 0 ; i--) {System.out.printf("stack[%d]=%d\n",i,stack[i]);}}//查看栈顶的值public int peek(){return stack[top];}// 符号的优先级,通过定义数值来表达符号的优先级,数值越大优先级越高// 目的直接将符号转换为成为数组,便于更好的进行比较优先级public int priority(int oper){ //oper 符号if(oper == '*' || oper == '/'){return 1;}else if (oper == '+' || oper == '-'){return 0;}else{return -1; //目前忽略了%、()、[] 等符号}}//判断是否为运算符,好处:不用判断字符是否为数值public boolean isOper(char val){return val == '*' || val == '/' || val == '+' || val == '-';}//计算public int cal(int num1,int num2,int oper){int res = 0;// 返回的结果switch (oper){case '*':res = num1 * num2;break;case '/':res = num2 / num1; //注意有向后顺序,从栈最先出来是num1,最后出来的是num2break;case '+':res = num1 + num2;break;case '-':res = num2 - num1;//注意有向后顺序,从栈最先出来是num1,最后出来的是num2break;}return res;}}缺点:只能计算数值为单个数据的,而不能计算数据为两位数的
(五)栈的三种表达式
前缀(波兰表达式)、中缀、后缀表达式(逆波兰表达式)
注意:中缀转后缀,再面试必问
前缀表达式相关知识
后缀表达式相关知识 ==>讲解了中缀表达式到后缀表达式
后缀表达式的计算
1、前缀表达式
又被称为波兰表达式,运算符位于操作数之前
eg:(3+4)x 5- 6 ==》前缀表达式:- x + 3 4 5 6
补充知识:
从右往左

2、后缀表达式
从左往右


注意:
-
通过两个栈:
符号栈s1(存储)、数据栈 s2来存储运算符和数值 -
从
左至右扫描中缀表达式 -
遇到数值直接入栈s2
-
遇到操作符,需要分成以下情况:
4.1 如果s1为空时,直接将**
符号入栈s1**中,或者为(时,也是==直接入栈s2中==4.2 不为空需要分成两种情况:
4.2.1 当待入栈的操作符,与栈顶的操作进行比较,栈顶操作符小于 等于 待入栈的操作符时,直接将待入栈的操作符直接入栈s1
4.2.2 当待入栈的操作符,与栈顶的操作进行比较,栈顶操作符大于等待入栈的操作符时,**需要将操作符中的栈pop出栈顶, 并入栈到s2的中**
注意:待入栈还是需要和栈顶继续比较,如果待入栈大于符号栈栈顶的(满足4.2.1的条件),直接入栈。如果不满足还是需要执 行4.2.2中
4.3 遇到左括号是直接入栈中,但是待入栈操作符为右括号时,需要将操作符栈的中的操作符pop出来,并pop出的操作符加入到s2中,一直都遇到操作符栈中的左操作符,停止pop。注意:左右括号去除掉,不用保存在操作符栈s1中
-
重复第二步到第四步,一直到表达式扫描结束。
-
扫描结束后,将s1中剩余的运算符依次出栈并加入到s2中
-
依次弹出s2,s2出栈的逆序就是后缀表达式

将(3+4)* 5-6 转换成后缀表达式
| 扫描到的元素:(3+4)*5-6 | s2(栈底到栈顶 )存储数据 | s1(栈底到栈顶) 存储操作符 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|---|
| ( | ( | s1栈为空,直接将操作符加入栈中 | |
| 3 | 3 | ( | 遇到数值直接加入到栈中 |
| + | 3 | (+ | 如果直接有左括号,符号不用比较直接加入 |
| 4 | 3 4 | (+ | 遇到数值直接加入到栈中 |
| ) | 3 4 + | 遇到右括号,需要将s1 pop出来,一直到pop都了右括号 | |
| * | 3 4 + | * | s1栈为空,直接将操作符加入栈中 |
| 5 | 3 4 + 5 | * | 遇到数值直接加入到栈中 |
| - | 3 4 + 5 * | - | - 优 先级比 * 低,需要将s1 pop 出来,加入到s2中,一直比较直到待入栈大于s1的栈顶,待入可以入栈中 |
| 6 | 3 4 + 5 * 6 | - | 扫描完后 |
| 3 4 + 5 * 6 - | 将s1全部pop到s2中 |
(六)逆波兰计算器
目前是个位数据
创建类:PolandNotation
方法一:通过系统提供的栈stack来实现
将后缀表达式存储到数组中,就不需要使用index进执行指向,数组遍历更加便捷
package com.lcj.stack;import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Stack;/*** @Version 1.0* @Author:lcj* @Date:2022/8/30* @Content: 通过自带的stack来,实现逆波兰计算器*/
public class PolandNotation {public static void main(String[] args){//定义一个后缀表达式// (3+4)*5-6 =》 3 4 + 5 * 6 -String suffixExpression = "3 4 + 5 * 6 -"; //通过空格进行分割,便于后面分割//将"3 4 + 5 * 6 -" 放进ArrayList中List rpnList = getListString(suffixExpression);//计算结果为:int res = cal(rpnList);System.out.println("计算结果为:"+res);}//将后缀表达式放进到ArrayList中public static List getListString(String expression){//将表达式:expression进行分割String[] split = expression.split(" ");List list = new ArrayList<>();for (String s : split) {list.add(s);}return list;}//完成计算public static int cal(List ls){//创建栈Stack stack = new Stack();for (String item : ls) {if (item.matches("\\d+")){ // 用正则表达式进行判断多位数stack.push(item); // 数据直接入栈}else{ //为操作符//需要从stack中取出两个值,并将计算结果进入到stacke中int num2 = Integer.parseInt(stack.pop()); // 栈的数据是字符串的,需要转换为整数int num1 = Integer.parseInt(stack.pop());int res = 0;switch (item){case "*":res = num1 * num2;break;case "/":res = num1 / num2;break;case "-":res = num1 - num2;break;case "+":res = num1 + num2;break;default:System.out.println("目前只支持* + - /");break;}//将结果入栈stack.push(res+""); //将整数转换字符串,因为创建的是字符串的Stack}}//到最后stack中只有一个值,即结果return Integer.parseInt(stack.pop());}
}
注意:将数值类型的字符串转换为int : Interget.parseInt('1');
