卷积神经网络的计算
计算卷积神经网络中的参数
填充
我们在使用多重卷积的时候,常常会丢失边缘像素。由于我们使用小卷积核,因此对于单个卷积,我们只可能丢失几个像素。但随着我们应用连着许多卷积层,累积丢失的像素就多了起来。解决这个问题的方法即为填充(padding):在输入图像的边界填充元素(基本填充的都是0)
通常,我们添加php_hph行填充,和pwp_wpw列填充,则输出的形状为
(nh−kh+ph+1)∗(nw−kw+pw+1)(n_h - k_h + p_h + 1)*(n_w-k_w+p_w+1)(nh−kh+ph+1)∗(nw−kw+pw+1)
许多情况下,我们需要设置ph=kh−1p_h=k_h-1ph=kh−1,pw=kw−1p_w=k_w-1pw=kw−1使输出具有相同的高度和宽度。这样可以更好的预测输出的情况。
1、假设khk_hkh为奇数,则高度的两侧分别填充ph/2p_h/2ph/2
2、假设khk_hkh为偶数,则宽度的上测分别填充pw/2p_w/2pw/2上取整,下侧下取整
步幅
每次滑动元素的数量叫做步幅(stride),为了高效计算或是缩减采样次数,卷积窗口可以跳过中间位置,每次滑动多个元素。
当垂直步幅为shs_hsh、水平步幅为sws_wsw输出的形状为
⌊(nh−kh+ph+sh)/sh⌋∗⌊(nw−kw+pw+sw)/sw⌋\lfloor(n_h - k _h + p_h + s_h)/s_h\rfloor *\lfloor(n_w-k_w+p_w+s_w)/s_w\rfloor⌊(nh−kh+ph+sh)/sh⌋∗⌊(nw−kw+pw+sw)/sw⌋
1X1的卷积层
需要特别注意的是一层一的卷积层,即kh=kw=1。它唯一的计算发生在通道上,经常用1X1的卷积层来代替全连接层减少运算。
池化层(pooling)
最大池化和平均池化
nn.MaxPool2d(size, stride, padding)
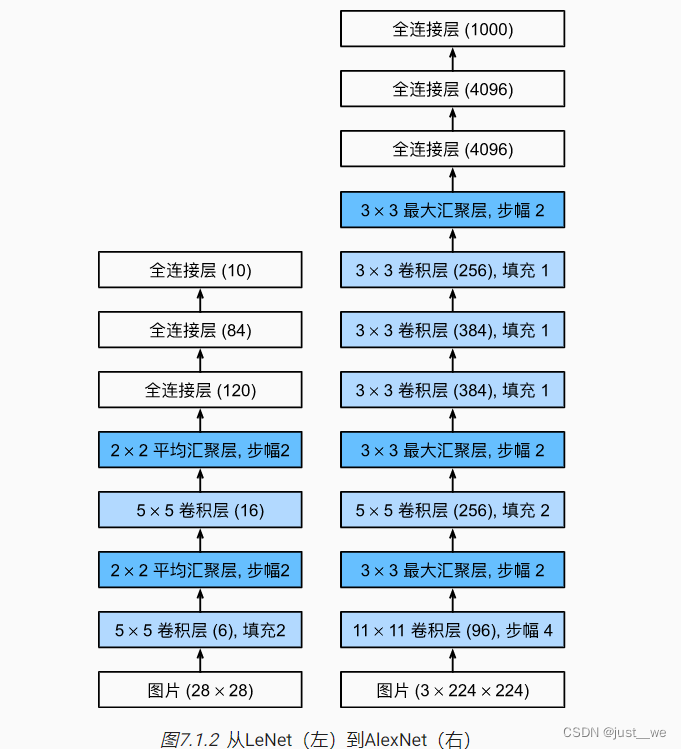
AlexNet
AlexNet与LeNet进行对比
import torch
from torch import nn
from d2l import torch as d2lnet = nn.Sequential(# 这里使用一个11*11的更大窗口来捕捉对象。# 同时,步幅为4,以减少输出的高度和宽度。# 另外,输出通道的数目远大于LeNetnn.Conv2d(1, 96, kernel_size=11, stride=4, padding=1), nn.ReLU(),nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2),# 减小卷积窗口,使用填充为2来使得输入与输出的高和宽一致,且增大输出通道数nn.Conv2d(96, 256, kernel_size=5, padding=2), nn.ReLU(),nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2),# 使用三个连续的卷积层和较小的卷积窗口。# 除了最后的卷积层,输出通道的数量进一步增加。# 在前两个卷积层之后,汇聚层不用于减少输入的高度和宽度nn.Conv2d(256, 384, kernel_size=3, padding=1), nn.ReLU(),nn.Conv2d(384, 384, kernel_size=3, padding=1), nn.ReLU(),nn.Conv2d(384, 256, kernel_size=3, padding=1), nn.ReLU(),nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2),nn.Flatten(),# 这里,全连接层的输出数量是LeNet中的好几倍。使用dropout层来减轻过拟合nn.Linear(6400, 4096), nn.ReLU(),nn.Dropout(p=0.5),nn.Linear(4096, 4096), nn.ReLU(),nn.Dropout(p=0.5),# 最后是输出层。由于这里使用Fashion-MNIST,所以用类别数为10,而非论文中的1000nn.Linear(4096, 10))
224224 stride为4,padding为1,核大小为1111
第一层conv2d(224-11 + 2 + 1)/4 = 54
MaxPooling (54-3+1)/2=26
Conv2d (26 - 5 + 4 + 1) = 26
……
全连接层参数需要进行计算
256 * 5 * 5 = 6400//属于torch中不那么简洁的地方
X = torch.randn(1, 1, 224, 224)
for layer in net:X=layer(X)print(layer.__class__.__name__,'output shape:\t',X.shape)
输出为
ReLU output shape: torch.Size([1, 96, 54, 54])
MaxPool2d output shape: torch.Size([1, 96, 26, 26])
Conv2d output shape: torch.Size([1, 256, 26, 26])
ReLU output shape: torch.Size([1, 256, 26, 26])
MaxPool2d output shape: torch.Size([1, 256, 12, 12])
Conv2d output shape: torch.Size([1, 384, 12, 12])
ReLU output shape: torch.Size([1, 384, 12, 12])
Conv2d output shape: torch.Size([1, 384, 12, 12])
ReLU output shape: torch.Size([1, 384, 12, 12])
Conv2d output shape: torch.Size([1, 256, 12, 12])
ReLU output shape: torch.Size([1, 256, 12, 12])
MaxPool2d output shape: torch.Size([1, 256, 5, 5])
Flatten output shape: torch.Size([1, 6400])
Linear output shape: torch.Size([1, 4096])
ReLU output shape: torch.Size([1, 4096])
Dropout output shape: torch.Size([1, 4096])
Linear output shape: torch.Size([1, 4096])
ReLU output shape: torch.Size([1, 4096])
Dropout output shape: torch.Size([1, 4096])
Linear output shape: torch.Size([1, 10])
d2l学习笔记