方法二:编写一个数组栈
自己编写一个数组栈,实现中缀表达式转换为后缀表达式,再通过后缀表达式的计算
ArrayList操作方法:
- add(data)
添加数据 - get(index)
获取值(eg:index 下标) - set(index,值)
修改值 - remove(index)
删除值
注意: 字符串比较大小,使用==是比较的字符串存储的内存位置是否相同,需要使用 equals进行比较
版本一:中缀表达式转为后缀表达式
实现中缀表达式转为后缀表达式
package com.lcj.stack;import com.sun.deploy.security.SelectableSecurityManager;
import sun.java2d.opengl.OGLRenderQueue;import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;/*** @Version 1.0* @Author:lcj* @Date:2022/8/30-17:00* @Content: 自己编写stack,实现:* 1. 将中缀表达式转换为后缀表达式,并输出后缀表达式* 2.计算后缀表达式的数据结果* 中缀表达式:(3+4)*5-6 ==> 后缀表达式:3 4 + 5 * 6 -*/
public class PolandNotationStack {public static void main(String[] args){stackDemon stack = new stackDemon(new ArrayList<>()); //链表:存储 后缀表达式的String exception = "(3+4)*5-6";
// String exception = "()";
// stack.push("1");
// stack.show();
// System.out.println( stack.transform("*"));//将中缀表达式 转成 后缀表达try {stackDemon suffix = transsuffix(exception, stack);suffix.show();System.out.println(suffix.show()); //后缀表达式的结果String suffixExpection = suffix.show();}catch (Exception e){System.out.println( e.getMessage());}}public static stackDemon transsuffix(String exception,stackDemon stack1){stackDemon stack = stack1;stackDemon operStack = new stackDemon(new ArrayList<>()); //存储操作符的String[] split = exception.split(""); //将表达式切分一个一个的//注意:后缀表达式是从左往右的,因此split切片出的数据,可以直接从左到右进行遍历for (String iteam : split) {// 1.如果数值直接加入if (iteam.matches("\\d+")){ //判断是否为多个数值,通过正则表达式stack.push(iteam); //数值存储到stack中}else{//2 判断operStack 中是否为空,直接将数据入栈,或者是左括号 (if (operStack.isEmpty() || iteam.equals("(")) {operStack.push(iteam);} else if (iteam.equals(")")){//将operStack进行pop,一直到(while (true){String oper = operStack.pop();
// if(operStack.pop() == "("){ // 该代码有问题,会删除多个operif (oper.equals("(")){break;}else{stack.push(oper); // 将操作符加入到栈中}}}else{//2.1 待入栈的操作符,比较栈顶操作符大小//2.1.1待入栈的操作符大于栈顶操作符,直接入栈if (operStack.compare(iteam, operStack.peek())){ //num1 待入栈的操作符 ,num2:栈顶的操作符,还有为空if (operStack.isEmpty() || operStack.compare(iteam, operStack.peek()) ){ //num1 待入栈的操作符 ,num2:栈顶的操作符operStack.push(iteam);}else if(!operStack.compare(iteam, operStack.peek())){ // 2.1.2 待入栈的操作符小于 等于 栈顶操作符,将operStack的栈顶pop出来,保存在stack中
// stack.push(operStack.pop());//待入栈的符号需要再一次比较栈顶操作符boolean loop = true;while (loop) {if (!operStack.isEmpty() && !operStack.compare(iteam, operStack.peek())) { // 不能为空,空了也没有数据stack.push(operStack.pop()); //一直将operStack加入到stack中去}else{loop = false;operStack.push(iteam); //将待入栈的操作符入栈}}}}}}//遍历完成后,将operStack中所有全部加入到stack中// System.out.println("测试"+operStack.show());String show = operStack.show();String[] s = show.split(" ");for (String s1 : s) {stack.push(s1);}return stack;}
}//创建stack
class stackDemon{//创建toppublic int top = -1; // 初始位置为:-1//数组Listprivate List stack;public stackDemon(List stack) {this.stack = stack;}//判断是否为空public boolean isEmpty(){return stack.size() == 0; //大小为0}//数据入栈public void push(String key){stack.add(key);}//数据出栈public String pop(){String value = "";//判断是否为空if (stack.size()!= 0) {value = stack.get(stack.size()-1);stack.remove(stack.size() - 1); // 删除最后一个数据}return value;}//展示数据public String show(){int i =0;String suffix = "";for (String s : stack) {if(i == 0){
// System.out.print(""+s);suffix += s;i++;continue;}
// System.out.print(" "+s);suffix += " "+s;}return suffix;}// 展示栈顶的元素public String peek(){if (isEmpty()){throw new RuntimeException("栈为空");}return stack.get(stack.size()-1);}//操作符转换,将操作符转换成数值,便于操作符的比较优先级public int transform(String num1){int grand = 0;switch (num1){case "+":grand = 0;break;case "-":grand = 0;break;case "*":grand = 1;break;case "/":grand = 1;break;default:grand = -1 ; // 目的是为了让待入栈的操作符和操作符进行比较,类似于 栈顶是( 左括号的情况break;}return grand;}//比较操作符的大小public boolean compare(String num1,String num2){ //num1 :为待入栈的操作符 num2:为入栈的操作符return transform(num1) > transform(num2); //待入栈的操作符大于栈顶操作符}//计算public int cal(int num1,int num2,String ch){int res = 0;switch (ch){case "+":res = num1 + num2;break;case "-":res = num1 - num2;break;case "*":res = num1 * num2;break;case "/":res = num1 / num2;break;}return res;}
}
版本二:功能完整实现
package com.lcj.stack;import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;/*** @Version 1.0* @Author:lcj* @Date:2022/8/30-17:00* @Content: 自己编写stack,实现:* 1. 将中缀表达式转换为后缀表达式,并输出后缀表达式* 2.计算后缀表达式的数据结果* 中缀表达式:(3+4)*5-6 ==> 后缀表达式:3 4 + 5 * 6 -*/
public class PolandNotationStack {public static void main(String[] args){stackDemon stack = new stackDemon(new ArrayList<>()); //链表:存储 后缀表达式的String exception = "(3+4)*5-6";String suffixExpection = "";
// String exception = "()";
// stack.push("1");
// stack.show();
// System.out.println( stack.transform("*"));//将中缀表达式 转成 后缀表达try {stackDemon suffix = transsuffix(exception, stack);suffix.show();System.out.println(suffix.show()); //后缀表达式的结果suffixExpection = suffix.show();}catch (Exception e){System.out.println( e.getMessage());}//结果为:suffixCal(suffixExpection);}//将后缀表达式进行计算结果public static void suffixCal(String su){String exp = su; //后缀表达式String[] s = exp.split(" ");int res = 0; //结果值ArrayList list = new ArrayList();for (String s1 : s) {//1.遇到数值直接将数值输入到list中if (s1.matches("\\d+")){ //用正则表达式中判断字符舒是否为数值list.add(s1);}else{ //不为数值时,遇到操作符需要将数值取出来int num2 = Integer.parseInt(list.get(list.size()-1));int num1 = Integer.parseInt(list.get(list.size()-2));switch (s1){case "+":res = num1 + num2;break;case "-":res = num1 - num2;break;case "*":res = num1 * num2;break;case "/":res = num1 / num2;break;}list.add(""+res); //将中间结果保存在list中}}System.out.println(res);}//实现将中缀表达式转换为后缀表达式中public static stackDemon transsuffix(String exception,stackDemon stack1){stackDemon stack = stack1;stackDemon operStack = new stackDemon(new ArrayList<>()); //存储操作符的String[] split = exception.split(""); //将表达式切分一个一个的//注意:后缀表达式是从左往右的,因此split切片出的数据,可以直接从左到右进行遍历for (String iteam : split) {// 1.如果数值直接加入if (iteam.matches("\\d+")){ //判断是否为多个数值,通过正则表达式stack.push(iteam); //数值存储到stack中}else{//2 判断operStack 中是否为空,直接将数据入栈,或者是左括号 (if (operStack.isEmpty() || iteam.equals("(")) {operStack.push(iteam);} else if (iteam.equals(")")){//将operStack进行pop,一直到(while (true){String oper = operStack.pop();
// if(operStack.pop() == "("){ // 该代码有问题,会删除多个operif (oper.equals("(")){break;}else{stack.push(oper); // 将操作符加入到栈中}}}else{//2.1 待入栈的操作符,比较栈顶操作符大小//2.1.1待入栈的操作符大于栈顶操作符,直接入栈if (operStack.compare(iteam, operStack.peek())){ //num1 待入栈的操作符 ,num2:栈顶的操作符,还有为空if (operStack.isEmpty() || operStack.compare(iteam, operStack.peek()) ){ //num1 待入栈的操作符 ,num2:栈顶的操作符operStack.push(iteam);}else if(!operStack.compare(iteam, operStack.peek())){ // 2.1.2 待入栈的操作符小于 等于 栈顶操作符,将operStack的栈顶pop出来,保存在stack中
// stack.push(operStack.pop());//待入栈的符号需要再一次比较栈顶操作符boolean loop = true;while (loop) {if (!operStack.isEmpty() && !operStack.compare(iteam, operStack.peek())) { // 不能为空,空了也没有数据stack.push(operStack.pop()); //一直将operStack加入到stack中去}else{loop = false;operStack.push(iteam); //将待入栈的操作符入栈}}}}}}//遍历完成后,将operStack中所有全部加入到stack中// System.out.println("测试"+operStack.show());String show = operStack.show();String[] s = show.split(" ");for (String s1 : s) {stack.push(s1);}return stack;}
}//创建stack
class stackDemon{//创建toppublic int top = -1; // 初始位置为:-1//数组Listprivate List stack;public stackDemon(List stack) {this.stack = stack;}//判断是否为空public boolean isEmpty(){return stack.size() == 0; //大小为0}//数据入栈public void push(String key){stack.add(key);}//数据出栈public String pop(){String value = "";//判断是否为空if (stack.size()!= 0) {value = stack.get(stack.size()-1);stack.remove(stack.size() - 1); // 删除最后一个数据}return value;}//展示数据public String show(){int i =0;String suffix = "";for (String s : stack) {if(i == 0){
// System.out.print(""+s);suffix += s;i++;continue;}
// System.out.print(" "+s);suffix += " "+s;}return suffix;}// 展示栈顶的元素public String peek(){if (isEmpty()){throw new RuntimeException("栈为空");}return stack.get(stack.size()-1);}//操作符转换,将操作符转换成数值,便于操作符的比较优先级public int transform(String num1){int grand = 0;switch (num1){case "+":grand = 0;break;case "-":grand = 0;break;case "*":grand = 1;break;case "/":grand = 1;break;default:grand = -1 ; // 目的是为了让待入栈的操作符和操作符进行比较,类似于 栈顶是( 左括号的情况break;}return grand;}//比较操作符的大小public boolean compare(String num1,String num2){ //num1 :为待入栈的操作符 num2:为入栈的操作符return transform(num1) > transform(num2); //待入栈的操作符大于栈顶操作符}//计算public int cal(int num1,int num2,String ch){int res = 0;switch (ch){case "+":res = num1 + num2;break;case "-":res = num1 - num2;break;case "*":res = num1 * num2;break;case "/":res = num1 / num2;break;}return res;}
}
第五章:递归
(一)递归介绍
应用场景:迷宫问题(回溯)、递归(recursion)、汉罗塔、阶乘问题、8皇后问题
- 算法中也会使用递归 eg:快排、归并排序、二分查找、分治算法
递归:方法自己调用自己,每次调用时传入不同的变量,有助于解决复杂的问题
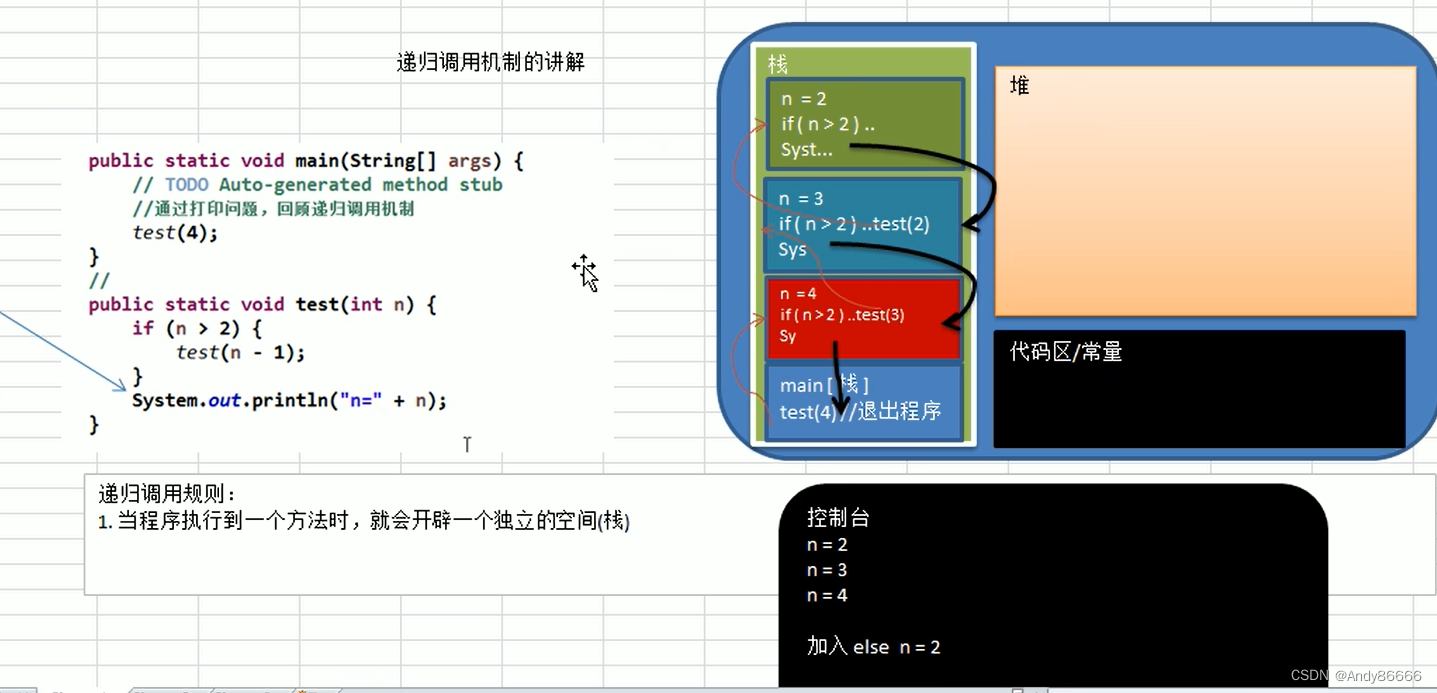
JVM组成:栈、堆、代码区(包括常量)
递归调用规则:
- 当程序执行到一个方法时,就会开辟一个独立的空间(栈空间)
- 方法的局部变量是独立的,不会相互影响的
- 如果方法中使用的是引用类型变量(eg:数组),就会共享该引用类型的数据
- 递归必须向退出的递归条件逼近,否则就死循环了
- 当一个方法执行完毕后,或者遇到了return,就会返回,遵守谁调用,就将结果返回给谁,同时当方法执行完毕或者返回时,该方法也就执行完毕
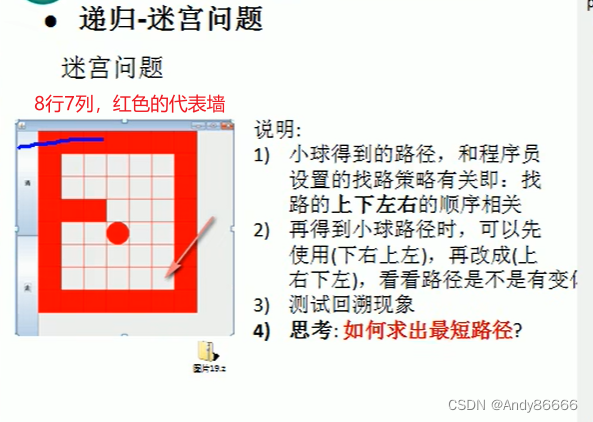
(二)迷宫回溯问题分析与实现
迷宫回溯问题:
创建package:com.lcj.recursion
创建class:MiGong
package com.lcj.recursion;/*** @Version 1.0* @Author:lcj* @Date:2022/9/2-21:17* @Content:*/
public class MiGong {public static void main(String[] args){//先创建一个二维数组,模型迷宫//地图为8行7列的int[][] map = new int[8][7];//用1来代表是墙//上下墙for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++) {map[0][i] = 1;map[7][i] = 1;}//左右为墙for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {map[i][0] = 1;map[i][6] = 1;}//创建墙map[3][1] = 1;map[3][2] = 1;// 找路方法setWay(map,1,1);//输出地图for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < 7; j++) {System.out.print(map[i][j]+" ");}System.out.println();}
// System.out.println(map[1].length);}//使用递归回溯小球/** 1、map :表示地图* 2、i,j 表示起始位置* 3、map[7][6] 为终点* 4、当map[i][j] 为 0表示 该节点没有走过,为1表示墙,2表示通路,3表示该节点已经走过,但是走不通* */public static boolean setWay(int[][] map,int i,int j){if(map[6][5] == 2){return true;}else{if (map[i][j] == 0){ // 当前的节点没有走过//按照的策略为:下 -> 右 ->上 ->左map[i][j] = 2;if (setWay(map,i+1,j)){return true;}else if(setWay(map,i,j+1)){return true;}else if(setWay(map,i-1,j)){return true;}else if(setWay(map,i,j-1)){return true;}else {//说明该点是走不通的map[i][j] = 3;return false;}}else { //该map[i][j]节点 不为0,可能是1(墙),2(已经走过),3(死路)return false; //不要再走}}}
}
注意:谁调用,谁用值
(三)八皇后问题(回溯问题)
1、介绍
任意两个皇后都不能同时处于同一行、同一列或者同一斜线


用一维数组解决棋盘位置:eg:arr[8] = {0,4,7,5,2,6,1,3} // arr对应的下标表示第几行,arr[i] = val ,val表示第i+1个皇后,放在第i+1行的第val+1列中
2、代码实现
创建class:Queue8
package com.lcj.recursion;/*** @Version 1.0* @Author:lcj* @Date:2022/9/5-21:05* @Content:*/
public class Queue8 {int max = 8; //皇后的个数//定义数值array,保存皇后放置位置的结果int[] array = new int[max];static int count = 0;public static void main(String[] args){//测试Queue8 queue8 = new Queue8();queue8.check(0); //第0行第0列开始System.out.printf("个数为:%d",count);}//编写一个方法,放置第n个皇后private void check(int n){if(n == max){ // n = 8print(); //输出结果return; //已经将结果放好}//依次放入皇后,并判断是否冲突for (int i = 0; i < max; i++) {//先把当前这个皇后n,放到该行的第1列中array[n] = i;if(judge(n)){ //不冲突check(n+1);}//如果冲突会跳转到array[n] = i 上面的,将n往后继续移动}}//判断是否冲突,查看当我们放置第n个皇后是否和前面的已经摆放的皇后冲突//同行(不需要判断,因为每次一行只有一个数值)、同列、同斜线private boolean judge(int n){for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {//array[i] == array[n] 判断是否在同一列/*Math.abs(n-i) ==Math.abs(array[n]-array[i]) 主要是判断是否在同一条斜线上Math.abs 是 绝对值,n-i 是行之差,array[n]-array[i] 是列之差,值相同说明是斜线* */if (array[i] == array[n] || Math.abs(n-i) ==Math.abs(array[n]-array[i])){return false;}}return true; // 不冲突}//将皇后摆放的位置输出来private void print(){for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {System.out.print(array[i] + " ");}System.out.println(); //换行count++;}
}
第六章:排序算法
一、排序算法
-
排序算法(
sort Algorithm):将数据按着一定的顺序进行排序的过程。 -
排序的分类:
内部排序:将数据加载到内存中进行排序外部排序法:数量大的时候,无法加载到内存中时,用外部存储进行排序
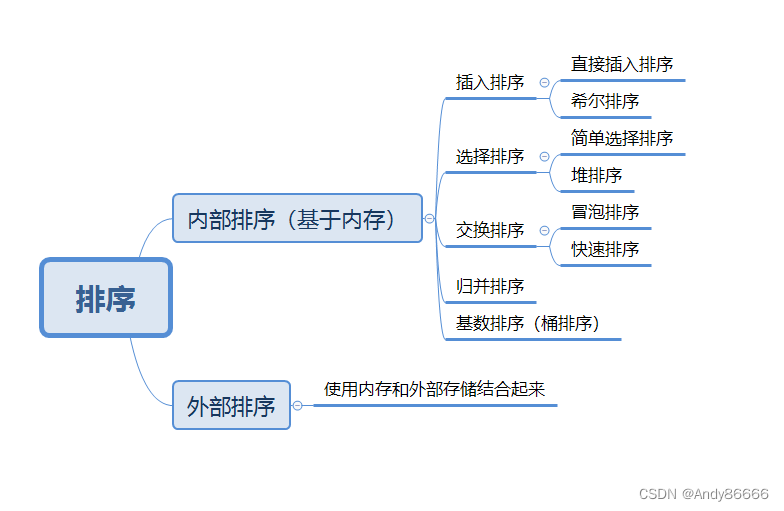
直接插入、简单选择、冒泡排序法必须要掌握
二、算法的时间复杂度
(一)算法的评判方法
-
事后统计的方法
在计算运行后,再计算运行时间
- 有问题需要运行程序,但是要受到计算机硬件性能的影响
- 运行程序可能需要很长的时间
-
事前估算的方法——时间复杂度
通过分析算法的
时间复杂度来判断那个算法比较优秀
(二)时间复杂度
1、时间频度
时间频数:一个算法花费时间与算法中语句执行次数成正比,即语句多花费时间多。
-
语句频数或者时间频数,记作T(n):算法中语句执行的次数
特点:
- 忽略时间频数中的常数项

-
忽略时间频数中低次项
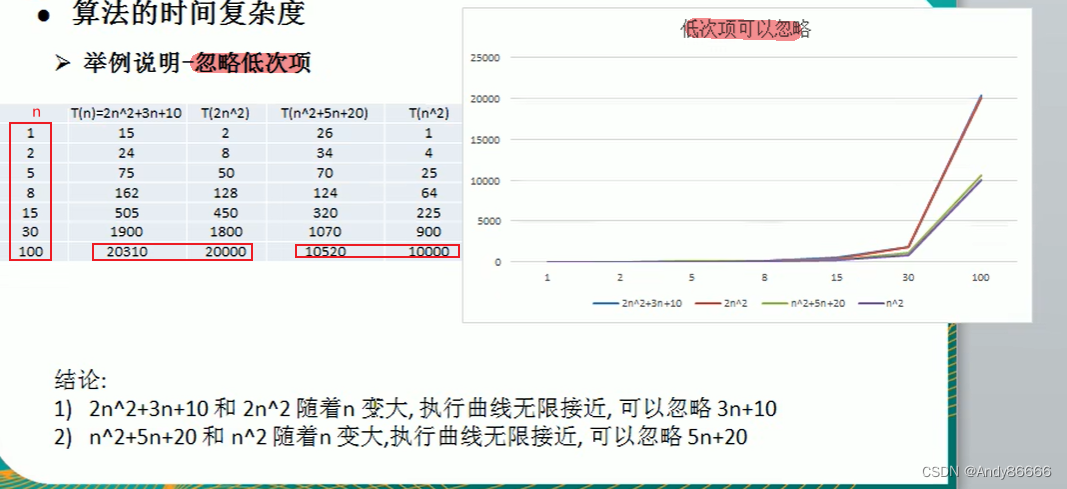
-
忽略时间频数的系数
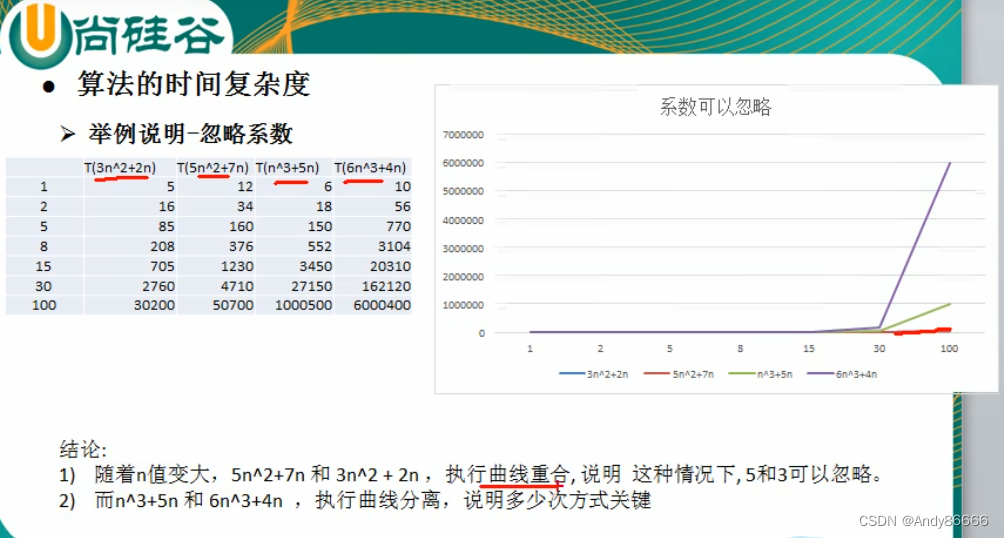
2 、时间复杂度
时间复杂度:
2.1 算法中基本操作语句的重复执行次数是问题规模n的某个函数,用T(n)表示(时间频数),若有某个辅助函数f(n),使得当n趋近于无穷大时,T(n)/f(n)的极限值为不等于零的常数,则称为f(n)是T(n)的同数量级函数。记作T(n)=O (f(n)) ,称O(f(n))为算法的渐进时间复杂度,简称时间复杂度。

T(n)=3n2+3n+1T(n)=3n^2+3n+1T(n)=3n2+3n+1 ==> T(n)=n2T(n)=n^2T(n)=n2
f(n)=n2f(n)=n^2f(n)=n2
结果为:
T(n)/f(n)=O(n2)T(n)/f(n)=O(n^2)T(n)/f(n)=O(n2)
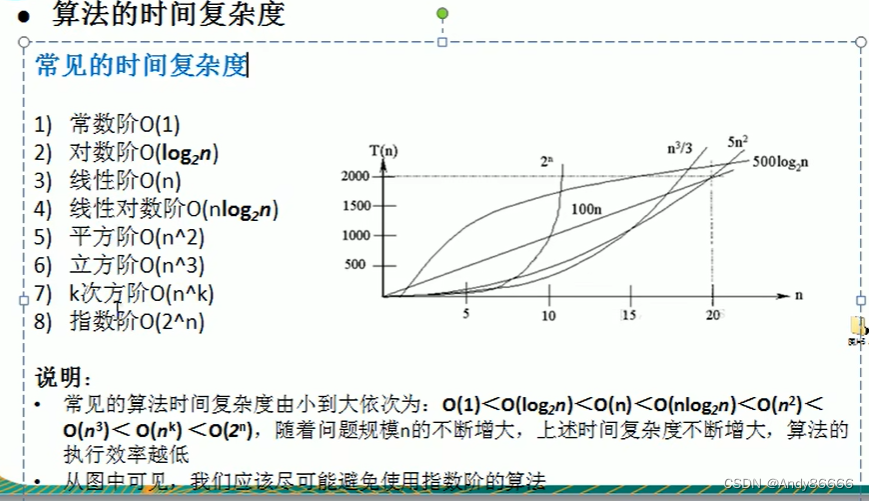
O(1) 常数阶O(1)O(1)O(1) :没有循环代码 平均时间复杂度:所有可能的输入实例的时间平均之后的算法运行时间 最坏时间复杂度:算法运行最坏的时间复杂度,作用:相对于算法的运行时间界限,不会出现最坏的结果 创建package: 创建class: 升级: 如果在排序中,如果数据已经排序完成了,直接中止排序输出结果 测试:将数量达到8万条时,运行时间较长 选择排序:是从待排序的的数据中,按指定规则选出某一元素,再依次交换位置后达到排序的目的。 案例:将 创建class: 时间复杂度:O(n2)O(n^2)O(n2) 注意:先将算法简单化,再将算法复杂化 ,一部分一部分进行实现 插入排序属于内部排序,通过将要排序的数据插入到指定位置来达到排序的 创建class: 自己实现: 版本一: 版本二: 测试: 希尔排序是经过改进之后的一个更高效的版本,也称为缩小增量排序 基本思想: 测试运行时间:1S 动画演示1 动画演示2 快排算法是对冒泡排序算法的升级。 基本思想:通过一趟排序将数据,将排序数据分成两部分,注意其他一部分要比另一部小,然后另外两部分也根据这样方式进行排序,最终实现排序数据有序。(可以采取递归实现) 压力测试: 运行时间: 将大问题分成小问题来解决 归并排序(merge-sort)是利用归并的思想实现排序,采用经典的 将 创建class: 基数排序( 思路: eg:{53,3,542,748,14,214} 进行升序排序 创建类: 注意事项:数据量特别大的时候会占用大量的内存 O(1)





(三)平均时间复杂度
1、平均时间复杂度
2、最坏时间复杂度

(四)空间复杂度——空间换时间

三、冒泡排序算法(bubble sorting)
(一)代码实现
com.lcj.sortBubble Sortingpackage com.lcj.sort;import java.lang.reflect.Array;
import java.util.Arrays;/*** @Version 1.0* @Author:lcj* @Date:2022/9/13-21:10* @Content: 创建冒泡排序法*/
public class BubblerSorting {public static void main(String[] args){int arr[] = {3,9,-1,10,-2};for(int i=0; ipackage com.lcj.sort;import java.lang.reflect.Array;
import java.util.Arrays;/*** @Version 1.0* @Author:lcj* @Date:2022/9/13-21:10* @Content: 创建冒泡排序法*/
public class BubblerSorting {public static void main(String[] args){
// int arr[] = {3,9,-1,10,-2};int arr[] = {1,3,2,4,5};boolean flage = false; // 目的:判断数据是否交换,如果没有发生交换说明数据已经排序完成for(int i=0; ipackage com.lcj.sort;import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Arrays;/*** @Version 1.0* @Author:lcj* @Date:2022/9/13-21:10* @Content: 创建冒泡排序法*/import java.util.Date;public class BubblerSorting {public static void main(String[] args){
// int arr[] = {3,9,-1,10,-2};// 测试当数据量的大的时候,执行时间的变化int[] arr = new int[80000];//添加数据for(int i=0; i<80000 ;i++){arr[i] = (int)(Math.random()*80000) ; // 生成[0,1) * 80000 范围为:[0,80000)}Date date1 = new Date(); //生成时间SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss"); //将时间进行格式化
// System.out.println(date1);System.out.println("开始时间:"+simpleDateFormat.format(date1));for(int i=0; i四、选择排序算法
(一)选举排序介绍

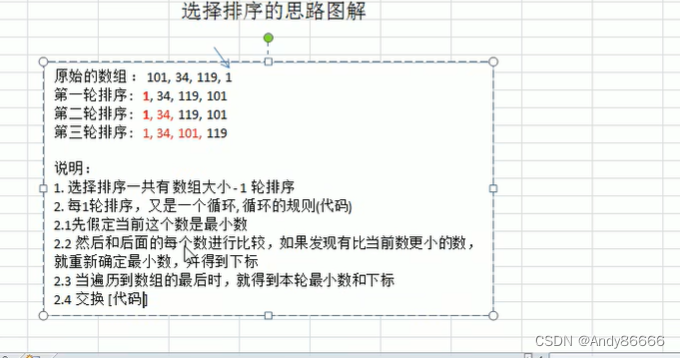
(二)代码实现
101,34,119,1,通过选择排序从==低到高进行排序==SelectSortpackage com.lcj.sort;import java.util.Arrays;/*** @Version 1.0* @Author:lcj* @Date:2022/9/14-20:59* @Content:选择排序实现*/
public class SelectSort {public static void main(String[] args){int[] arr1 = new int[]{101, 34, 119, 1};selectSort(arr1);}//选择排序的方法public static void selectSort(int[] arr){int temp =0;for (int i=0;i五、插入排序算法
(一)介绍

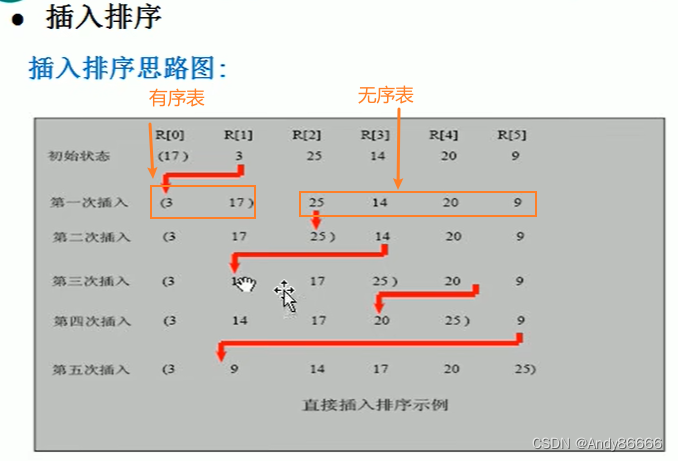
(二)代码实现
IndexSortpackage com.lcj.sort;import java.util.Arrays;/*** @Version 1.0* @Author:lcj* @Date:2022/9/16-22:06* @Content: 自己实现插入排序 :从小到大*/
public class IndexSort {public static void main(String[] args){int arr[] = {17,3,25,14,20,9};indexSorting(arr);}public static void indexSorting(int[] arr){int index = 0;//待插入数据的下标int indexNum = 0; //待插入数据for(int i=1;ipackage com.lcj.sort;import java.util.Arrays;/*** @Version 1.0* @Author:lcj* @Date:2022/9/16-22:06* @Content: 自己实现插入排序 :从小到大*/
public class IndexSort {public static void main(String[] args){int arr[] = {17,3,25,14,20,9};indexSorting(arr);}public static void indexSorting(int[] arr){int index = 0;//待插入数据的下标int indexNum = 0; //待插入数据for(int i=1;ipackage com.lcj.sort;import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Date;/*** @Version 1.0* @Author:lcj* @Date:2022/9/16-22:06* @Content: 自己实现插入排序 :从小到大*/
public class IndexSort {public static void main(String[] args){
// int arr[] = {17,3,25,14,20,9};int[] arr = new int[80000];for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {arr[i] = (int)(Math.random()*arr.length);}Date date1 = new Date();SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss");System.out.println("开始时间"+simpleDateFormat.format(date1));indexSorting(arr);Date date2 = new Date();
// SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss");System.out.println("开始时间"+simpleDateFormat.format(date2));}public static void indexSorting(int[] arr){int index = 0;//待插入数据的下标int indexNum = 0; //待插入数据for(int i=1;i六、希尔排序算法(shell)

(一)希尔排序算法介绍
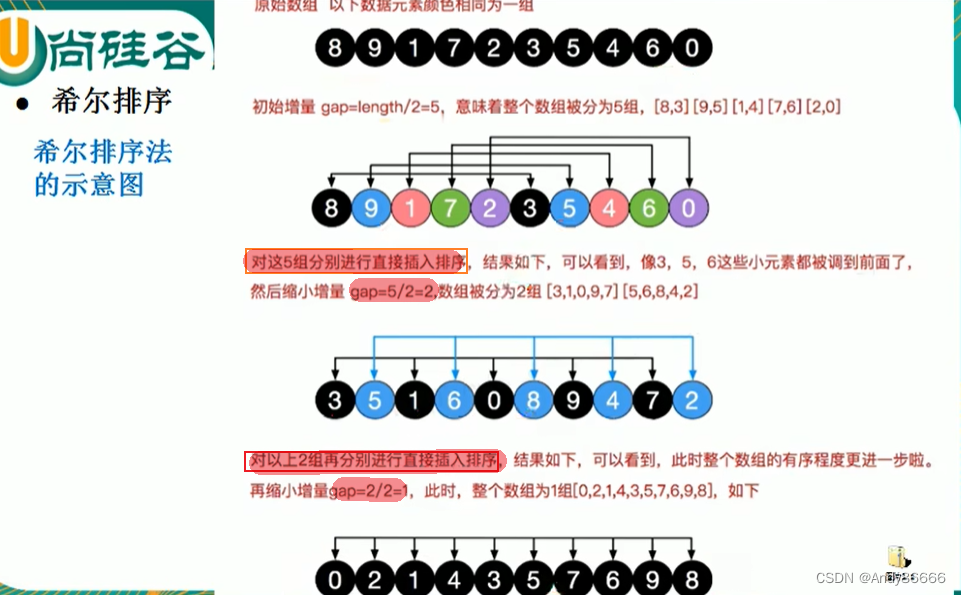

(二)代码实现
方法一:交换法
package com.lcj.sort;import java.util.Arrays;/*** @Version 1.0* @Author:lcj* @Date:2022/9/19-10:40* @Content:希尔排序算法,自己排序实现*/
public class ShellSort {public static void main(String[] args){int[] arr = {8,9,1,7,2,3,5,4,6,0};shellSort(arr);}//使用逐步推导的过程进行实现代码public static void shellSort(int[] arr){int temp = 0;for(int grap=arr.length/2; grap > 0; grap/=2){ // 分组的次数 5,2,1
// System.out.println(grap); //测试for(int i=grap;i方法二:移动法——插入法
package com.lcj.sort;import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Date;/*** @Version 1.0* @Author:lcj* @Date:2022/9/19-10:40* @Content:希尔排序算法,自己排序实现*/
public class ShellSort {public static void main(String[] args){int[] arr = {8,9,1,7,2,3,5,4,6,0};shellSort(arr); // 移动式}//使用逐步推导的过程进行实现代码public static void shellSort(int[] arr){int temp = 0;for(int grap=arr.length/2; grap > 0; grap/=2){ // 分组的次数 5,2,1
// System.out.println(grap); //测试for(int i=grap;ipackage com.lcj.sort;import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Date;/*** @Version 1.0* @Author:lcj* @Date:2022/9/19-10:40* @Content:希尔排序算法,自己排序实现*/
public class ShellSort {public static void main(String[] args){//int[] arr = {8,9,1,7,2,3,5,4,6,0};int arr[] = new int[80000];for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {arr[i] = (int)(Math.random()*arr.length);}Date date1 = new Date();SimpleDateFormat simple = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");String dateString = simple.format(date1);System.out.println(dateString);shellSort(arr); // 移动式Date date2 = new Date();String date2String = simple.format(date2);System.out.println(date2String);}//使用逐步推导的过程进行实现代码public static void shellSort(int[] arr){int temp = 0;for(int grap=arr.length/2; grap > 0; grap/=2){ // 分组的次数 5,2,1
// System.out.println(grap); //测试for(int i=grap;i七、快排算法——Quicksort
(一)快排算法介绍
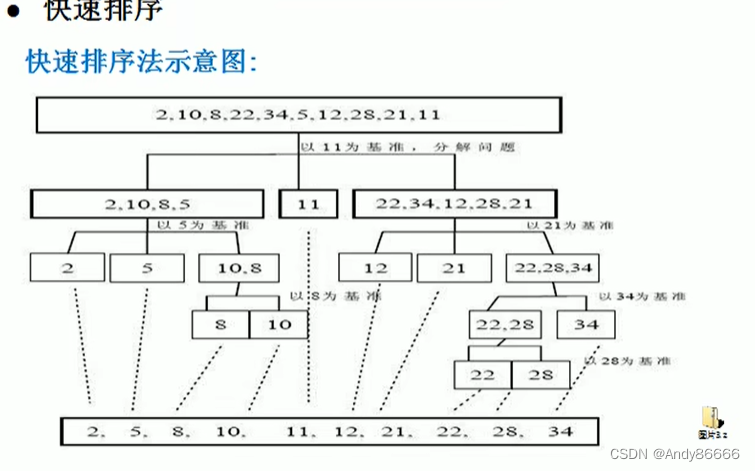
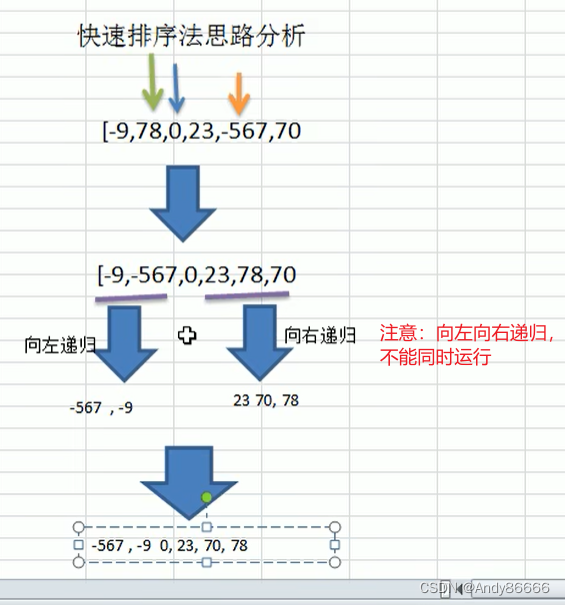
(二)代码实现
package com.lcj.sort;import java.util.Arrays;/*** @Version 1.0* @Author:lcj* @Date:2022/9/21-22:08* @Content:*/
public class QuickSort {public static void main(String[] arg){int arr[] = {-9,78,0,23,-567,70};quickSort(arr,0, arr.length-1);}public static void quickSort(int[] arr,int left,int right){int l = left; //左下标int r = right; //右下标int pivot = arr[(left+right)/2]; //取左右的中间值,作为基准,左边是全部小于int temp = 0;//临时变量while(l < r){//只要arr[l] 小于 pivot ,将l向右移动一格,只要arr[l] > pivot就终止移动if(arr[l] < pivot){l+=1;}//只要arr[r] 大于 pivot ,将r向左移动一格,只要arr[r] < pivot就终止移动if(arr[r] > pivot ){r -=1;}//如果l大于r说明privot 左边的数据已经是最小的了,右边的数据是最大的了if(l >= r){break;}//交换temp = arr[l];arr[l] = arr[r];arr[r] = temp;//如果交换完后,发现这个arr[l] == pivot 值,相等于r--,前移if(arr[l] == pivot){ //注意:r指向的是交换的元素,如果不说不进行后移的话,会死循环r -=1;}//如果交换完后,发现这个arr[r] == pivot 值,相等于l++,后移if(arr[r] == pivot){l +=1;}}// 如果l==r,必须l++,r--,否则出现栈溢出,即死循环if (l==r){l += 1;r -= 1;}//向左递归if (left < r){quickSort(arr,left,r);}//向右递归,if (l < right){quickSort(arr,l,right);}System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));}
}
package com.lcj.sort;import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Date;/*** @Version 1.0* @Author:lcj* @Date:2022/9/21-22:08* @Content:*/
public class QuickSort {public static void main(String[] arg){
// int arr[] = {-9,78,0,23,-567,70};int[] arr = new int[80000];for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {arr[i] = (int)(Math.random()*80000);}Date date1 = new Date();SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss");System.out.println(simpleDateFormat.format(date1));quickSort(arr,0, arr.length-1);Date date = new Date();System.out.println(simpleDateFormat.format(date));}public static void quickSort(int[] arr,int left,int right){int l = left; //左下标int r = right; //右下标int pivot = arr[(left+right)/2]; //取左右的中间值,作为基准,左边是全部小于int temp = 0;//临时变量while(l < r){//只要arr[l] 小于 pivot ,将l向右移动一格,只要arr[l] > pivot就终止移动if(arr[l] < pivot){l+=1;}//只要arr[r] 大于 pivot ,将r向左移动一格,只要arr[r] < pivot就终止移动if(arr[r] > pivot ){r -=1;}//如果l大于r说明privot 左边的数据已经是最小的了,右边的数据是最大的了if(l >= r){break;}//交换temp = arr[l];arr[l] = arr[r];arr[r] = temp;//如果交换完后,发现这个arr[l] == pivot 值,相等于r--,前移if(arr[l] == pivot){ //注意:r指向的是交换的元素,如果不说不进行后移的话,会死循环r -=1;}//如果交换完后,发现这个arr[r] == pivot 值,相等于l++,后移if(arr[r] == pivot){l +=1;}}// 如果l==r,必须l++,r--,否则出现栈溢出,即死循环if (l==r){l += 1;r -= 1;}//向左递归if (left < r){quickSort(arr,left,r);}//向右递归,if (l < right){quickSort(arr,l,right);}
// System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));}
}
2022-09-269 04:37:14
2022-09-269 04:37:14
八、归并排算法
(一)介绍
分治(divide-and-conquer)策略(分治问题是将问题:1.分成一些小的问题,然后递归求解,2.治:将分阶段得到的各答案“修补”在一起,即分而治之)84571362 按照从小到大进行排序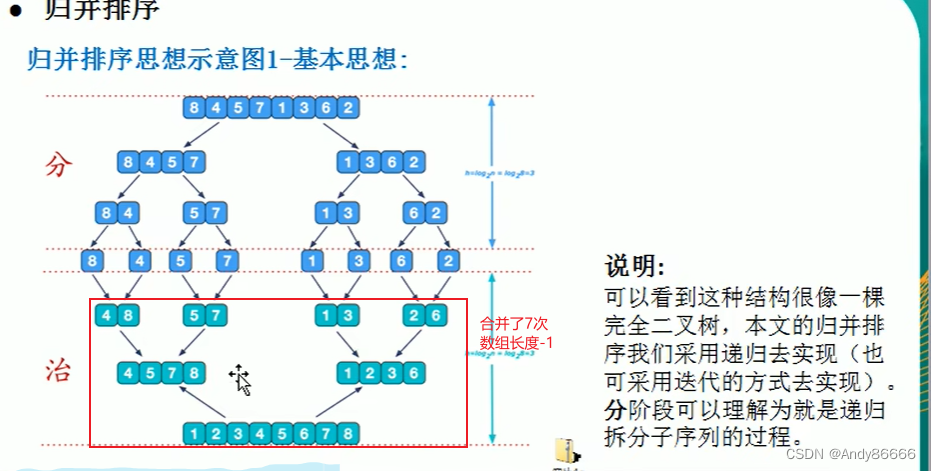
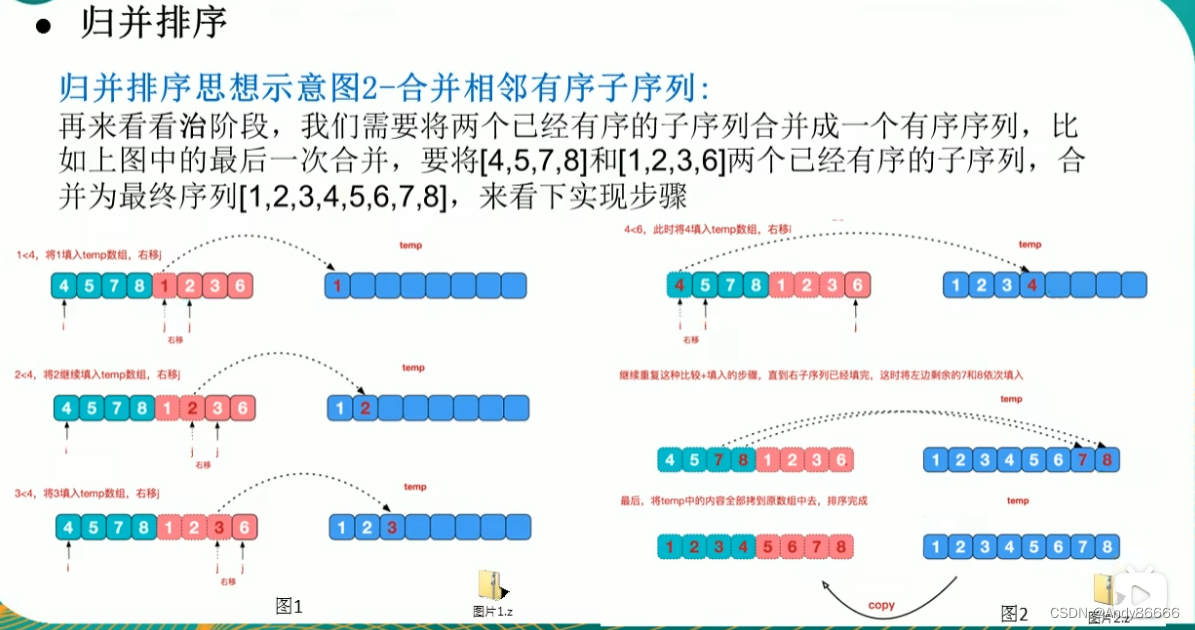
(二)代码实现
MergetSortpackage com.lcj.sort;import java.util.Arrays;/*** @Version 1.0* @Author:lcj* @Date:2022/10/13-22:09* @Content:归并排序算法*/
public class MergeSort {public static void main(String[] args) {int arr[] = {8, 4, 5, 6, 1, 3, 6, 2};int[] temp = new int[arr.length];mergeSort(arr,0,arr.length - 1,temp);System.out.println("归并排序后"+ Arrays.toString(arr));}//分+合的算法public static void mergeSort(int[] arr,int left,int right,int[] temp){if(left < right){int mid = (left + right)/2;//向左进行递归mergeSort(arr,left,mid,temp);//向右进行递归mergeSort(arr,mid+1,right,temp);//合并merg(arr,left,mid,right,temp);}}//合并方法/** arr:数据数值* left:左边有序数列的初始索引* right:右边有序数列的最右边索引* mid :是中间索引* tmp:临时数组* */public static void merg(int[] arr,int left,int mid,int right,int[] tmp){int i = left; //初始化最左边的索引int j = mid +1 ;int t = 0 ; //临时数组的初始索引//第一步:先将左右两边(),按照从小到的大顺序将数据放进到临时数组中,直到一边处理完成// 注意:左右两边的数据分别是有序的while(i<=mid && j<=right){// 如果左边的数据小于右边时,将左边数据移动到tmp中if (arr[i] <= arr[j]){tmp[t] = arr[i];t += 1; //将t往后进行移动i += 1; // 将i往后进行移动}else{ // 将右边的数据大于左边的数据时tmp[t] = arr[j];t += 1; // 将t往后进行移动j += 1;}}// 第二步:将剩下的数组依次放进到临时数组中while(i <= mid){ // 左边数据剩余tmp[t] = arr[i];i ++;t ++;}while(j <= right){ // 右边数据剩余tmp[t] = arr[j];j ++;t ++;}// 第三步:将临时数组数据放进arr中t =0;int tempLeft = left;while(tempLeft <= right){arr[tempLeft] = tmp[t];t += 1;tempLeft +=1;}}
}
九、基数排序
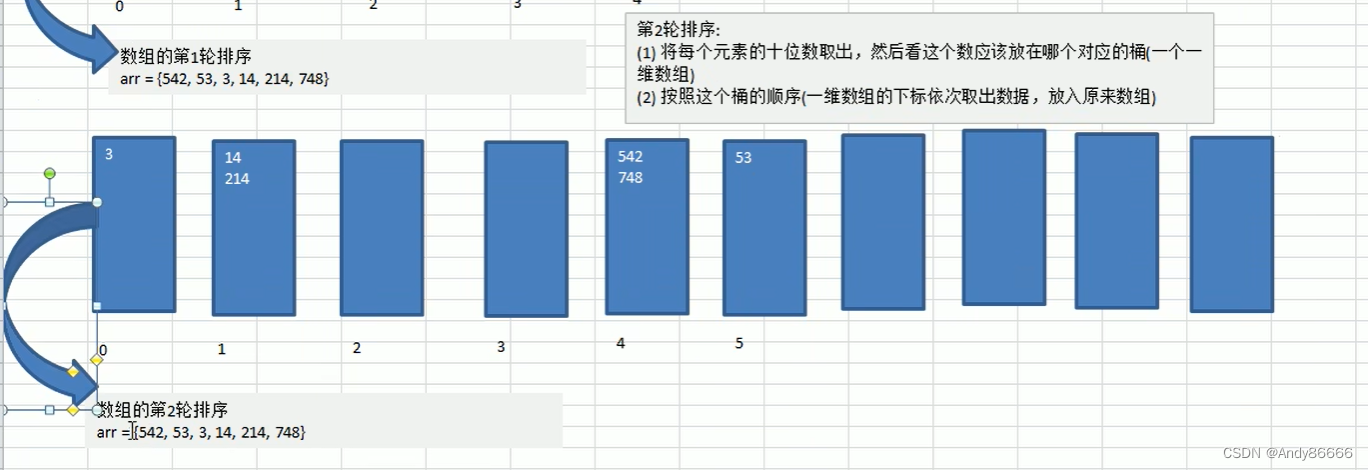
(一)基础知识
radix sort)属于“分配式排序” ,或者称为“桶子排序”。主要是通过将数据的个位、十位等位数放进行相应的“桶”中,来达到排序的效果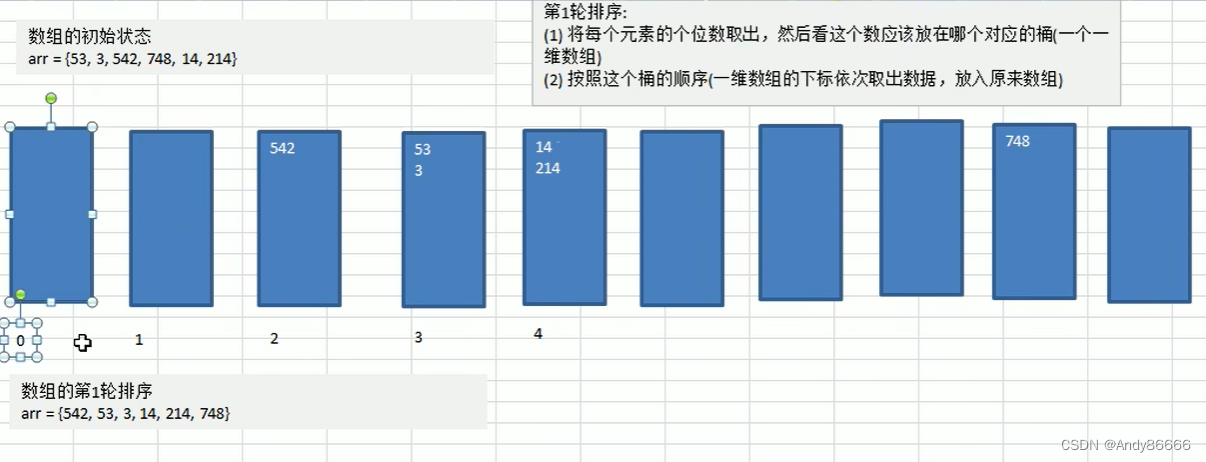
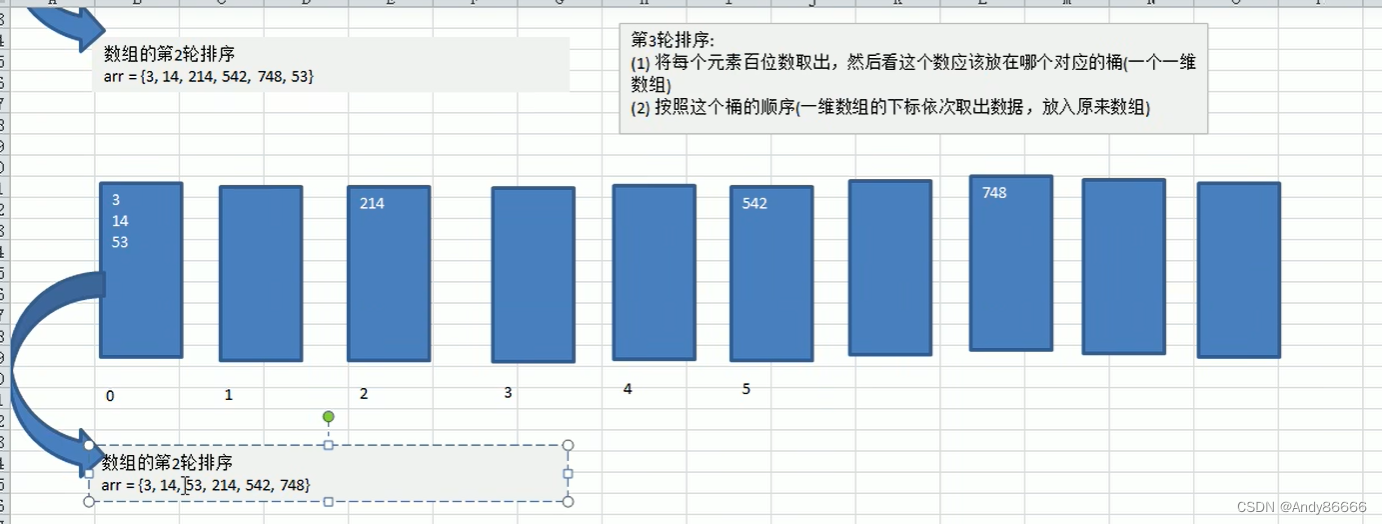
(二)代码实现
RadixSortpackage com.lcj.sort;import java.util.Arrays;/*** @Version 1.0* @Author:lcj* @Date:2022/10/16-10:44* @Content:基数排序* 主要思路:* 1. 创建对应的10个桶,即十个数组,分别代表的是从0-9的数字* 2. 获取个位、十位等数据,将数据对应放进到数组中,并数据读取到原来的数组中,进行排序* 3. 重复第2步骤,循环次数为数据中最大值的个数* */
public class RadixSort {public static void main(String[] args){int arr[] = {53,3,42,748,14,214};radixSort(arr);System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));}//基数排序方法public static void radixSort(int[] arr){//1.通过创建二维数据,来表示桶,长度为arr.length来避免数据溢出的问题//通过空间换时间int[][] bucket = new int[10][arr.length];//记录每一个桶中的数量,并不是所有的桶中有数据// eg:bucketElementCounts[1] 存储的是bucket[1]中的数据个数int[] bucketElementCounts = new int[10];//2.获取到最大值的长度int max = arr[0];for(int i = 0;i < arr.length-1;i++){if(max <= arr[i]){max = arr[i];}}int maxLength = (max+"").length(); //最大值的长度,决定循环的次数// 4. 循环执行for(int k = 0 ,n=1;k< maxLength ;k++,n *= 10) {// 3,获取数据循环for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {//遍历所有数据,获取位数//取除元素的位数int digitOfELement = arr[i]/n % 10;bucket[digitOfELement][bucketElementCounts[digitOfELement]] = arr[i];bucketElementCounts[digitOfELement]++; //元素的个数统计需要改变}//将二维数组中的数据转移到arr中int index = 0; //初始化的索引下标for (int j = 0; j < bucketElementCounts.length; j++) { //bucketElementCounts = 10if (bucketElementCounts[j] > 0) {for (int l = 0; l < bucketElementCounts[j]; l++) {arr[index] = bucket[j][l]; // 将二维数组的元素重新赋给arr数组中index++;}bucketElementCounts[j] = 0 ; //注意一定要将这点的数据清为0}}}}}
~~~java
Date date1 = new Date(); //生成时间SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss"); //将时间进行格式化
// System.out.println(date1);System.out.println("开始时间:"+simpleDateFormat.format(date1));
十、排序总结
排序算法 平均时间复杂度 最好情况 最坏情况 空间复杂度 排序方式 稳定性 冒泡排序 O(n2)O(n^2)O(n2) O(n)O(n)O(n) O(n2)O(n^2)O(n2) O(n2)O(n^2)O(n2) In-Place 稳定 选择排序 O(n2)O(n^2)O(n2) O(n2)O(n^2)O(n2) O(n2)O(n^2)O(n2) O(1)O(1)O(1) In-Place 不稳定 插入排序 O(n2)O(n^2)O(n2) O()O()O() 希尔排序 归并排序 快速排序 堆排序 计数排序 桶排序 基数排序
上一篇:【iOS】—— ARC学习
下一篇:【数据结构与算法】快速排序的优化
